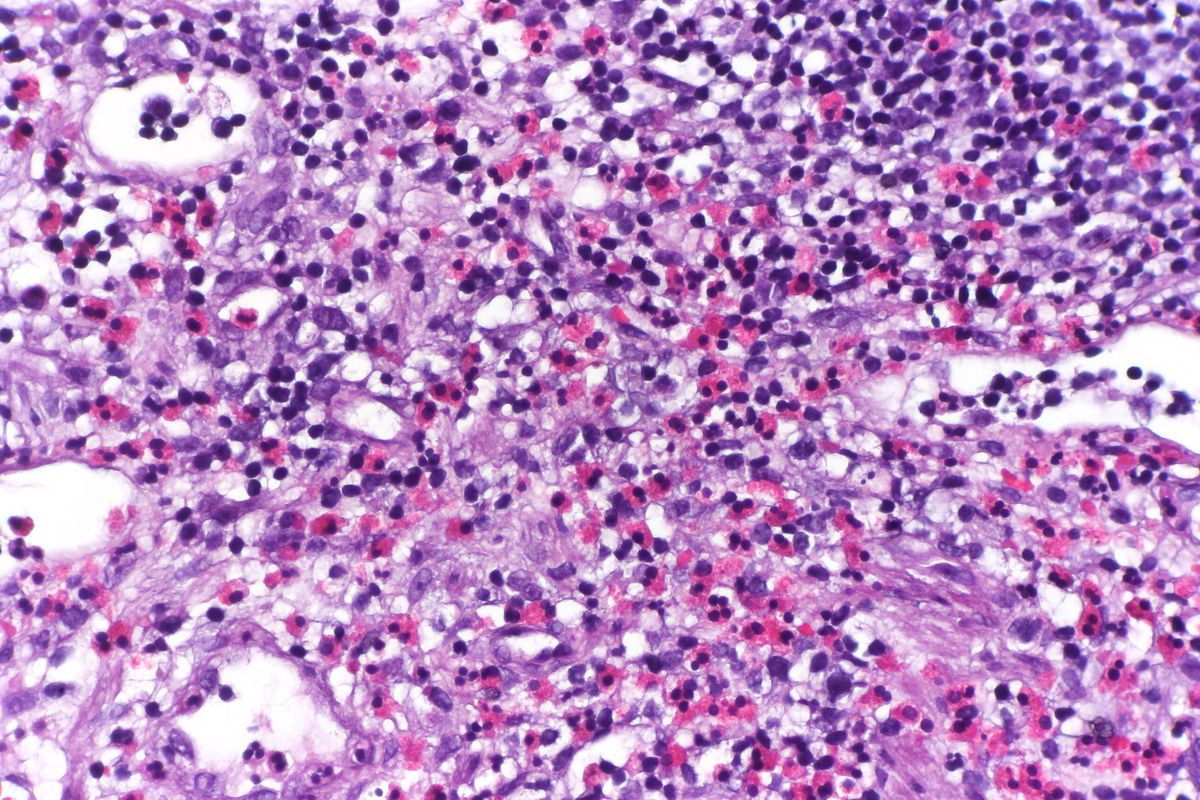
Eosinophilic cystitis is a rare inflammatory condition affecting the bladder. It involves an abnormal accumulation of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, in the bladder wall. This can lead to symptoms like painful urination, frequent urges to urinate, and blood in the urine. Eosinophilic cystitis can affect both adults and children, though it is more commonly seen in males. The exact cause remains unclear, but it is often linked to allergies, infections, or autoimmune disorders. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of urine tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a biopsy. Treatment varies depending on the severity and underlying cause, ranging from medications to manage symptoms to more invasive procedures in severe cases. Understanding eosinophilic cystitis is crucial for effective management and improving quality of life for those affected.
Key Takeaways:
- Eosinophilic cystitis is a rare bladder condition linked to allergies, infections, and autoimmune responses. It can cause painful urination, blood in the urine, and may require bladder biopsies for diagnosis.
- Managing eosinophilic cystitis involves anti-inflammatory medications, antihistamines, corticosteroids, antibiotics, and dietary changes. Complications may include chronic pain, bladder scarring, urinary retention, and recurrent infections.
What is Eosinophilic Cystitis?
Eosinophilic cystitis (EC) is a rare inflammatory condition affecting the bladder. It involves the presence of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, in the bladder wall. This condition can cause various symptoms and complications.
-
Eosinophilic cystitis is rare. It occurs in both adults and children but is not commonly seen in medical practice.
-
Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell. They play a role in the body's immune response, particularly in allergic reactions and parasitic infections.
-
The exact cause of EC is unknown. Researchers believe it may be linked to allergies, infections, or autoimmune responses.
-
Symptoms can vary widely. Common symptoms include painful urination, frequent urination, and blood in the urine.
-
Diagnosis often involves a biopsy. A tissue sample from the bladder is examined under a microscope to identify eosinophils.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how eosinophilic cystitis is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively.
-
Painful urination is a common symptom. This pain can range from mild discomfort to severe burning sensations.
-
Frequent urination is another sign. Patients may feel the need to urinate more often than usual, sometimes every hour.
-
Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can occur. This can be visible to the naked eye or detected through a urine test.
-
Bladder biopsies are crucial for diagnosis. They help confirm the presence of eosinophils in the bladder wall.
-
Urine tests can indicate inflammation. These tests may show elevated white blood cells or other signs of infection.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of eosinophilic cystitis remains unclear, several factors may contribute to its development.
-
Allergies may play a role. Some patients have a history of allergic reactions or asthma.
-
Infections could trigger EC. Bacterial or parasitic infections might lead to the condition in some cases.
-
Autoimmune responses are suspected. The body's immune system may mistakenly attack the bladder, causing inflammation.
-
Certain medications might be linked. Some drugs, particularly those affecting the immune system, could contribute to EC.
-
Genetic factors may influence susceptibility. A family history of similar conditions might increase the risk.
Treatment Options
Managing eosinophilic cystitis involves various treatment approaches to alleviate symptoms and address underlying causes.
-
Anti-inflammatory medications are often used. These drugs help reduce inflammation in the bladder.
-
Antihistamines can be effective. They may alleviate symptoms if allergies are a contributing factor.
-
Corticosteroids are sometimes prescribed. These powerful anti-inflammatory drugs can help control severe symptoms.
-
Antibiotics may be necessary. If an infection is present, antibiotics can treat the underlying cause.
-
Dietary changes might help. Avoiding foods that trigger allergic reactions can reduce symptoms.
Complications and Prognosis
Understanding potential complications and the long-term outlook for eosinophilic cystitis is important for patients and caregivers.
-
Chronic pain can be a complication. Persistent bladder pain may affect the quality of life.
-
Bladder scarring might occur. Inflammation can lead to scarring, which may reduce bladder capacity.
-
Urinary retention is a risk. Severe inflammation can obstruct urine flow, leading to retention.
-
Recurrent infections are possible. Ongoing inflammation can make the bladder more susceptible to infections.
-
Prognosis varies widely. Some patients experience complete resolution, while others may have chronic symptoms.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand eosinophilic cystitis and develop more effective treatments.
-
New diagnostic tools are being explored. Researchers are investigating less invasive methods for diagnosing EC.
-
Genetic studies are underway. These studies aim to identify genetic factors that may contribute to the condition.
-
Immunotherapy is a potential treatment. Modulating the immune response could help manage EC symptoms.
-
Clinical trials are testing new medications. These trials aim to find more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
-
Patient registries are being established. Collecting data from patients worldwide can help improve understanding of EC.
Living with Eosinophilic Cystitis
Managing daily life with eosinophilic cystitis involves coping strategies and support systems.
-
Support groups can be beneficial. Connecting with others who have EC can provide emotional support and practical advice.
-
Pain management techniques are important. Methods like relaxation exercises and physical therapy can help manage pain.
-
Regular medical check-ups are crucial. Ongoing monitoring can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
-
Lifestyle adjustments may be necessary. Changes in diet, exercise, and stress management can improve quality of life.
-
Education about the condition is key. Understanding EC helps patients make informed decisions about their care.
Pediatric Eosinophilic Cystitis
Eosinophilic cystitis can affect children, and their symptoms and treatment needs may differ from adults.
-
Children can develop EC. Although rare, it can occur in pediatric patients.
-
Symptoms in children may differ. Young patients might experience bedwetting or abdominal pain.
-
Pediatric treatment approaches vary. Treatment plans are tailored to the child's age and specific symptoms.
-
Family support is essential. Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in managing the child's condition.
-
Early diagnosis can improve outcomes. Prompt identification and treatment can help prevent complications in children.
Final Thoughts on Eosinophilic Cystitis
Eosinophilic cystitis, though rare, can significantly impact those affected. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments is crucial for managing this condition. Symptoms often include painful urination, frequent urination, and blood in the urine. Causes can range from allergic reactions to infections. Treatments vary but may involve medications, diet changes, or even surgery in severe cases.
Early diagnosis and proper treatment can improve quality of life. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms, consult a healthcare professional. Staying informed and proactive can make a big difference. Remember, while eosinophilic cystitis is challenging, it's manageable with the right approach. Keep these facts in mind, and don't hesitate to seek help when needed. Your health is worth it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
