Electromagnetic radiation is a fascinating phenomenon that plays a crucial role in our everyday lives. From the light we see to the signals that power our smartphones, electromagnetic radiation is all around us. Understanding the principles of electromagnetic radiation is not only important for physicists and engineers but also for anyone curious about the workings of the world.
In this article, we will explore nine captivating facts about electromagnetic radiation that will help shed light on this intriguing subject. We’ll delve into the different types of electromagnetic radiation, their properties, and their wide-ranging applications. So, get ready to embark on a journey through the electrifying world of electromagnetic radiation!
Key Takeaways:
- Electromagnetic radiation is all around us, from sunlight to radio waves, and plays a crucial role in communication and medical imaging. It can be harmful if not used responsibly.
- Different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation have unique properties and are used in various technological applications, making it indispensable in our modern world.
Electromagnetic radiation is all around us
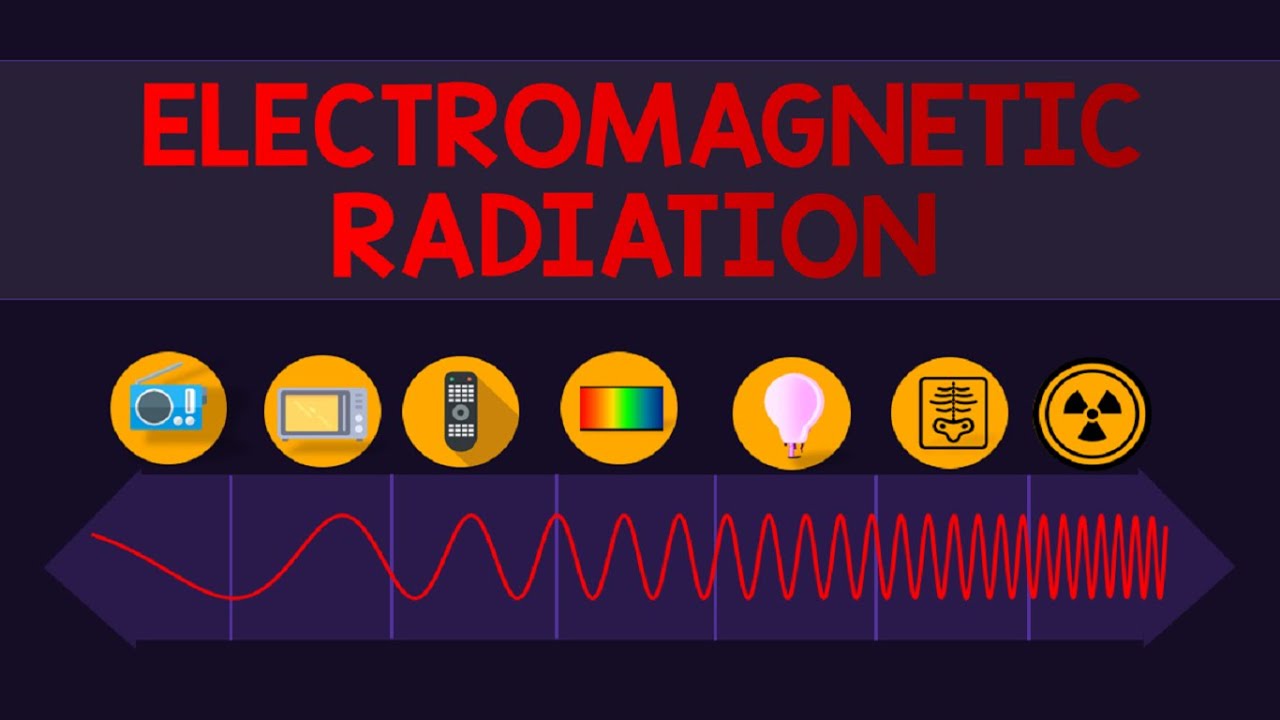
From the light emitted by the sun to the radio waves that transmit our favorite songs, electromagnetic radiation is present everywhere in our daily lives. It encompasses a wide range of wavelengths and frequencies, spanning from the shorter, high-energy gamma rays to the longer, low-energy radio waves.
It travels at the speed of light
Electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travels at a staggering speed of approximately 299,792,458 meters per second in a vacuum. This incredible speed allows electromagnetic waves to traverse vast distances in relatively short periods of time.
Electromagnetic radiation can be harmful
While electromagnetic radiation is essential for various applications and technologies, prolonged exposure to certain types can have adverse effects on living organisms. For instance, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can lead to skin damage or even increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
It plays a crucial role in communication
Electromagnetic radiation is the backbone of modern communication systems. Radio waves are used to transmit radio and television signals, while microwaves are employed in cellular networks and satellite communication. The higher frequency ranges, such as infrared and visible light, are used for fiber-optic communication.
Electromagnetic radiation can be classified into different categories
Electromagnetic radiation can be broadly classified into seven categories, known as the electromagnetic spectrum: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each category has distinct properties and applications.
It plays a vital role in medical imaging
Electromagnetic radiation, particularly X-rays, is widely used in medical imaging. X-ray machines help doctors visualize internal structures within the body, making it a valuable tool for diagnosing various conditions and injuries.
Different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation have unique properties
Each category of electromagnetic radiation exhibits different properties. For example, radio waves have long wavelengths and can easily pass through obstacles, while gamma rays have high energy and are used in radiation therapy to target and destroy cancer cells.
Electromagnetic radiation is influenced by magnetic and electric fields
As the name suggests, electromagnetic radiation is a combination of electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicular to each other. These fields interact with matter, leading to a wide range of phenomena such as reflection, refraction, and absorption.
Electromagnetic radiation is used in various technological applications
Electromagnetic radiation finds applications in numerous technologies across different fields. From microwave ovens and Wi-Fi networks to satellite communication and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), its versatility makes it indispensable in our modern world.
Conclusion
Electromagnetic radiation is a fascinating and essential aspect of our modern world. From the radio waves that deliver our favorite tunes to the X-rays that help diagnose illnesses, electromagnetic radiation plays a crucial role in various aspects of our daily lives. Through the exploration of these nine captivating facts, we have gained a deeper understanding of the diverse nature and applications of electromagnetic radiation.
By appreciating the electromagnetic spectrum’s vast range, from long-wavelength radio waves to high-energy gamma rays, we can better comprehend how this form of energy interacts with the world around us. Whether it’s understanding how our smartphones communicate wirelessly or unraveling the mysteries of star formation through infrared imaging, electromagnetic radiation continues to amaze and shape our understanding of the universe.
With ongoing advancements in technology and scientific research, the potential applications of electromagnetic radiation are boundless. From improving communication systems to enhancing medical imaging techniques, this field holds immense promise for the future. By continuing to explore and expand our knowledge of electromagnetic radiation, we can unlock new frontiers and make groundbreaking discoveries that propel us forward as a society.
FAQs
Q: What is electromagnetic radiation?
A: Electromagnetic radiation refers to the waves of energy formed by the interplay of electric and magnetic fields. It encompasses a wide spectrum, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Q: How is electromagnetic radiation produced?
A: Electromagnetic radiation is produced when an electrically charged particle, such as an electron, accelerates or decelerates. This acceleration creates oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which radiate energy in the form of electromagnetic waves.
Q: What are the practical applications of electromagnetic radiation?
A: Electromagnetic radiation has numerous practical applications in our daily lives, including wireless communication, medical imaging, cooking with microwaves, remote sensing, and astronomy.
Q: How does electromagnetic radiation interact with matter?
A: The interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter depends on its energy and frequency. Higher-energy radiation, such as X-rays and gamma rays, can penetrate through materials and cause ionization, while lower-energy radiation, such as visible light and radio waves, can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted by various substances.
Q: Is electromagnetic radiation harmful?
A: The potential harm of electromagnetic radiation depends on its intensity and frequency. While high-energy radiation like X-rays and gamma rays can be damaging, most everyday exposure to electromagnetic radiation, such as visible light and radio waves, poses no significant health risks.
Q: How do we measure electromagnetic radiation?
A: Electromagnetic radiation is typically measured in terms of its wavelength or frequency. Wavelength is measured in meters, while frequency is measured in hertz (cycles per second) or its multiples (kilohertz, megahertz, gigahertz, etc.).
Q: What is the speed of electromagnetic radiation?
A: Electromagnetic radiation travels at the speed of light, which is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (186,282 miles per second) in a vacuum.
Q: Can electromagnetic radiation be used for power generation?
A: Yes, electromagnetic radiation can be harnessed for power generation. Solar panels, for example, convert sunlight (which consists of electromagnetic radiation) into electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
Q: Are there any practical limitations to using electromagnetic radiation?
A: While electromagnetic radiation has numerous applications, there are practical limitations to consider. Factors such as the range of frequencies available for specific purposes, signal interference, and potential health concerns may impact its implementation in certain situations.
Electromagnetic radiation captivates minds, but have you ever wondered about spectroscopy's role in unraveling its secrets? Plancks law of blackbody radiation also holds intriguing insights into this phenomenon. Photoemission, too, plays a fascinating part in our understanding of electromagnetic radiation.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


