Periodic acid might sound like something from a sci-fi movie, but it's a real chemical with some pretty cool uses. Ever wondered what makes it special? Periodic acid is a powerful oxidizing agent, which means it can break down complex molecules into simpler ones. This makes it super useful in labs, especially for studying carbohydrates. Scientists love it because it helps them understand how sugars and other molecules work. But that's not all! Periodic acid also plays a role in creating certain dyes and even in some medical tests. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 40 fascinating facts about this amazing chemical!
Key Takeaways:
- Periodic acid is a powerful chemical compound used in various scientific fields. It can be dangerous to handle, so proper safety measures and training are essential for anyone working with it.
- From cleaving glycols to detecting polysaccharides, periodic acid has a wide range of applications. Its strong oxidizing properties require careful handling and disposal to ensure safety.
What is Periodic Acid?
Periodic acid is a chemical compound with the formula HIO4 or H5IO6. It is known for its strong oxidizing properties and is used in various chemical reactions and laboratory processes. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this compound.
-
Periodic acid exists in two forms: Orthoperiodic acid (H5IO6) and metaperiodic acid (HIO4). Both forms are used in different chemical applications.
-
Strong oxidizing agent: Periodic acid is a powerful oxidizing agent, meaning it can accept electrons from other substances during a chemical reaction.
-
Named after iodine: The name "periodic acid" comes from the element iodine, which is a key component of the compound.
-
Discovered in the 19th century: Heinrich Gustav Magnus and C. F. Ammermüller first identified periodic acid in 1833.
-
Used in organic chemistry: Periodic acid is commonly used to cleave vicinal diols, which are compounds with two hydroxyl groups on adjacent carbon atoms.
-
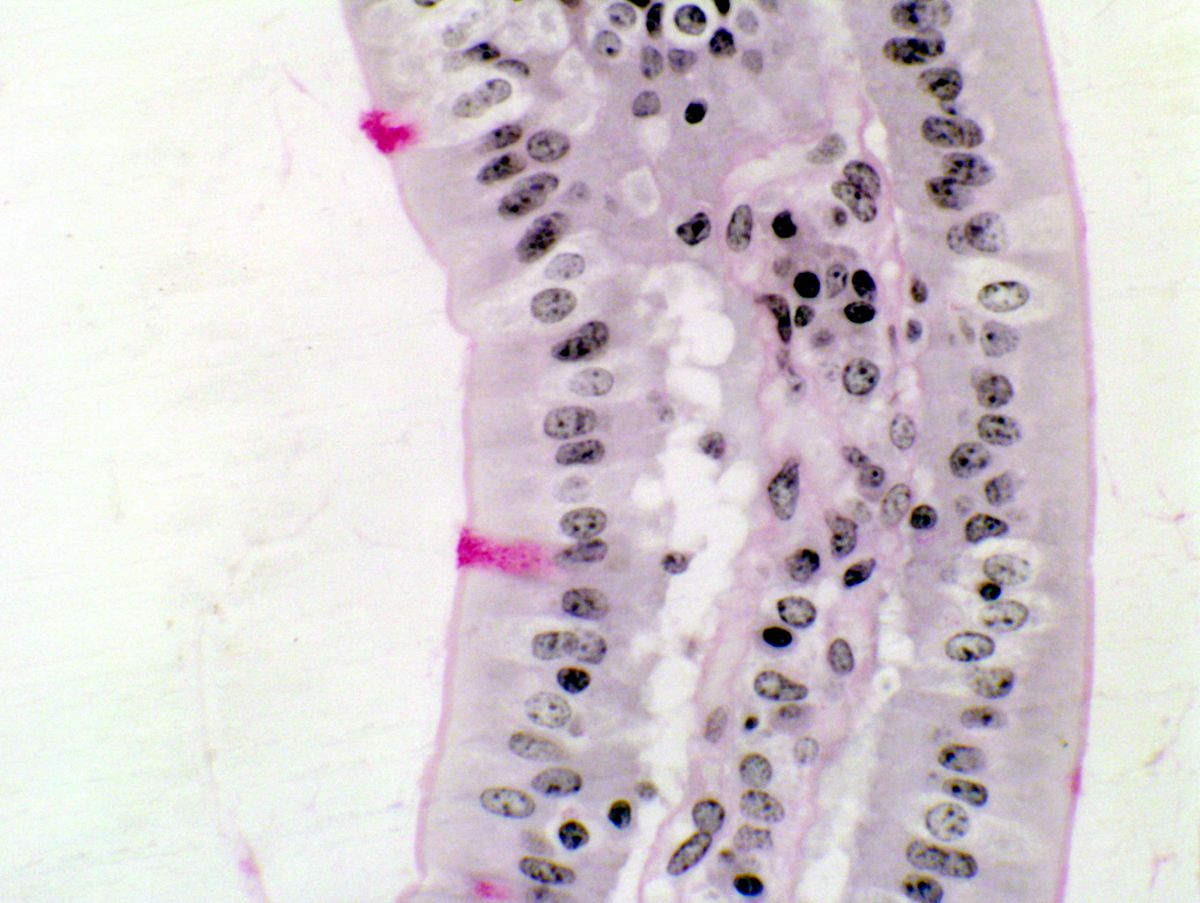
Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain: In histology, the PAS stain uses periodic acid to detect polysaccharides, such as glycogen, in tissues.
-
Crystalline solid: Periodic acid typically appears as a white crystalline solid at room temperature.
-
Soluble in water: Both forms of periodic acid are highly soluble in water, making them easy to use in aqueous solutions.
-
Decomposes upon heating: When heated, periodic acid decomposes into iodine pentoxide (I2O5), water, and oxygen.
-
Used in analytical chemistry: Periodic acid is employed in various analytical techniques to determine the presence of specific functional groups in organic compounds.
Chemical Properties of Periodic Acid
Understanding the chemical properties of periodic acid helps us appreciate its versatility and applications in different fields.
-
Molecular weight: The molecular weight of orthoperiodic acid (H5IO6) is 227.94 g/mol, while metaperiodic acid (HIO4) has a molecular weight of 191.91 g/mol.
-
Acidic nature: Periodic acid is a strong acid, capable of donating protons (H+) in aqueous solutions.
-
Oxidation states: Iodine in periodic acid can exhibit oxidation states of +7 in HIO4 and +5 in H5IO6.
-
Reactivity with alcohols: Periodic acid reacts with alcohols to form aldehydes or ketones, depending on the structure of the alcohol.
-
Formation of esters: Periodic acid can form esters with certain organic compounds, which are useful in synthetic chemistry.
-
Redox reactions: In redox reactions, periodic acid acts as an oxidizing agent, gaining electrons and being reduced to iodic acid (HIO3) or iodine (I2).
-
Hydrolysis: When dissolved in water, periodic acid undergoes hydrolysis to form iodic acid and oxygen.
-
Stability: Periodic acid is stable under normal conditions but can decompose when exposed to light or heat.
-
pH sensitivity: The reactivity of periodic acid can be influenced by the pH of the solution, with different reactions occurring in acidic or basic environments.
-
Complex formation: Periodic acid can form complexes with various metal ions, which can be used in coordination chemistry.
Applications of Periodic Acid
Periodic acid has a wide range of applications in different scientific fields, from organic chemistry to histology.
-
Cleavage of glycols: Periodic acid is used to cleave glycols into aldehydes or ketones, a reaction known as the Malaprade reaction.
-
Histological staining: The PAS stain, which uses periodic acid, is a crucial technique for identifying carbohydrates in tissue samples.
-
Synthesis of iodates: Periodic acid is used in the synthesis of iodates, which are salts containing the IO3- ion.
-
Oxidation of carbohydrates: Periodic acid can oxidize carbohydrates, breaking them down into smaller molecules for further analysis.
-
Detection of polysaccharides: In biochemistry, periodic acid is used to detect polysaccharides in various biological samples.
-
Preparation of aldehydes: Periodic acid is employed in the preparation of aldehydes from primary alcohols.
-
Oxidation of sulfides: Periodic acid can oxidize sulfides to sulfoxides or sulfones, which are important intermediates in organic synthesis.
-
Analytical reagent: Periodic acid is used as an analytical reagent to identify specific functional groups in organic compounds.
-
Oxidation of amines: Periodic acid can oxidize primary amines to nitro compounds, which are useful in synthetic chemistry.
-
Synthesis of heterocycles: Periodic acid is used in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds, which are important in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Safety and Handling of Periodic Acid
Handling periodic acid requires caution due to its strong oxidizing properties and potential hazards.
-
Corrosive: Periodic acid is corrosive and can cause severe burns upon contact with skin or eyes.
-
Toxicity: Inhalation or ingestion of periodic acid can be harmful, causing respiratory and gastrointestinal irritation.
-
Protective equipment: When handling periodic acid, it is essential to wear appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats.
-
Storage: Periodic acid should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from light and heat sources to prevent decomposition.
-
Disposal: Waste containing periodic acid must be disposed of according to local regulations, as it can be hazardous to the environment.
-
Emergency measures: In case of accidental exposure, it is crucial to rinse the affected area with plenty of water and seek medical attention immediately.
-
Ventilation: Working with periodic acid should be done in a well-ventilated area to minimize inhalation risks.
-
Spill management: In the event of a spill, it is important to contain and neutralize the acid using appropriate materials, such as sodium bicarbonate.
-
First aid: If periodic acid comes into contact with skin or eyes, rinse thoroughly with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical help.
-
Training: Proper training on the safe handling and use of periodic acid is essential for anyone working with this compound.
Final Thoughts on Periodic Acid
Periodic acid, a powerful oxidizing agent, plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions. Its ability to break down complex molecules into simpler ones makes it indispensable in both research and industrial applications. From its discovery to its diverse uses, periodic acid has proven to be a versatile and essential compound in the world of chemistry.
Understanding its properties and applications can provide valuable insights into the intricate workings of chemical processes. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or just someone curious about chemistry, knowing these facts about periodic acid can deepen your appreciation for this remarkable substance.
So, next time you encounter periodic acid in a lab or read about it in a textbook, you'll have a better grasp of its significance and the many ways it contributes to scientific advancements. Keep exploring and stay curious!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
