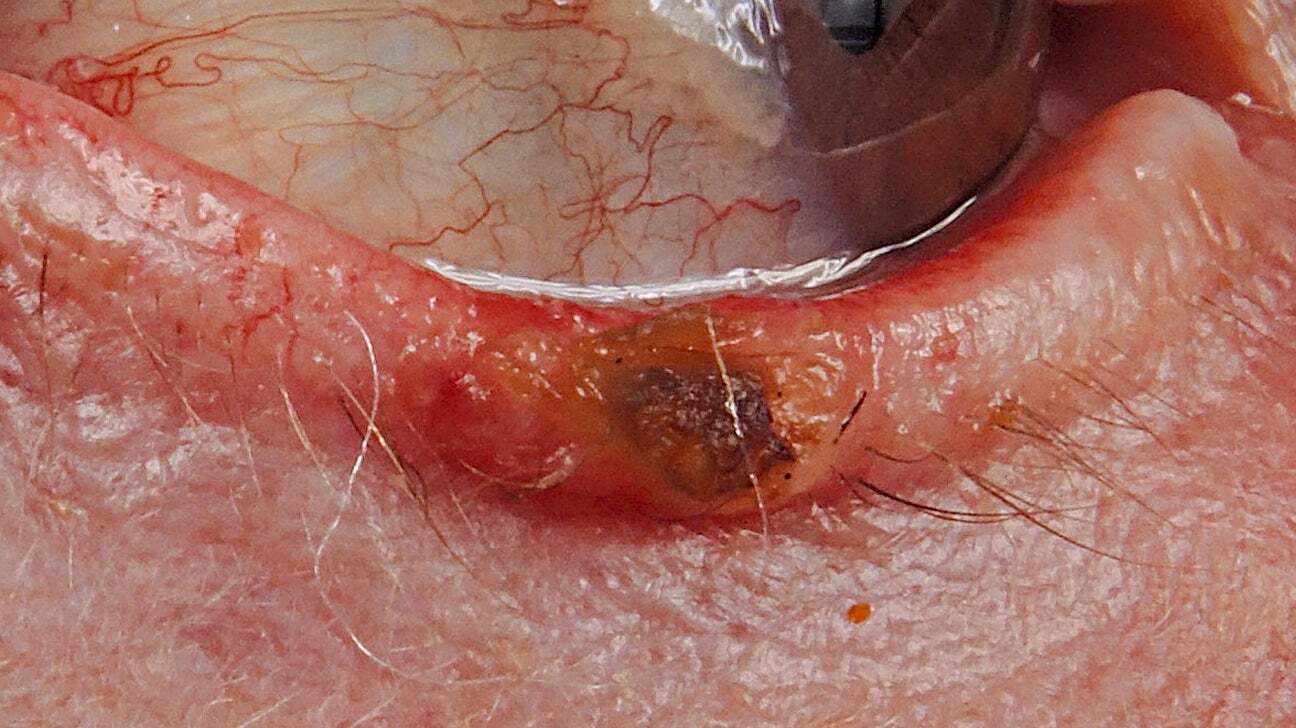
Epidermoid carcinoma, also known as squamous cell carcinoma, is a type of skin cancer that starts in the squamous cells. These cells make up the outer layer of the skin. This cancer can appear as scaly red patches, open sores, or warts. It often develops on areas exposed to the sun, like the face, ears, neck, lips, and hands. However, it can also form in other parts of the body, including the mouth, throat, and lungs. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options can help manage and prevent this common yet serious condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Epidermoid carcinoma, also known as squamous cell carcinoma, is the second most common type of skin cancer, often appearing as red, scaly patches on sun-exposed areas. Early detection and regular skin checks are crucial for effective treatment.
- Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption, can positively impact the survival rates of epidermoid carcinoma. Regular follow-ups and mental health support are also important for overall well-being.
What is Epidermoid Carcinoma?
Epidermoid carcinoma, also known as squamous cell carcinoma, is a type of cancer that begins in the squamous cells. These cells are flat, thin cells found in the skin and tissues lining some organs. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Epidermoid carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. It accounts for about 20% of all skin cancer cases.
-
It often appears as a red, scaly patch or a sore that doesn't heal. These lesions can be found on sun-exposed areas like the face, ears, neck, and hands.
-
Chronic sun exposure is a major risk factor. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to cancer.
-
Fair-skinned individuals are more susceptible. People with lighter skin have less melanin, which provides some protection against UV radiation.
-
It can also develop in other parts of the body. Besides the skin, it can occur in the lungs, esophagus, and other organs lined with squamous cells.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to more effective treatment. Here are some key points about the symptoms and diagnosis of epidermoid carcinoma.
-
Persistent sores or ulcers are common symptoms. These sores may bleed or form a crust and do not heal over time.
-
A biopsy is the definitive way to diagnose this cancer. A small sample of the affected tissue is examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
-
Lymph nodes may be checked for spread. If the cancer has spread, it often moves to nearby lymph nodes first.
-
Imaging tests like CT scans can help determine the extent. These tests provide detailed pictures of the inside of the body to see if the cancer has spread.
-
Early detection significantly improves the prognosis. When caught early, treatment is more likely to be successful.
Treatment Options
Various treatments are available depending on the stage and location of the cancer. Here are some treatment facts.
-
Surgery is a common treatment method. The goal is to remove the cancerous tissue along with some surrounding healthy tissue.
-
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It is often used when surgery isn't an option or to kill any remaining cancer cells post-surgery.
-
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to destroy cancer cells. It can be administered orally or intravenously and is often used for more advanced stages.
-
Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. These drugs can block the growth and spread of cancer cells while minimizing damage to normal cells.
-
Immunotherapy boosts the body's natural defenses to fight cancer. It uses substances made by the body or in a lab to improve or restore immune system function.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Understanding the risk factors can help in taking preventive measures. Here are some important facts about risk factors and prevention.
-
Age is a significant risk factor. Most cases occur in individuals over 50 years old.
-
A history of sunburns increases the risk. Severe sunburns, especially during childhood, can elevate the risk of developing this cancer later in life.
-
Exposure to certain chemicals can be a risk factor. Arsenic and industrial tar are known to increase the risk of epidermoid carcinoma.
-
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is linked to this cancer. Certain strains of HPV can cause changes in squamous cells, leading to cancer.
-
Regular use of sunscreen can help prevent it. Sunscreen with a high SPF can protect the skin from harmful UV rays.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The outlook for patients with epidermoid carcinoma varies based on several factors. Here are some facts about prognosis and survival rates.
-
The 5-year survival rate is high for localized cases. When the cancer is confined to the primary site, the survival rate is around 90%.
-
Survival rates drop if the cancer has spread. If it has metastasized to distant organs, the 5-year survival rate falls to about 34%.
-
Regular follow-ups are crucial for monitoring. Even after successful treatment, regular check-ups are necessary to catch any recurrence early.
-
Lifestyle changes can improve outcomes. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption can positively impact survival rates.
-
Support groups can provide emotional and practical support. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can be beneficial for mental health.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research continues to improve the understanding and treatment of epidermoid carcinoma. Here are some exciting developments.
-
New drugs are being tested in clinical trials. These trials aim to find more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
-
Genetic research is uncovering new insights. Understanding the genetic mutations involved in this cancer can lead to targeted therapies.
-
Artificial intelligence is aiding in early detection. AI algorithms can analyze images of skin lesions to identify potential cancers.
-
Personalized medicine is becoming more common. Treatments tailored to an individual's genetic makeup are showing promise in improving outcomes.
-
Vaccines are being developed to prevent HPV-related cancers. These vaccines could reduce the incidence of epidermoid carcinoma linked to HPV.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are many myths surrounding epidermoid carcinoma. Here are some facts to set the record straight.
-
Myth: Only fair-skinned people get this cancer. Fact: While fair-skinned individuals are at higher risk, anyone can develop epidermoid carcinoma.
-
Myth: It only affects older adults. Fact: Although more common in older adults, younger people can also be affected, especially with significant sun exposure.
-
Myth: Sunscreen is unnecessary on cloudy days. Fact: UV rays can penetrate clouds, so sunscreen is important even on overcast days.
-
Myth: Tanning beds are safer than the sun. Fact: Tanning beds emit UV radiation that can increase the risk of skin cancer.
-
Myth: Once treated, it won't come back. Fact: There is always a risk of recurrence, so regular monitoring is essential.
Living with Epidermoid Carcinoma
Managing life with epidermoid carcinoma involves various strategies. Here are some facts about living with this condition.
-
Skin checks should be part of your routine. Regular self-examinations can help detect any new or changing lesions early.
-
A balanced diet can support overall health. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can help the body fight cancer.
-
Physical activity can improve well-being. Regular exercise can boost mood and energy levels, helping to cope with treatment side effects.
-
Mental health support is crucial. Counseling or therapy can help manage the emotional impact of a cancer diagnosis.
-
Educating yourself about the condition can empower you. Understanding your diagnosis and treatment options can help you make informed decisions about your care.
Final Thoughts on Epidermoid Carcinoma
Epidermoid carcinoma, a common type of skin cancer, demands attention. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Regular skin checks, using sunscreen, and avoiding excessive sun exposure are key preventive measures. If you notice any unusual changes in your skin, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Understanding the risk factors, such as prolonged UV exposure and family history, helps in taking proactive steps. Treatments range from surgical removal to radiation and chemotherapy, depending on the stage and location of the cancer.
Staying informed about the latest research and advancements in treatment options can empower patients and their families. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to managing health. Stay vigilant, protect your skin, and prioritize regular check-ups to catch any issues early. Your skin's health is in your hands.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
