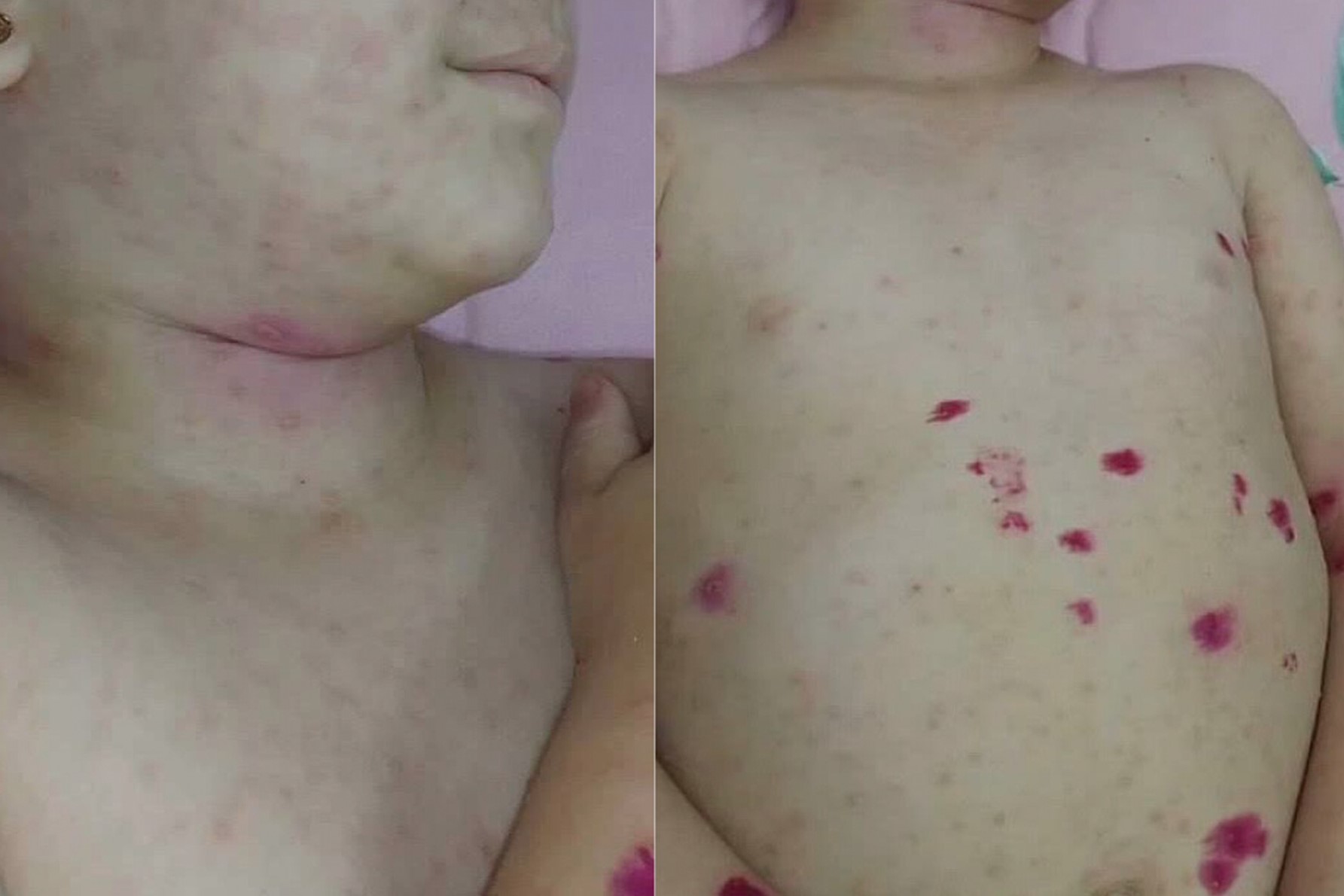
Hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome (HIDS) is a rare genetic disorder that causes recurrent fevers, abdominal pain, and joint inflammation. HIDS is part of a group of diseases known as autoinflammatory syndromes, which result from an overactive immune system. This condition is caused by mutations in the MVK gene, leading to a deficiency in the enzyme mevalonate kinase. Symptoms often begin in infancy or early childhood and can be triggered by stress, infections, or vaccinations. Although there is no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms and reducing inflammation. Understanding HIDS can help those affected and their families navigate this challenging condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Hyperimmunoglobulinemia D Syndrome (HIDS) is a rare genetic disorder causing recurrent fevers, abdominal pain, and skin rashes. It is diagnosed through genetic testing and managed with medications and lifestyle adjustments.
- Living with HIDS can be challenging, but education, support groups, healthy lifestyle choices, and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers can help individuals lead fulfilling lives. Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of HIDS.
What is Hyperimmunoglobulinemia D Syndrome (HIDS)?
Hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome (HIDS) is a rare genetic disorder. It falls under the category of periodic fever syndromes. People with HIDS experience recurrent episodes of fever and inflammation. Here are some intriguing facts about HIDS.
-
HIDS is caused by mutations in the MVK gene. This gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called mevalonate kinase.
-
The MVK gene mutation leads to a deficiency in mevalonate kinase enzyme activity. This deficiency disrupts the production of cholesterol and other essential molecules.
-
HIDS is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. Both parents must carry one copy of the mutated gene to pass it on to their child.
-
The syndrome is also known as Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency (MKD). This name reflects the underlying genetic cause.
-
HIDS typically presents in early childhood. Symptoms often appear within the first year of life.
Symptoms of HIDS
HIDS manifests through a variety of symptoms. These symptoms can vary in severity and frequency among individuals.
-
Recurrent fevers are a hallmark of HIDS. Fevers can last from a few days to a week.
-
During fever episodes, individuals may experience abdominal pain. This pain can be severe and debilitating.
-
Skin rashes are common during fever episodes. These rashes can appear anywhere on the body.
-
Swollen lymph nodes often accompany fever episodes. Lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, and groin are usually affected.
-
Joint pain and swelling can occur. This symptom is particularly common in the knees and ankles.
Diagnosis of HIDS
Diagnosing HIDS can be challenging due to its rarity. However, certain tests and evaluations can help confirm the diagnosis.
-
Genetic testing is the most definitive method for diagnosing HIDS. It can identify mutations in the MVK gene.
-
Elevated levels of immunoglobulin D (IgD) in the blood can suggest HIDS. However, not all patients with HIDS have high IgD levels.
-
Urine tests can detect elevated levels of mevalonic acid. This finding supports the diagnosis of HIDS.
-
Family history is an important factor. A history of similar symptoms in relatives can indicate a genetic disorder like HIDS.
-
Clinical evaluation by a specialist in genetic disorders or immunology is crucial. They can assess symptoms and recommend appropriate tests.
Treatment and Management of HIDS
There is no cure for HIDS, but various treatments can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of fever episodes.
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce fever and inflammation.
-
Corticosteroids may be prescribed during severe episodes. These drugs can help control inflammation.
-
Biologic agents such as anakinra or canakinumab can be effective. These medications target specific inflammatory pathways.
-
Colchicine is sometimes used to prevent fever episodes. It is more commonly used for other periodic fever syndromes.
-
Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is essential. This helps manage symptoms and adjust treatments as needed.
Living with HIDS
Living with HIDS can be challenging, but with proper management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
-
Education and awareness are important. Understanding the condition helps patients and families cope better.
-
Support groups can provide emotional and practical support. Connecting with others who have HIDS can be beneficial.
-
Healthy lifestyle choices can improve overall well-being. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate rest.
-
Avoiding triggers that may provoke fever episodes is crucial. Stress, infections, and certain foods can trigger symptoms.
-
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure optimal management. This includes monitoring for potential complications.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand HIDS and develop more effective treatments.
-
Genetic studies are exploring new mutations in the MVK gene. This research may lead to improved diagnostic methods.
-
Clinical trials are testing new medications. These trials aim to find more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
-
Biomarker research is identifying new indicators of disease activity. This could lead to earlier diagnosis and better monitoring.
-
Patient registries are collecting data on HIDS. These registries help researchers understand the condition's natural history.
-
International collaborations are advancing HIDS research. Scientists from different countries are working together to find solutions.
Interesting Facts about HIDS
Here are some additional intriguing facts about HIDS that highlight its unique aspects.
-
HIDS is more common in certain populations. It is particularly prevalent among people of Dutch descent.
-
The first case of HIDS was described in 1984. Since then, hundreds of cases have been reported worldwide.
-
Fever episodes in HIDS can be triggered by vaccinations. This is due to the immune system's heightened response.
-
Carrier testing is available for families with a history of HIDS. This can help identify individuals who carry the MVK gene mutation.
-
Awareness campaigns are raising the profile of HIDS. These campaigns aim to improve diagnosis and support for affected individuals.
Final Thoughts on HIDS
Hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome (HIDS) is a rare genetic disorder that causes recurrent fevers, abdominal pain, and joint inflammation. Understanding the symptoms and seeking early diagnosis can help manage the condition more effectively. While there’s no cure, treatments like anti-inflammatory drugs and biologics can reduce flare-ups and improve quality of life.
Raising awareness about HIDS is crucial for better support and research funding. If you or someone you know shows signs of HIDS, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment options. Staying informed and connected with support groups can make a significant difference in managing this challenging condition.
Knowledge empowers patients and their families to navigate the complexities of HIDS with greater confidence and hope.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
