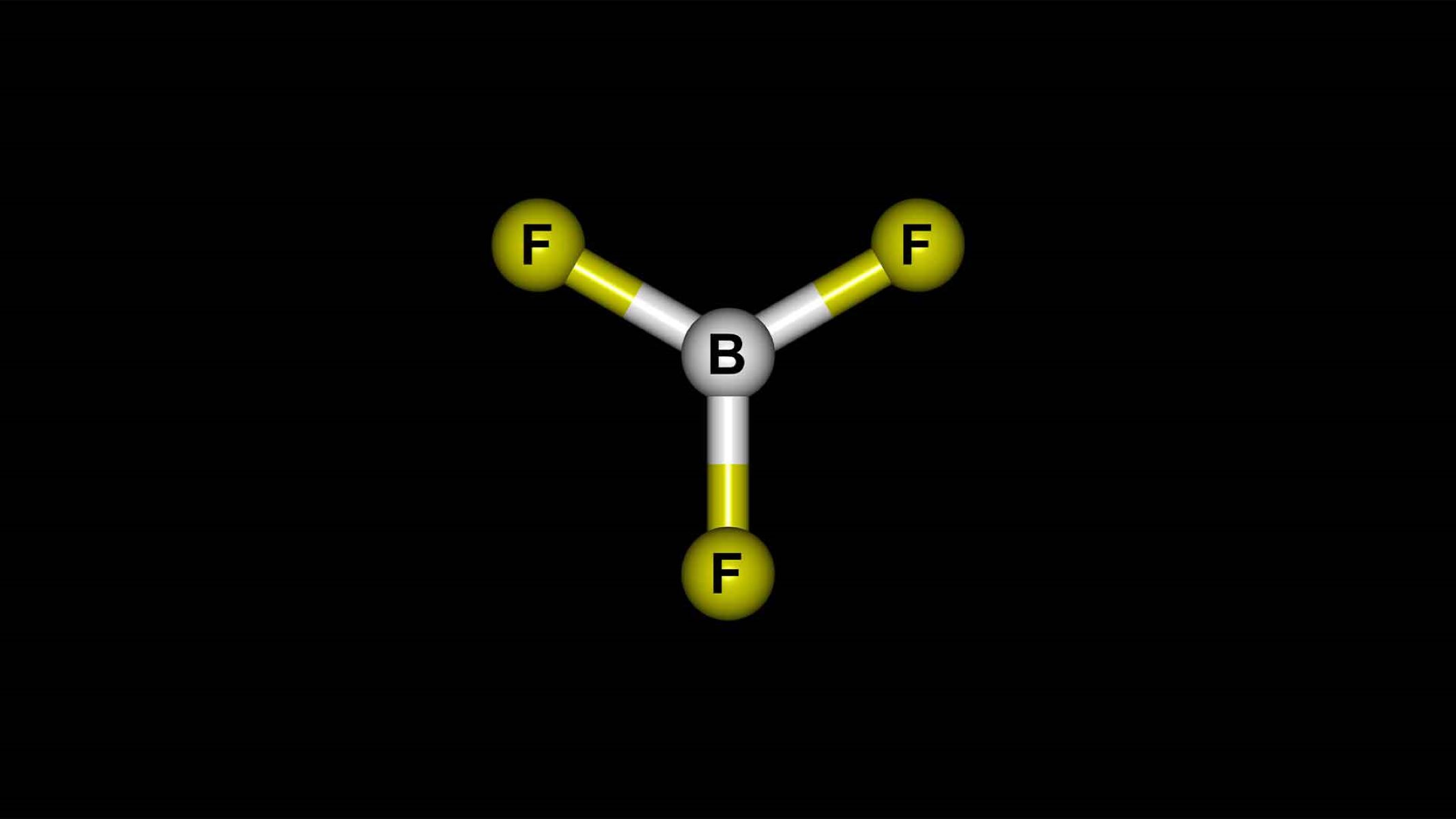
Boron Trifluoride might sound like a mouthful, but this chemical compound packs a punch in the world of chemistry. What is Boron Trifluoride? It's a colorless gas with a pungent odor, often used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. This compound, with the formula BF3, is known for its strong Lewis acid properties, making it a key player in various industrial applications. From polymerization to alkylation, Boron Trifluoride is a versatile tool in the chemist's toolkit. But there's more to this compound than meets the eye. Ready to dive into 50 intriguing facts about Boron Trifluoride? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Boron Trifluoride, a colorless gas with a pungent odor, is used in making high-purity boron and in the semiconductor industry. It's important to handle it with care due to its toxic and corrosive nature.
- BF3, a strong Lewis acid, has unique chemical properties and is used in various industrial applications, from organic synthesis to the production of plastics. Safety measures, including proper ventilation and protective equipment, are crucial when handling it.
What is Boron Trifluoride?
Boron trifluoride (BF3) is a chemical compound composed of boron and fluorine. It is a colorless gas with a pungent odor and is widely used in various industrial applications. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this compound.
- Boron trifluoride has the chemical formula BF3.
- It is a colorless gas at room temperature.
- BF3 has a pungent, suffocating odor.
- It is highly toxic and corrosive.
- Boron trifluoride is a Lewis acid, meaning it can accept electron pairs.
- It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis.
- BF3 is commonly used in the production of high-purity boron.
- It is also used in the semiconductor industry.
- Boron trifluoride forms complexes with ethers and alcohols.
- It is used in the polymerization of olefins.
Physical Properties of Boron Trifluoride
Understanding the physical properties of BF3 helps in its safe handling and application. Here are some key physical properties of boron trifluoride.
- The molecular weight of BF3 is 67.81 g/mol.
- It has a boiling point of -100.3°C (-148.5°F).
- The melting point of BF3 is -126.8°C (-196.2°F).
- It is soluble in water, forming hydrofluoric acid and boric acid.
- Boron trifluoride is denser than air.
- It has a density of 1.6 g/L at 0°C.
- BF3 is non-flammable.
- It has a critical temperature of -12.3°C.
- The critical pressure of BF3 is 49.85 atm.
- It has a vapor pressure of 1.5 atm at -100°C.
Chemical Properties of Boron Trifluoride
Boron trifluoride exhibits unique chemical properties that make it useful in various reactions. Here are some important chemical properties.
- BF3 is a strong Lewis acid.
- It reacts with water to form boric acid and hydrofluoric acid.
- Boron trifluoride forms adducts with amines.
- It can form complexes with nitriles.
- BF3 reacts with alcohols to form alkoxyboranes.
- It can polymerize olefins.
- Boron trifluoride is used in Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions.
- It can catalyze the formation of esters from carboxylic acids and alcohols.
- BF3 forms stable complexes with ethers.
- It can act as a fluorinating agent.
Industrial Applications of Boron Trifluoride
Boron trifluoride is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties. Here are some of its industrial applications.
- BF3 is used in the production of high-purity boron.
- It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis.
- Boron trifluoride is used in the semiconductor industry.
- It is used in the polymerization of olefins.
- BF3 is used in the production of boron-containing compounds.
- It is used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals.
- Boron trifluoride is used in the production of perfumes.
- It is used in the synthesis of esters.
- BF3 is used in the production of plastics.
- It is used in the manufacture of lubricants.
Safety and Handling of Boron Trifluoride
Due to its toxic and corrosive nature, proper safety measures must be taken when handling BF3. Here are some important safety and handling facts.
- BF3 is highly toxic and corrosive.
- It can cause severe burns upon contact with skin.
- Inhalation of BF3 can cause respiratory irritation.
- Proper ventilation is required when handling BF3.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) should be worn when handling BF3.
- BF3 should be stored in a cool, dry place.
- It should be kept away from moisture.
- Emergency procedures should be in place for BF3 spills.
- BF3 should be handled in a fume hood.
- Proper training is required for personnel handling BF3.
Final Thoughts on Boron Trifluoride
Boron trifluoride, a fascinating compound, plays a crucial role in various industries. From its use as a catalyst in organic chemistry to its application in semiconductor manufacturing, this compound proves its versatility. Its unique properties, such as being a strong Lewis acid, make it indispensable in many chemical reactions. However, handling boron trifluoride requires caution due to its toxicity and corrosiveness. Proper safety measures are essential to prevent accidents. Understanding its characteristics and applications can help harness its potential while minimizing risks. Whether you're a student, a professional chemist, or just curious, knowing these facts about boron trifluoride can deepen your appreciation for this remarkable compound. Stay informed, stay safe, and keep exploring the wonders of chemistry.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
