Digermane might sound like a term from a sci-fi novel, but it's actually a fascinating chemical compound. Digermane is a molecule consisting of two germanium atoms bonded together, often used in semiconductor research. This compound plays a crucial role in the development of advanced materials and electronics. But what makes digermane so special? Its unique properties and potential applications make it a subject of interest for scientists and tech enthusiasts alike. In this post, we’ll dive into 30 intriguing facts about digermane that will shed light on its significance in modern technology. Get ready to be amazed by the wonders of this tiny yet mighty molecule!
Key Takeaways:
- Digermane is a reactive, colorless gas with applications in electronics and materials science. It requires careful handling due to its flammability and potential environmental impact.
- Understanding digermane's properties and environmental impact is crucial for safe handling and developing greener synthesis methods. Its reactivity makes it a subject of interest for chemical researchers.
What is Digermane?
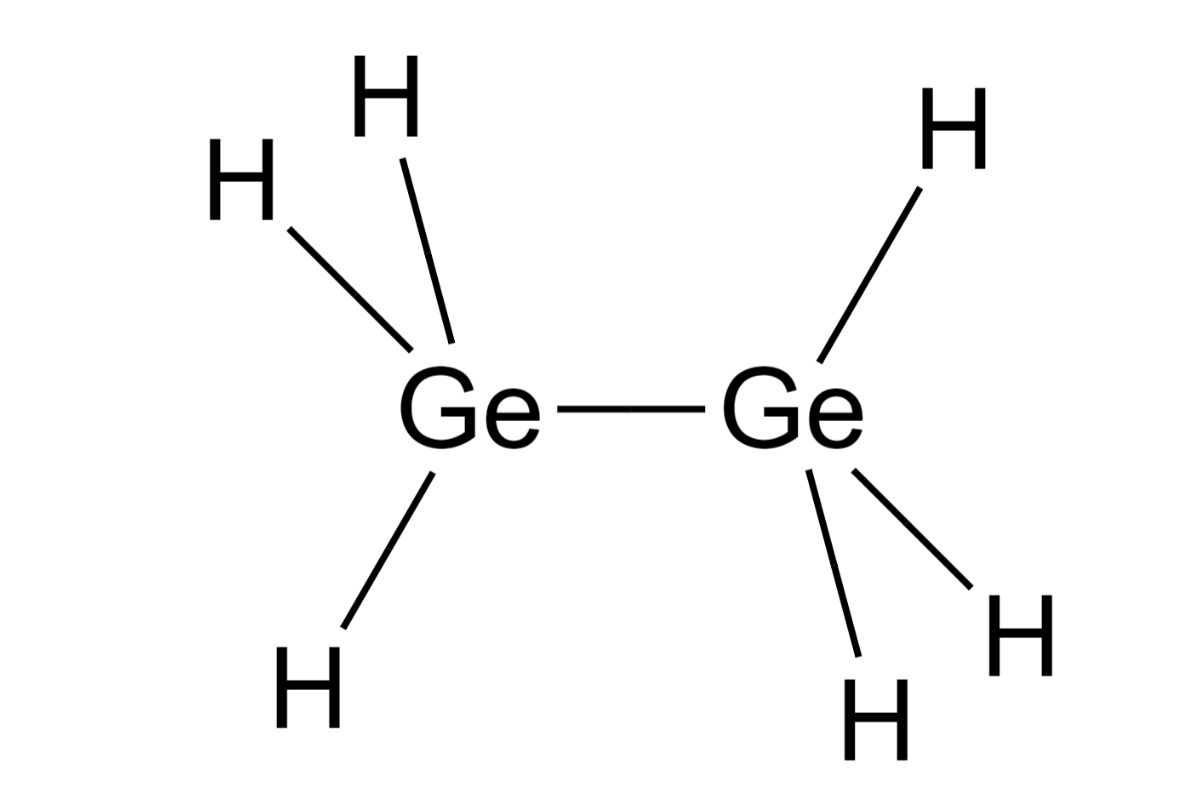
Digermane, a chemical compound with the formula Ge2H6, is a fascinating subject in the world of chemistry. This compound, consisting of two germanium atoms bonded to six hydrogen atoms, has unique properties and applications. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about digermane.
Chemical Properties of Digermane
Understanding the chemical properties of digermane helps in grasping its behavior and uses. Here are some key points:
- Digermane is a colorless gas at room temperature.
- It has a boiling point of -14°C (6.8°F).
- The molecular weight of digermane is 151.32 g/mol.
- It is less stable than its silicon counterpart, disilane.
- Digermane is highly reactive with oxygen, forming germanium dioxide and water.
- It decomposes at temperatures above 100°C (212°F).
Synthesis of Digermane
Creating digermane involves specific chemical reactions. Here are some interesting facts about its synthesis:
- Digermane can be synthesized by the reduction of germanium tetrachloride (GeCl4) with lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4).
- Another method involves the reaction of germanium hydride (GeH4) with germanium tetrachloride.
- The synthesis process requires careful control of temperature and pressure.
- Purification of digermane often involves distillation techniques.
Applications of Digermane
Digermane has various applications, particularly in the field of electronics and materials science. Here are some notable uses:
- It is used in the deposition of germanium-containing thin films.
- Digermane serves as a precursor for the production of germanium nanowires.
- It plays a role in the semiconductor industry for doping processes.
- Researchers use digermane in the study of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) techniques.
- It is explored for potential applications in photovoltaic cells.
Safety and Handling of Digermane
Handling digermane requires caution due to its reactive nature. Here are some safety considerations:
- Digermane is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air.
- It should be stored in a cool, dry place away from oxidizing agents.
- Proper ventilation is essential when working with digermane to avoid inhalation.
- Protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, is necessary to prevent skin and eye contact.
- In case of a digermane leak, evacuate the area and ventilate thoroughly.
Interesting Facts About Digermane
Beyond its chemical properties and applications, digermane has some fascinating aspects worth noting:
- Digermane was first synthesized in the early 20th century.
- It is part of a larger family of compounds known as germanes.
- The study of digermane contributes to the understanding of group 14 hydrides.
- Digermane's reactivity makes it a subject of interest for chemical researchers.
- It is often compared to its silicon and tin counterparts, disilane and distannane.
Environmental Impact of Digermane
Considering the environmental impact of chemical compounds is crucial. Here are some points about digermane's environmental footprint:
- Digermane can contribute to air pollution if not handled properly.
- Its decomposition products, germanium dioxide and water, are less harmful.
- Proper disposal methods are necessary to prevent environmental contamination.
- Research is ongoing to develop greener synthesis methods for digermane.
- Understanding digermane's environmental impact helps in developing safer handling practices.
The Final Word on Digermane
Digermane, a fascinating compound, holds a unique place in chemistry. With its formula Ge2H6, it’s a member of the germanium hydrides family. This compound, while not widely known, plays a crucial role in semiconductor research. Its structure, featuring two germanium atoms bonded to six hydrogen atoms, makes it intriguing for scientists.
Handling digermane requires caution. It’s highly reactive and can decompose explosively. Researchers must use specialized equipment and safety protocols. Despite these challenges, its potential in creating advanced materials keeps it relevant.
Understanding digermane’s properties and applications can open doors to new technological advancements. Whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast or a professional, knowing about this compound enriches your knowledge of the chemical world. Keep exploring, stay curious, and who knows? You might uncover the next big breakthrough in materials science.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
