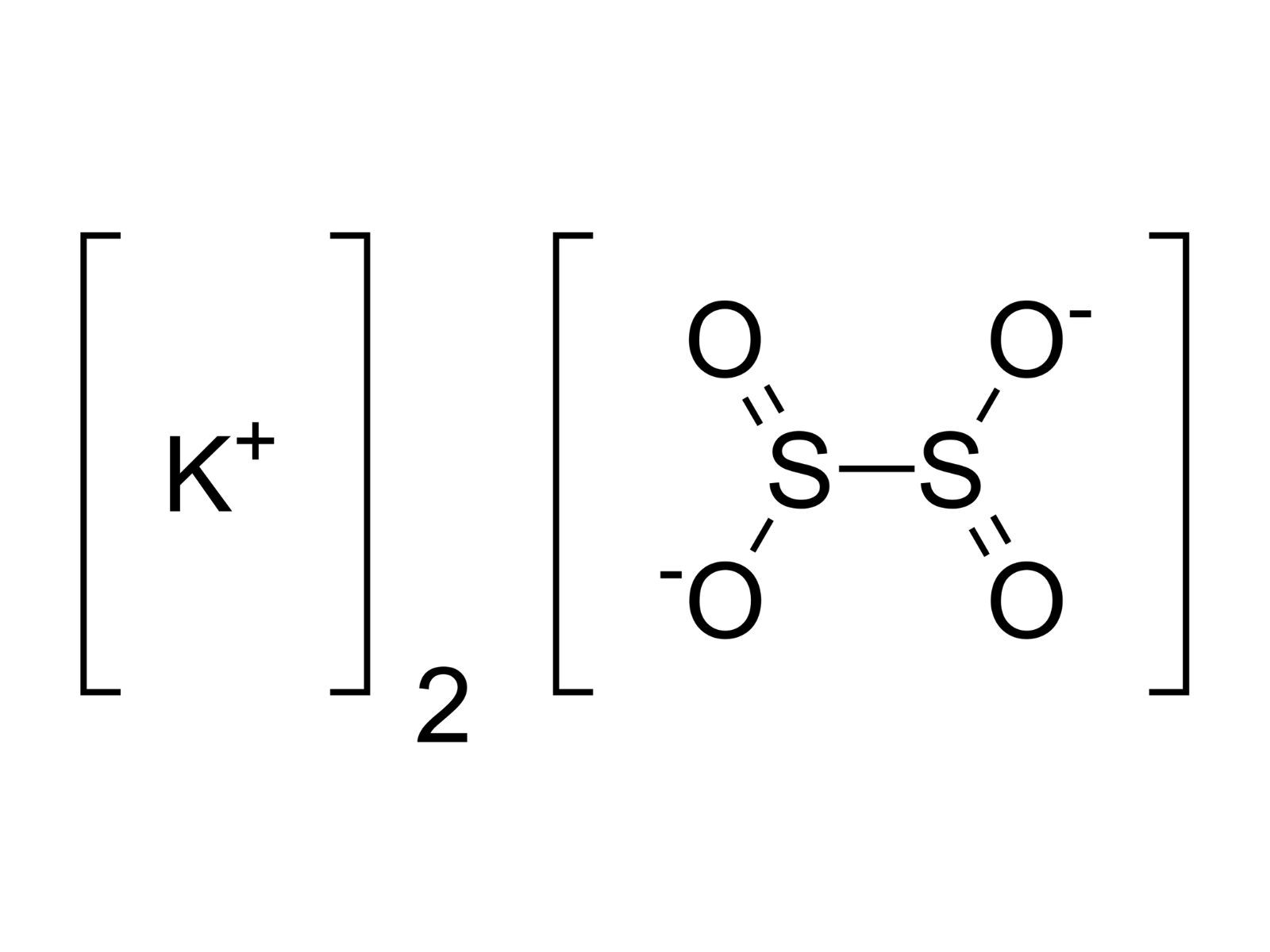
What is potassium dithionite? Potassium dithionite, also known as potassium hydrosulfite, is a white crystalline powder with the chemical formula K2S2O4. It’s primarily used as a reducing agent in various industrial processes, including textile dyeing, paper bleaching, and water treatment. This compound is highly soluble in water and decomposes in acidic conditions, releasing sulfur dioxide gas. Its unique properties make it valuable in applications requiring the removal of oxygen or other oxidizing agents. However, handling potassium dithionite requires caution due to its potential to cause skin irritation and its reactivity with acids. Understanding its uses and safety measures is crucial for anyone working with this chemical.
Key Takeaways:
- Potassium dithionite is a versatile compound used in industries like textiles, paper, food, and mining due to its reducing properties. It's crucial for bleaching, preserving food, and extracting precious metals.
- While potassium dithionite has many uses, it requires careful handling to avoid environmental impact and potential hazards. Proper storage, protective gear, and disposal are essential for safe use.
What is Potassium Dithionite?
Potassium dithionite, also known as potassium hydrosulfite, is a chemical compound with the formula K2S2O4. It's widely used in various industries due to its reducing properties. Here are some interesting facts about this versatile compound.
-
Potassium dithionite is a white crystalline powder that dissolves easily in water, making it useful in many applications.
-
It has a molar mass of 174.26 g/mol, which helps in calculating the amount needed for chemical reactions.
-
This compound is often used as a reducing agent in chemical processes, meaning it helps other substances gain electrons.
-
In the textile industry, potassium dithionite is employed to bleach fabrics and remove dyes.
-
It plays a crucial role in the paper industry, where it helps in the bleaching of wood pulp.
Chemical Properties of Potassium Dithionite
Understanding the chemical properties of potassium dithionite can help explain its various applications and behaviors in different environments.
-
Potassium dithionite decomposes when heated, releasing sulfur dioxide (SO2) and potassium sulfate (K2SO4).
-
It is highly reactive with oxygen, which is why it must be stored in airtight containers to prevent oxidation.
-
The compound is stable under normal conditions but can decompose in the presence of moisture and heat.
-
It has a pH of around 4.5-5.5 in a 1% aqueous solution, making it slightly acidic.
-
Potassium dithionite is not flammable, but it can release flammable gases when it decomposes.
Uses in Various Industries
Potassium dithionite's reducing properties make it valuable in several industries. Here are some of its most common uses.
-
In the food industry, it is used as a preservative and antioxidant, helping to maintain the color and flavor of foods.
-
It is used in the leather industry to remove excess dye from leather products.
-
Potassium dithionite is also used in the mining industry to extract precious metals from ores.
-
In photography, it serves as a reducing agent in developing solutions.
-
It is used in water treatment plants to remove chlorine and other contaminants from water.
Safety and Handling
Handling potassium dithionite requires caution due to its reactive nature. Here are some safety tips and guidelines.
-
Always store potassium dithionite in a cool, dry place away from moisture and heat sources.
-
Use protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, when handling the compound to avoid skin and eye irritation.
-
In case of contact with skin or eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical attention if necessary.
-
Ensure proper ventilation when using potassium dithionite to avoid inhaling any fumes.
-
Dispose of any waste containing potassium dithionite according to local regulations to prevent environmental contamination.
Environmental Impact
Potassium dithionite can have various effects on the environment, depending on how it is used and disposed of.
-
When released into water bodies, it can deplete oxygen levels, harming aquatic life.
-
Proper disposal methods are essential to prevent soil and water contamination.
-
It can break down into less harmful substances over time, but this process can be slow.
-
Using potassium dithionite in controlled environments minimizes its environmental impact.
-
Recycling and reusing the compound in industrial processes can reduce waste and environmental harm.
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known but fascinating facts about potassium dithionite.
-
It was first synthesized in the 19th century and has since become a staple in many industries.
-
The compound is sometimes used in scientific research to study redox reactions.
-
Potassium dithionite can act as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions, speeding up the process without being consumed.
-
It is often used in combination with other chemicals to achieve desired results in industrial applications.
-
Despite its many uses, potassium dithionite must be handled with care to avoid potential hazards.
Final Thoughts on Potassium Dithionite
Potassium dithionite, a powerful reducing agent, plays a crucial role in various industries. From textile dyeing to water treatment, its applications are vast. This compound, known for its ability to break down stubborn dyes, also helps in preserving food and improving soil quality. Despite its benefits, handling potassium dithionite requires caution due to its reactive nature. Proper storage and usage ensure safety and effectiveness. Understanding these facts about potassium dithionite not only highlights its importance but also underscores the need for responsible use. Whether you're a student, a professional, or just curious, knowing about this compound can be quite enlightening. So next time you encounter potassium dithionite, you'll appreciate its significance and the science behind it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
