The electromagnetic spectrum is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a vital role in our understanding of the universe. It encompasses a wide range of electromagnetic waves, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. From the mundane to the mind-boggling, the electromagnetic spectrum offers a multitude of fascinating facts that will captivate your imagination. In this article, we will delve into 17 unbelievable facts about the electromagnetic spectrum, shedding light on the incredible properties and applications of these invisible waves. Whether you’re a science enthusiast or simply curious about the wonders of the natural world, get ready to embark on a journey through the astonishing realm of the electromagnetic spectrum!
Key Takeaways:
- The electromagnetic spectrum is a diverse range of energy waves, from radio waves to gamma rays, with unique properties and uses. It’s crucial for communication, medicine, and exploring the universe.
- Different types of electromagnetic waves, like radio waves and X-rays, have diverse applications, from wireless communication to medical imaging. Understanding and harnessing this spectrum is essential for our technological advancements.
The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of different types of electromagnetic waves.
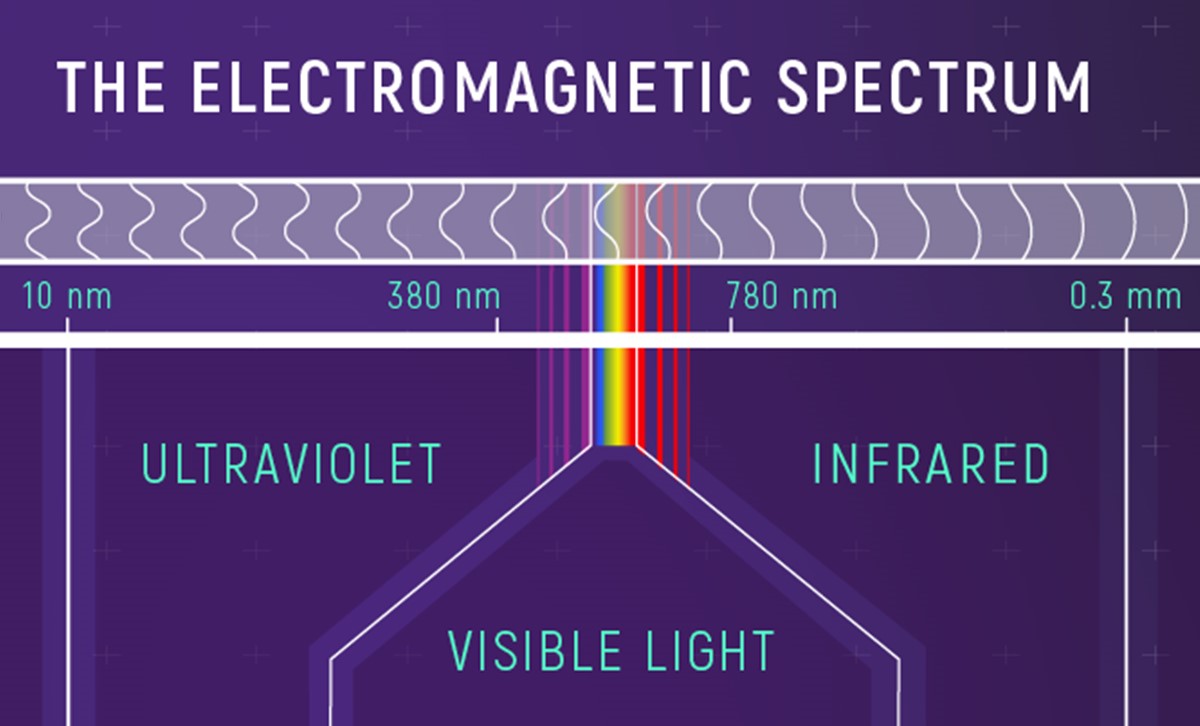
From the longest wavelength, which is radio waves, to the shortest wavelength, which is gamma rays, the electromagnetic spectrum consists of various waves with different properties and uses.
Each type of wave in the electromagnetic spectrum has a distinct range of frequencies and energy levels.
Radio waves have the lowest frequency and energy, while gamma rays have the highest. In between, there are microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, and X-rays.
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of wavelengths.
There are no clear boundaries between the different types of waves in the spectrum. Instead, they blend seamlessly into one another.
The speed of light is the fastest speed in the universe and is constant for all electromagnetic waves.
Light travels at a speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second in a vacuum, which is equivalent to about 186,282 miles per second.
Visible light, which is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, is the range of wavelengths that the human eye can detect.
It includes the colors of the rainbow, from red to violet, and is essential for our sense of vision.
The electromagnetic spectrum has applications in various fields, including communication, medicine, and astronomy.
Radio waves are used for broadcasting, cell phone communication, and radar systems. X-rays find applications in medical imaging and security screening. In astronomy, telescopes detect electromagnetic waves from celestial objects to study their properties.
The electromagnetic spectrum enables wireless communication.
Cell phones, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth all rely on electromagnetic waves to transmit information wirelessly.
Different materials interact with electromagnetic waves in various ways.
Some materials absorb certain wavelengths, while others reflect or transmit them. This property is the basis for technologies like solar panels, fiber optics, and filters.
Infrared waves in the electromagnetic spectrum are commonly used for remote sensing.
These waves can be used to capture thermal images, detect heat signatures, and even monitor Earth’s climate patterns.
The study of the electromagnetic spectrum has led to the development of advanced medical technologies.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines utilize radio waves and strong magnetic fields to produce detailed images of the human body.
Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum.
Unlike sound waves, which require a medium to propagate, electromagnetic waves can travel through outer space, making them crucial for studying distant celestial objects.
The electromagnetic spectrum plays a vital role in understanding the origins of the universe.
By detecting cosmic microwave background radiation, scientists have gained insights into the early stages of the universe’s formation.
Gamma rays, the highest-energy waves in the electromagnetic spectrum, are produced by celestial events such as supernovae and black holes.
Studying gamma rays helps astronomers unravel the mysteries of these powerful cosmic phenomena.
Radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum allow us to communicate with spacecraft and explore the depths of space.
By sending and receiving radio signals, we can gather information about distant planets, stars, and galaxies.
Ultraviolet waves in the electromagnetic spectrum are responsible for causing sunburns and can be harmful to living organisms.
It’s important to protect ourselves from excessive exposure to UV radiation, which can lead to skin damage and other health issues.
The electromagnetic spectrum is constantly being studied and researched to unlock new possibilities and applications.
Scientists continue to explore different ways to harness and manipulate electromagnetic waves for various purposes.
Understanding and harnessing the electromagnetic spectrum is essential for our technological advancements and overall understanding of the universe.
From communication to healthcare to space exploration, electromagnetic waves shape our world in unimaginable ways.
These 17 unbelievable facts about the electromagnetic spectrum only scratch the surface of its importance and impact on our lives. As we delve deeper into the mysteries of this vast realm of energy, we are sure to uncover even more incredible discoveries.
Conclusion
The electromagnetic spectrum is a fascinating and wide-ranging subject that plays a significant role in our everyday lives. From the radio waves that transmit our favorite songs to the X-rays that help diagnose medical conditions, the electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a vast range of phenomena.In this article, we’ve explored 17 unbelievable facts about the electromagnetic spectrum. We’ve learned about the different types of waves that make up the spectrum, from the shortest gamma rays to the longest radio waves. We’ve discovered how these waves are used in various applications, such as communication, imaging, and astronomy.Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum is not only important for scientific research but also for appreciating the technological advancements that it enables. By delving into its fascinating properties, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the invisible forces that surround us.So next time you use your smartphone, watch TV, or undergo a medical scan, take a moment to reflect on the incredible power and versatility of the electromagnetic spectrum.
FAQs
Q: What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
A: The electromagnetic spectrum refers to the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy gamma rays to lower-energy radio waves.
Q: How is the electromagnetic spectrum divided?
A: The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into different regions based on the wavelengths or frequencies of the waves. These regions include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Q: How do different waves in the electromagnetic spectrum interact with matter?
A: Waves in the electromagnetic spectrum interact with matter in different ways. For example, radio waves are used for communication and can pass through buildings, while X-rays can penetrate tissues and help with medical imaging.
Q: What are some everyday applications of the electromagnetic spectrum?
A: The electromagnetic spectrum is involved in numerous everyday applications. For instance, radio waves are used for broadcasting, microwaves for cooking, infrared for remote controls, and visible light for illumination and visual perception.
Q: How does the electromagnetic spectrum contribute to scientific research?
A: Scientists use different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum to study various aspects of the universe. For example, telescopes detect visible light and other forms of radiation to observe celestial objects, while X-rays and gamma rays help uncover the mysteries of the cosmos.
Q: Can humans see the entire electromagnetic spectrum?
A: No, the human eye can only perceive a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum known as visible light. However, advancements in technology have allowed us to explore and harness other regions, extending our understanding and capabilities.
Electromagnetic spectrum facts are truly mind-boggling, but there's even more to explore! Delve into the captivating world of gamma rays and their incredible properties. Shed light on visible light waves and how they impact our daily lives. Unravel the intriguing mysteries of the entire spectrum, from radio waves to X-rays. Continue your journey of discovery and expand your knowledge with these engaging articles that will leave you in awe of the electromagnetic wonders surrounding us.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
