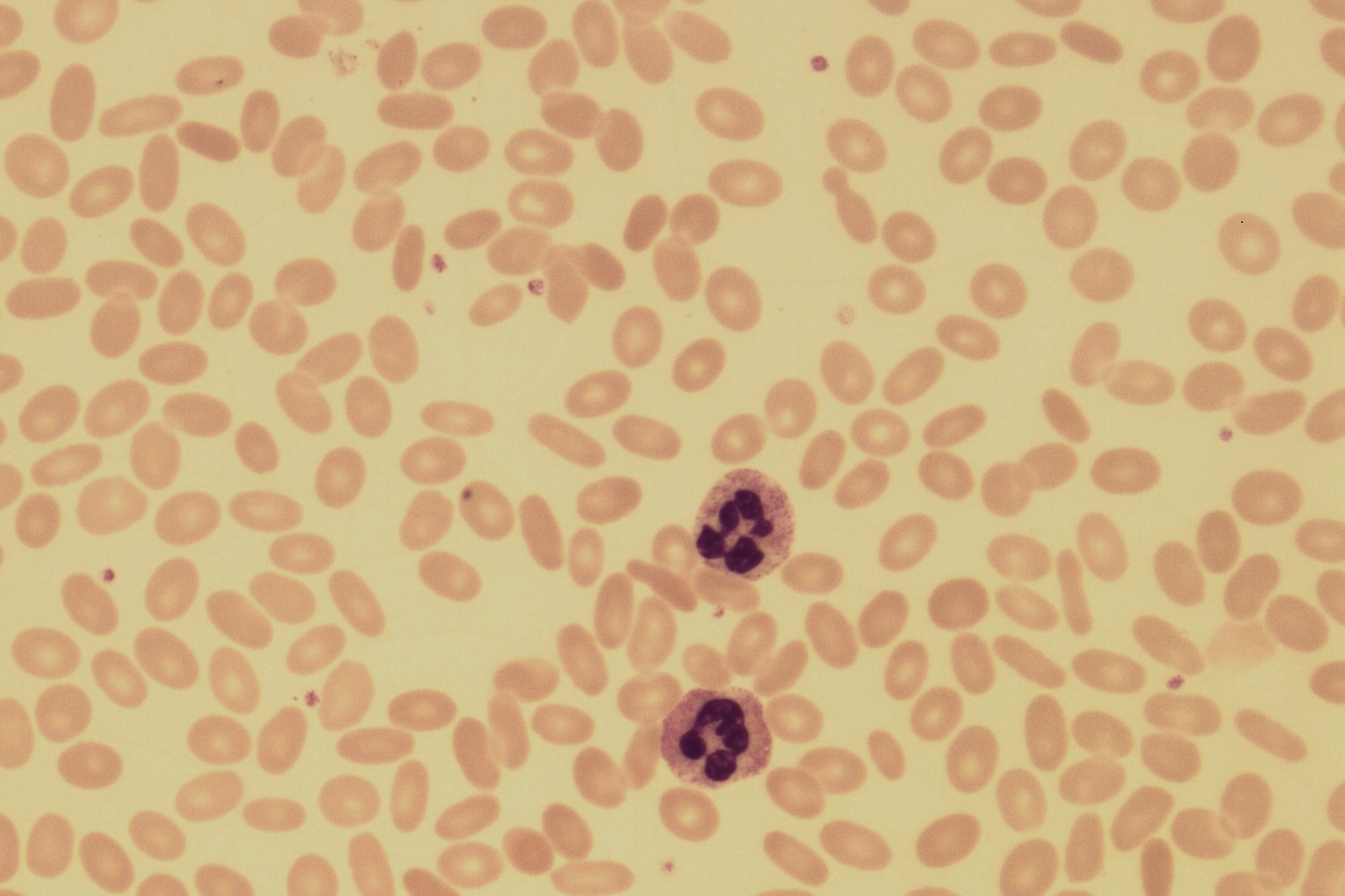
Hereditary Elliptocytosis is a rare blood disorder that affects the shape of red blood cells, making them oval or elliptical instead of the usual round shape. This condition can lead to various health issues, including anemia, jaundice, and an enlarged spleen. But what causes hereditary elliptocytosis? It's a genetic mutation passed down from parents to children. If one parent has the condition, there's a 50% chance their child will inherit it. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, and some people might not even know they have it. Understanding this condition is crucial for managing its effects and improving quality of life.
Key Takeaways:
- Hereditary Elliptocytosis is a rare genetic blood disorder causing oval-shaped red blood cells, leading to symptoms like fatigue and jaundice. Genetic testing and regular check-ups are crucial for managing the condition.
- Living with Hereditary Elliptocytosis requires a balanced diet, regular exercise, and staying hydrated. Joining support groups and educating others can improve quality of life for those with the condition.
What is Hereditary Elliptocytosis?
Hereditary Elliptocytosis (HE) is a genetic blood disorder affecting the shape of red blood cells. Instead of being round, these cells are elliptical. This condition can lead to various health issues.
- Genetic Origin: HE is caused by mutations in genes responsible for red blood cell membrane proteins.
- Inheritance Pattern: It follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, meaning one copy of the mutated gene can cause the disorder.
- Prevalence: HE is relatively rare, affecting about 1 in 2,000 to 4,000 individuals globally.
- Symptoms: Symptoms can range from mild to severe, including fatigue, jaundice, and an enlarged spleen.
- Diagnosis: Blood tests and genetic testing are used to diagnose HE.
- Red Blood Cell Shape: In HE, red blood cells are oval or elliptical instead of the typical round shape.
- Severity: The severity of HE can vary widely among individuals, even within the same family.
- Splenomegaly: An enlarged spleen is a common symptom due to the spleen working harder to remove abnormal cells.
- Hemolysis: Increased destruction of red blood cells, known as hemolysis, can occur in HE.
- Anemia: Chronic hemolysis can lead to anemia, causing fatigue and weakness.
Causes and Genetic Mutations
Understanding the genetic mutations behind HE helps in diagnosing and managing the condition. These mutations affect the proteins that maintain the red blood cell's shape.
- Spectrin Mutation: Mutations in the spectrin protein are a common cause of HE.
- Protein 4.1: Defects in protein 4.1 can also lead to HE.
- Ankyrin: Mutations in ankyrin, another membrane protein, are sometimes involved.
- Band 3 Protein: Changes in the band 3 protein can contribute to HE.
- Genetic Testing: Identifying specific mutations through genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of HE.
- Family History: A family history of HE increases the likelihood of inheriting the condition.
- De Novo Mutations: In some cases, HE can result from new mutations not inherited from parents.
- Gene Penetrance: The degree to which a gene mutation causes symptoms can vary, known as penetrance.
- Genetic Counseling: Families with HE can benefit from genetic counseling to understand risks and inheritance patterns.
- Research: Ongoing research aims to better understand the genetic basis of HE and develop targeted treatments.
Symptoms and Complications
HE can present with a variety of symptoms and complications. These can affect the quality of life and require medical attention.
- Fatigue: Chronic anemia can cause persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to increased bilirubin from red blood cell breakdown.
- Gallstones: Increased bilirubin can lead to the formation of gallstones.
- Leg Ulcers: Poor circulation can cause painful sores on the legs.
- Growth Delay: Children with severe HE may experience delayed growth and development.
- Infections: Splenectomy, a treatment for HE, can increase the risk of infections.
- Heart Problems: Severe anemia can strain the heart, leading to complications.
- Bone Marrow Stress: The bone marrow works harder to produce more red blood cells, leading to stress.
- Iron Overload: Repeated blood transfusions, a treatment for severe anemia, can cause iron overload.
- Psychological Impact: Chronic illness can affect mental health, leading to anxiety and depression.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Accurate diagnosis and effective treatment are crucial for managing HE. Various methods are used to diagnose and treat this condition.
- Blood Smear: A blood smear can reveal the characteristic elliptical shape of red blood cells.
- Osmotic Fragility Test: This test measures the red blood cells' resistance to breaking down in different solutions.
- Flow Cytometry: A technique used to analyze the physical and chemical characteristics of cells.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: In some cases, a bone marrow biopsy may be needed to assess red blood cell production.
- Splenectomy: Surgical removal of the spleen can reduce hemolysis and improve anemia.
- Folic Acid Supplements: Folic acid helps in the production of red blood cells and can be beneficial for HE patients.
- Blood Transfusions: Severe anemia may require blood transfusions to maintain adequate red blood cell levels.
- Iron Chelation Therapy: Used to remove excess iron from the body due to repeated blood transfusions.
- Hydroxyurea: A medication that can reduce the need for blood transfusions in some HE patients.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups and blood tests are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
Living with Hereditary Elliptocytosis
Living with HE requires ongoing management and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding how to cope with the condition can improve quality of life.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in iron and vitamins supports overall health.
- Avoiding Infections: Taking precautions to avoid infections is crucial, especially after a splenectomy.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate exercise can help maintain energy levels and overall health.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated helps maintain blood volume and circulation.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Education: Educating family members and friends about HE can foster understanding and support.
- Medical Alert: Wearing a medical alert bracelet can be helpful in emergencies.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation and yoga can help manage stress.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular visits to a hematologist ensure proper management of the condition.
- Advocacy: Advocating for awareness and research can help improve the lives of those with HE.
Final Thoughts on Hereditary Elliptocytosis
Hereditary Elliptocytosis (HE) is a rare genetic condition that affects the shape of red blood cells, making them elliptical instead of round. This can lead to various symptoms, including anemia, jaundice, and fatigue. Understanding the genetic mutations behind HE helps in diagnosing and managing the condition. While there’s no cure, treatments like blood transfusions and medications can help manage symptoms. Genetic counseling is also crucial for families affected by HE, providing insights into the inheritance patterns and risks for future generations. Awareness and early diagnosis play key roles in improving the quality of life for those with HE. By staying informed and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals with HE can lead healthier lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
