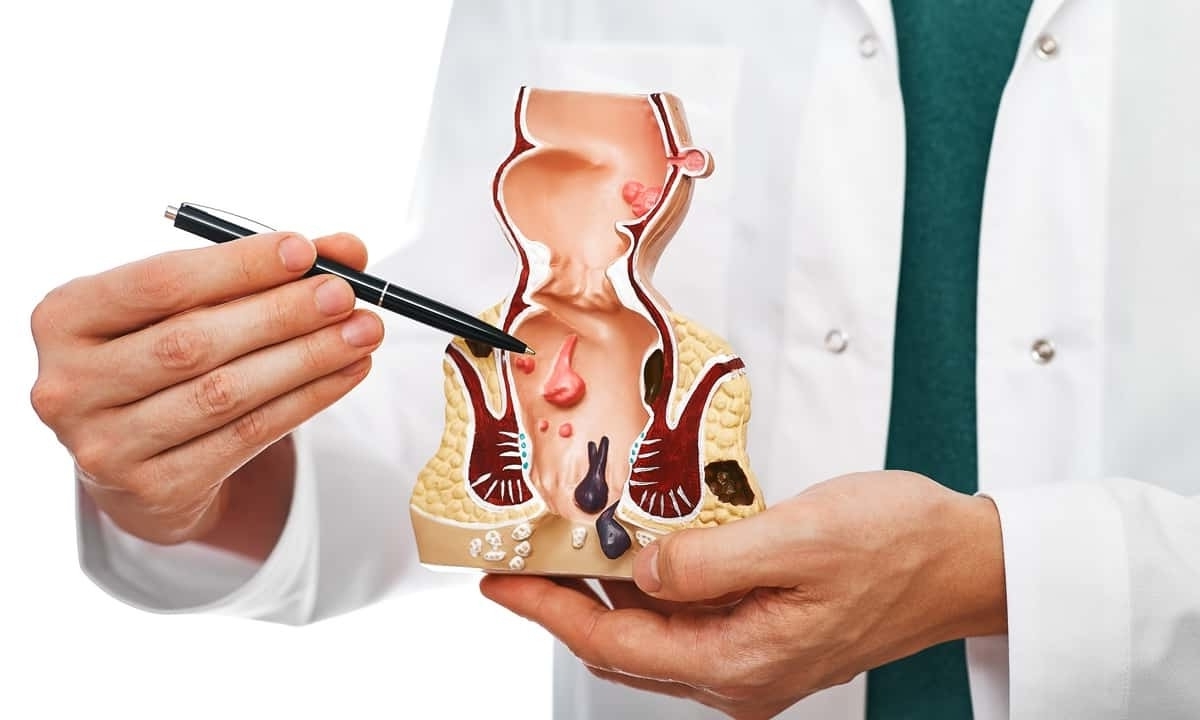
Anal cancer might not be a topic that comes up often, but understanding it is crucial. What exactly is anal cancer? It's a rare type of cancer that forms in the tissues of the anus, the opening at the end of the digestive tract. This condition can be tricky to spot early on because its symptoms often mimic less serious issues like hemorrhoids. Common signs include bleeding, pain, or a lump near the anus. Risk factors include smoking, HPV infection, and a weakened immune system. Early detection can make a big difference in treatment success. Learning about anal cancer helps in recognizing symptoms and understanding treatment options. Knowledge is power, and being informed can lead to better health decisions.
Key Takeaways:
- Anal cancer is rare but can be prevented with HPV vaccination and safe sex. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
- Support and education are essential for individuals with anal cancer. Research and advocacy efforts offer hope for improved treatment options.
Understanding Anal Cancer
Anal cancer is a rare type of cancer that forms in the tissues of the anus. It's essential to know more about this condition to raise awareness and promote early detection. Here are some intriguing facts about anal cancer.
-
Anal cancer occurs when cells in the anus grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. This can happen in any part of the anal canal.
-
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is a significant risk factor for developing anal cancer. HPV is a common virus that can cause changes in the cells of the anus.
-
Anal cancer is more common in women than in men. However, men who have sex with men are at a higher risk.
-
The incidence of anal cancer has been increasing over the past few decades. This rise is partly due to better screening and detection methods.
-
Symptoms of anal cancer can include bleeding, pain, or lumps around the anus. However, some people may not experience any symptoms at all.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Understanding the risk factors can help in preventing anal cancer. Here are some key points to consider.
-
Smoking is a known risk factor for anal cancer. Tobacco use can damage the cells in the anus, increasing cancer risk.
-
A weakened immune system, such as in individuals with HIV, can increase the likelihood of developing anal cancer.
-
Having multiple sexual partners can raise the risk of HPV infection, which is linked to anal cancer.
-
Regular screening and vaccination against HPV can significantly reduce the risk of anal cancer.
-
Practicing safe sex and using protection can help prevent HPV infection and lower the risk of anal cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for a better prognosis. Here's what you need to know about diagnosing and treating anal cancer.
-
Anal cancer is often diagnosed through a physical exam and imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan.
-
A biopsy, where a small tissue sample is taken from the anus, is used to confirm the diagnosis of anal cancer.
-
Treatment options for anal cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on the cancer stage and location.
-
Radiation therapy is often combined with chemotherapy to increase the effectiveness of treatment.
-
Surgery may be necessary if the cancer does not respond to other treatments or if it has spread to nearby tissues.
Living with Anal Cancer
Living with anal cancer can be challenging, but support and resources are available. Here are some facts about managing life with this condition.
-
Support groups and counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological impact of anal cancer.
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can improve overall well-being during treatment.
-
Follow-up care is essential for monitoring any recurrence of cancer and managing side effects of treatment.
-
Palliative care can provide relief from symptoms and improve the quality of life for those with advanced anal cancer.
-
Advances in research and treatment continue to improve the outlook for individuals diagnosed with anal cancer.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are many myths surrounding anal cancer. Let's clear up some common misconceptions.
-
Anal cancer is not the same as colorectal cancer, though they may share some symptoms.
-
Not everyone with HPV will develop anal cancer. Most HPV infections clear up on their own without causing cancer.
-
Anal cancer is not caused by poor hygiene. It is primarily linked to HPV infection and other risk factors.
-
Anal cancer is not contagious. It cannot be spread from person to person through casual contact.
-
Early detection of anal cancer can lead to successful treatment and a good prognosis.
Statistics and Research
Statistics and ongoing research provide valuable insights into anal cancer. Here are some important facts.
-
Anal cancer accounts for about 2% of all gastrointestinal cancers in the United States.
-
The five-year survival rate for anal cancer is approximately 68%, but this can vary depending on the stage at diagnosis.
-
Research is ongoing to develop better screening methods and treatments for anal cancer.
-
Clinical trials are exploring new therapies, including immunotherapy, for treating anal cancer.
-
Awareness campaigns and education are crucial for increasing understanding and reducing stigma around anal cancer.
Global Perspective
Anal cancer affects people worldwide, but its impact varies across different regions. Here are some global insights.
-
The incidence of anal cancer is higher in developed countries, partly due to better detection and reporting.
-
HPV vaccination programs in many countries aim to reduce the incidence of anal cancer and other HPV-related cancers.
-
Access to healthcare and screening can significantly impact anal cancer outcomes in different parts of the world.
-
Cultural attitudes towards discussing anal cancer can affect awareness and early detection efforts.
-
International collaborations in research and treatment are helping to improve outcomes for anal cancer patients globally.
Personal Stories and Advocacy
Personal stories and advocacy efforts play a vital role in raising awareness about anal cancer. Here are some inspiring examples.
-
Many individuals with anal cancer share their stories to educate others and reduce stigma.
-
Advocacy groups work tirelessly to promote HPV vaccination and screening for anal cancer.
-
Survivors often participate in fundraising events to support research and patient support services.
-
Social media platforms provide a space for individuals to connect and share their experiences with anal cancer.
-
Public figures and celebrities who speak out about their experiences can help raise awareness and encourage others to seek screening.
Future Directions
The future of anal cancer research and treatment holds promise. Here are some exciting developments on the horizon.
-
Advances in genetic research may lead to personalized treatment options for anal cancer patients.
-
New imaging technologies are being developed to improve the accuracy of anal cancer diagnosis.
-
Researchers are exploring the use of artificial intelligence to enhance screening and detection methods.
-
Immunotherapy, which harnesses the body's immune system to fight cancer, shows promise in treating anal cancer.
-
Collaborative efforts between scientists, healthcare providers, and patients are driving innovation in anal cancer research.
Final Thoughts
Anal cancer is a complex and challenging condition, but understanding it can lead to better prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Here are a few more facts to consider.
-
Early detection of anal cancer can lead to more effective treatment and improved survival rates.
-
Education and awareness are key to reducing the stigma associated with anal cancer.
-
Support from family, friends, and healthcare providers is crucial for individuals living with anal cancer.
-
Ongoing research and clinical trials offer hope for new and improved treatment options.
-
By raising awareness and promoting prevention, we can work towards reducing the impact of anal cancer on individuals and communities.
Final Thoughts on Anal Cancer
Understanding anal cancer is crucial for awareness and prevention. This type of cancer, though less common, can have serious implications if not detected early. Knowing the risk factors like HPV infection, smoking, and a weakened immune system can help in taking preventive measures. Regular screenings and being attentive to symptoms such as bleeding, pain, or lumps around the anus can lead to early diagnosis, which significantly improves treatment outcomes.
Advancements in medical research continue to improve treatment options, offering hope for those affected. Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery are common treatments, often used in combination for better results.
Raising awareness and educating others about anal cancer can lead to early detection and save lives. Stay informed, consult healthcare professionals for regular check-ups, and encourage open conversations about this important health issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
