Hydrogen bonding is a fascinating topic that plays a crucial role in many aspects of chemistry and biology. Ever wondered why water has such unique properties or why DNA strands stick together? The answer lies in hydrogen bonds. These special interactions occur when a hydrogen atom, covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom like oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, experiences an attraction to another electronegative atom nearby. This bond is not as strong as a covalent bond but significantly influences the behavior of molecules. Understanding hydrogen bonding can help explain phenomena like the high boiling point of water, the structure of proteins, and even the properties of ice. Let's dive into 23 intriguing facts about hydrogen bonding that will enhance your appreciation for this essential chemical interaction.
Key Takeaways:
- Hydrogen bonding is a special attraction between molecules, crucial in biology and chemistry. It affects everything from DNA structure to the fluffiness of bread!
- Hydrogen bonding isn't just for scientists; it's in everyday life, from the texture of food to the properties of hair. It even plays a role in outer space phenomena!
What is Hydrogen Bonding?
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of attraction between molecules. It plays a crucial role in many chemical and biological processes. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about hydrogen bonding.
-
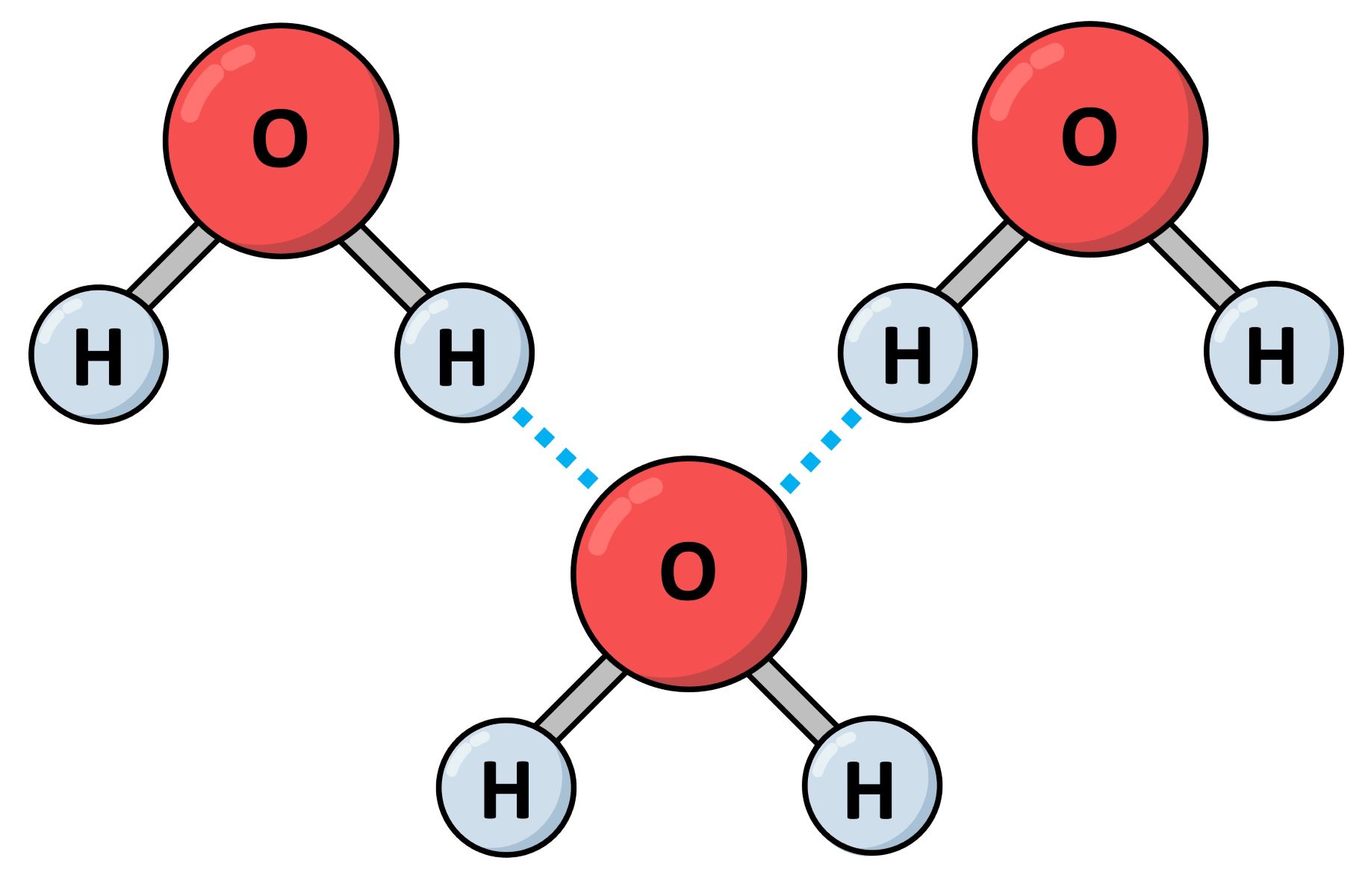
Hydrogen bonds form between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom. Typically, this electronegative atom is oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
-
Water molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds. This is why water has such unique properties, like high surface tension and boiling point.
-
Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds. However, they are stronger than van der Waals forces, making them a middle ground in terms of bond strength.
-
DNA's double helix structure relies on hydrogen bonds. These bonds hold the two strands of DNA together, allowing it to maintain its shape.
-
Hydrogen bonding is responsible for ice floating on water. In ice, water molecules form a crystalline structure due to hydrogen bonds, making ice less dense than liquid water.
Importance in Biology
Hydrogen bonds are vital in biological systems. They influence the structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules.
-
Proteins rely on hydrogen bonds for their secondary structure. Alpha helices and beta sheets in proteins are stabilized by these bonds.
-
Enzyme-substrate interactions often involve hydrogen bonds. These bonds help enzymes recognize and bind to their specific substrates.
-
Hydrogen bonds play a role in antibody-antigen interactions. This is crucial for the immune system to identify and neutralize pathogens.
-
Cellulose fibers in plants are held together by hydrogen bonds. This gives plants their structural strength and rigidity.
-
Hydrogen bonds help stabilize the structure of RNA. This is important for its function in protein synthesis and other cellular processes.
Role in Chemistry
In chemistry, hydrogen bonding affects the properties and behaviors of various substances. It can influence boiling points, solubility, and more.
-
Hydrogen bonding increases the boiling point of substances. For example, water has a higher boiling point than other similar-sized molecules due to hydrogen bonding.
-
Hydrogen bonds affect the solubility of compounds. Substances that can form hydrogen bonds with water are usually more soluble in water.
-
Hydrogen bonding can influence reaction mechanisms. It can stabilize transition states and intermediates, affecting the rate and outcome of chemical reactions.
-
Hydrogen bonds can affect the physical properties of polymers. For instance, nylon's strength and elasticity are due to hydrogen bonding between its polymer chains.
-
Hydrogen bonding is crucial in the formation of certain crystals. It helps determine the crystal structure and stability of compounds like ice and certain organic crystals.
Everyday Examples
Hydrogen bonding isn't just a scientific concept; it has practical implications in everyday life.
-
Hydrogen bonds are responsible for water's high heat capacity. This allows water to absorb and release heat slowly, moderating Earth's climate.
-
Hydrogen bonding affects the texture of food. For example, the fluffiness of bread and cakes is partly due to hydrogen bonds in gluten proteins.
-
Hydrogen bonds play a role in the properties of hair. The shape and strength of hair are influenced by hydrogen bonds between keratin molecules.
-
Hydrogen bonding is involved in the action of detergents. These bonds help detergents dissolve grease and grime in water.
-
Hydrogen bonds contribute to the unique properties of alcohols. For instance, ethanol's ability to mix with water is due to hydrogen bonding.
Fun Facts
Let's explore some intriguing and lesser-known facts about hydrogen bonding.
-
Hydrogen bonds can form in the gas phase. Though less common, they can occur in gases like hydrogen fluoride.
-
Hydrogen bonding can influence taste and smell. Certain flavors and aromas are a result of hydrogen bonds between molecules.
-
Hydrogen bonds can be found in outer space. They play a role in the formation of interstellar ice and other cosmic phenomena.
The Power of Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding plays a crucial role in many aspects of our daily lives. From the structure of DNA to the properties of water, these bonds are everywhere. They help proteins fold correctly, making life possible. Without hydrogen bonds, ice wouldn't float, and water wouldn't have its unique properties. These bonds also influence the boiling and melting points of substances, making them essential in chemistry and biology.
Understanding hydrogen bonding can help us appreciate the complexity and beauty of the natural world. It’s fascinating how such a small interaction can have such a big impact. Next time you drink water or think about DNA, remember the humble hydrogen bond. It’s a small force with a big role, shaping the world in ways we often take for granted.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
