Photosynthesis is a remarkable process that sustains life on Earth. It is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight into energy in the form of glucose. While many of us may have learned the basic concept of photosynthesis in school, there are several mind-blowing facts that are often overlooked. From the incredible efficiency of plants to the fascinating adaptations that have evolved over millions of years, photosynthesis is a topic that continues to captivate scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. In this article, we will delve into 15 unbelievable facts about photosynthesis that will deepen your understanding of this essential biological process. So, get ready to be amazed by the incredible world of photosynthesis and the wonders it holds!
Key Takeaways:
- Photosynthesis is a remarkable process where plants use sunlight to make food and oxygen, which is essential for all living things on Earth. It’s like a magical energy factory powered by the sun!
- Photosynthesis is not just important for plants, but for the whole planet. It helps regulate the climate, produces food for animals, and even serves as the basis for renewable energy technologies. It’s like nature’s superpower!
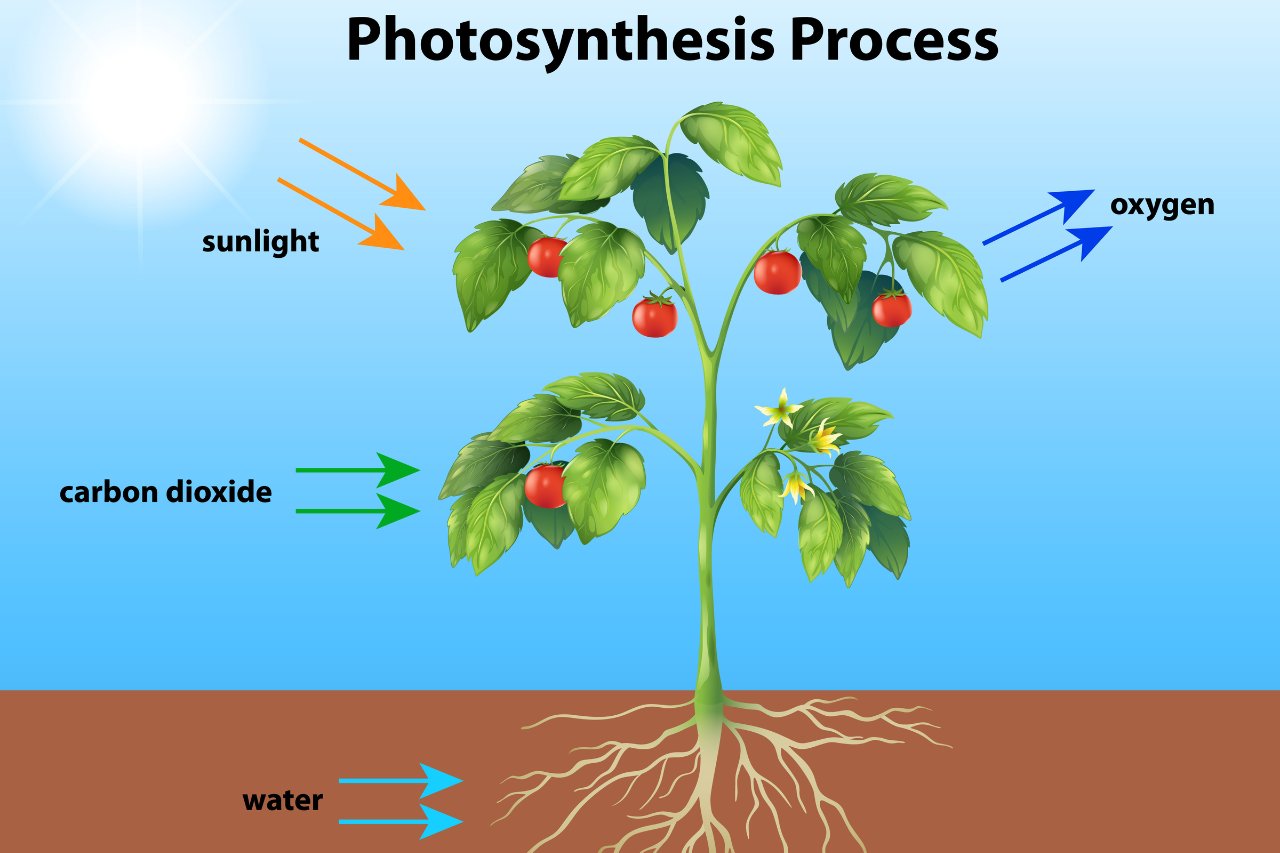
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
Plants have a fascinating ability to harness the power of the sun and convert it into usable energy through a complex biochemical process known as photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis produces oxygen as a byproduct.
During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen, which is vital for the survival of all living organisms on Earth.
Photosynthesis takes place in specialized structures called chloroplasts.
Within the cells of green plants, chloroplasts contain the pigment chlorophyll, which captures sunlight and initiates the photosynthetic process.
Photosynthesis is essential for the growth and development of plants.
Without photosynthesis, plants would not be able to produce the glucose they need to fuel their growth, maintain their structure, and carry out vital biological functions.
Photosynthesis is responsible for the green color of plants.
The chlorophyll present in chloroplasts absorbs light in the blue and red regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, reflecting green light, which gives plants their characteristic green color.
Photosynthesis is a vital source of food for all organisms.
Photosynthetic organisms, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, serve as the primary producers in food chains, converting solar energy into chemical energy that is consumed by other organisms.
Photosynthesis has been occurring for billions of years.
This process has been taking place on Earth since the emergence of early photosynthetic bacteria, playing a crucial role in shaping the planet’s atmosphere and supporting diverse forms of life.
Photosynthesis can be divided into two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions.
The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and involve the capture and conversion of light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. The light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, occur in the stroma of chloroplasts and involve the conversion of carbon dioxide into glucose using the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions.
Photosynthesis plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate.
Through the process of photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change by reducing greenhouse gas levels.
Photosynthesis can occur in different environmental conditions.
While photosynthesis is most efficient under ideal conditions of light, temperature, and carbon dioxide levels, certain plants have adapted to survive and conduct photosynthesis in extreme environments, such as deserts and icy regions.
Photosynthesis is influenced by environmental factors.
Factors such as light intensity, temperature, water availability, and the presence of pollutants can affect the rate and efficiency of photosynthesis in plants.
Photosynthesis is responsible for the production of organic compounds.
Through photosynthesis, plants produce a wide range of organic compounds, including sugars, starches, cellulose, and other essential molecules needed for growth and survival.
Photosynthesis is not limited to plants.
While plants are the primary organisms that carry out photosynthesis, some other organisms, such as algae, certain bacteria, and even some protists, also possess photosynthetic capabilities.
Photosynthesis is the foundation of renewable energy sources.
Many renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels and biofuels, rely on the principles of photosynthesis to capture and convert sunlight into usable energy.
Photosynthesis is a complex and interconnected process.
Photosynthesis involves a series of intricate biochemical reactions and pathways, with each step relying on the previous ones to efficiently convert sunlight into energy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, photosynthesis is an extraordinary process that enables plants to convert sunlight into energy and produce oxygen. It is a complex biochemical reaction that plays a vital role in the sustenance of life on Earth. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants provide food, generate oxygen, and contribute to the balance of the Earth’s atmosphere.Understanding the fascinating facts about photosynthesis enhances our appreciation for the intricate workings of nature. From the discovery of photosynthesis by Jan Ingenhousz in the 18th century to the exploration of the different types of photosynthesis in various organisms, each fact sheds light on the importance and marvel of this fundamental process.As we continue to delve deeper into the world of photosynthesis and uncover new discoveries, we gain insights into how we can harness its potential for various applications. From generating renewable energy to developing sustainable agricultural practices, photosynthesis continues to inspire scientists and researchers to explore its boundless possibilities.
FAQs
1. What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. It is a fundamental process that sustains life on Earth.
2. How does photosynthesis occur?
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells. Chlorophyll, the pigment that gives plants their green color, absorbs sunlight. This energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
3. What are the different types of photosynthesis?
The most common type of photosynthesis is oxygenic photosynthesis, which produces oxygen as a byproduct. However, certain bacteria perform anoxygenic photosynthesis, which does not produce oxygen.
4. What is the significance of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is essential for the production of oxygen, food, and biomass. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of atmospheric gases and sustaining life on Earth.
5. Can photosynthesis be utilized for renewable energy?
Yes, scientists are exploring ways to harness the energy of photosynthesis for renewable energy production. One approach is using artificial photosynthesis to generate fuels like hydrogen from sunlight.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
