Coenzymes are crucial components in various biochemical reactions, playing a fundamental role in facilitating metabolic processes in living organisms. From aiding in energy production to supporting DNA synthesis, coenzymes are involved in numerous vital functions within the body.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of coenzymes and uncover 20 mind-blowing facts about these essential molecules. Whether you are a chemistry enthusiast or simply curious about the inner workings of the human body, join us as we explore the remarkable properties and functions of coenzymes. Get ready to be amazed by the incredible impact that these tiny entities have on our health and well-being!
Key Takeaways:
- Coenzymes are like “helper molecules” that assist enzymes in carrying out important tasks in the body, such as breaking down food and producing energy. They are essential for overall health and well-being.
- Some coenzymes, like NAD+ and CoQ10, act as superheroes inside our bodies, protecting cells from damage and helping with important processes like DNA synthesis and brain function. They are like tiny but mighty helpers!
Coenzymes are essential for enzyme function.
Coenzymes play a crucial role in facilitating enzymatic reactions in the body. Without coenzymes, many enzymatic reactions would not occur efficiently or at all.
Coenzymes can be organic molecules.
Coenzymes can be organic molecules such as vitamins or derivatives of vitamins. They are often required in small amounts and act as co-factors for specific enzymes.
Coenzymes can bind loosely or tightly to enzymes.
Depending on the specific coenzyme, it can bind loosely or tightly to the enzyme it is assisting. This binding is essential for the proper functioning of the enzyme.
Coenzymes can participate in a wide range of biochemical reactions.
Coenzymes can participate in various important biochemical reactions such as redox reactions, transfer of functional groups, and carrying chemical groups between enzymes.
NAD+ and NADP+ are coenzymes involved in redox reactions.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+) are coenzymes that play a key role in redox reactions in cells. They are involved in energy metabolism and cellular respiration.
Coenzyme A is involved in the metabolism of fatty acids.
Coenzyme A (CoA) is an essential coenzyme that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of fatty acids. It carries and transfers acyl groups during the breakdown of fatty acids, enabling energy production.
Coenzymes can be synthesized in the body.
Although some coenzymes are obtained through diet, the body is capable of synthesizing certain coenzymes. This ensures a continuous supply for various biochemical reactions.
Coenzymes are essential for the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
Coenzymes such as folate and cobalamin (Vitamin B12) are crucial for DNA and RNA synthesis. They play a vital role in maintaining genetic integrity and proper cell division.
Coenzymes function as carriers of small chemical groups.
Coenzymes can bind and carry small chemical groups such as methyl, acyl, and amino groups. They transport these groups between enzymes, enabling diverse metabolic reactions to occur.
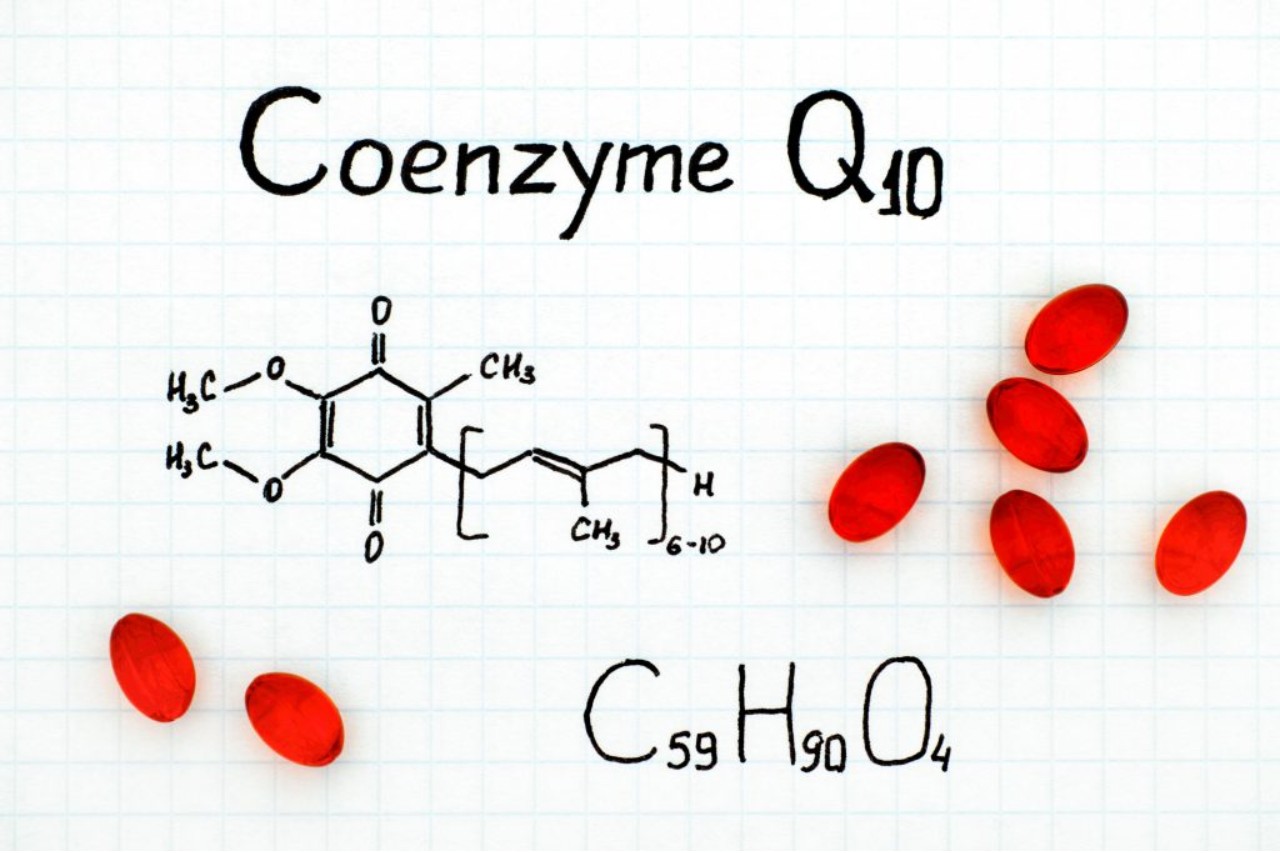
Coenzyme Q10 is an antioxidant.
Coenzyme Q10, also known as CoQ10, is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative stress and damage. It is involved in energy production within the mitochondria.
Coenzymes can be recycled and reused.
Many coenzymes can be recycled and used again in enzymatic reactions. This recycling process ensures the efficient utilization of coenzymes and reduces the need for constant replenishment.
Coenzymes can be divided into water-soluble and lipid-soluble groups.
Coenzymes can be categorized into two groups based on their solubility: water-soluble coenzymes, such as B vitamins, and lipid-soluble coenzymes, such as coenzyme Q10.
Coenzymes are essential for the functioning of neurotransmitters.
Coenzymes such as pyridoxal phosphate (Vitamin B6) are critical for the synthesis and metabolism of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA. They play a vital role in brain function and mood regulation.
Coenzymes can influence gene expression.
Some coenzymes, like NAD+, have the ability to modify and influence gene expression. They can act as signaling molecules that regulate various cellular processes and control the expression of specific genes.
Coenzymes are involved in the breakdown of carbohydrates.
Coenzymes such as thiamine pyrophosphate (Vitamin B1) are essential for the breakdown of carbohydrates through glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. They help extract energy from glucose.
Coenzymes play a role in the production of collagen.
Coenzymes like ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) are crucial for the production and stabilization of collagen, a protein that provides structure and strength to connective tissues, skin, and blood vessels.
Coenzymes can act as co-substrates in enzymatic reactions.
In some enzymatic reactions, coenzymes can participate as co-substrates, undergoing chemical changes along with the substrate. This active involvement is crucial for the completion of the reaction.
Coenzymes can act as “molecular switches” in signaling pathways.
Certain coenzymes, such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), play a role in cellular signaling pathways by acting as “molecular switches.” They regulate protein activity and influence intracellular communication.
Coenzymes can be derived from the breakdown of vitamins.
Some coenzymes are derived from the breakdown of vitamins within the body. For example, niacin (Vitamin B3) can be converted into its coenzyme form, NAD+.
Coenzymes are essential for overall health and well-being.
Coenzymes play a vital role in various biochemical processes that are necessary for maintaining overall health and well-being. They are involved in energy production, metabolism, DNA synthesis, and many other vital functions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, coenzymes play a crucial role in various biological processes and are essential for maintaining our health and wellbeing. Understanding the fascinating facts about coenzymes can give us a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of biochemistry and how it impacts our daily lives.From their involvement in energy production to their participation in the synthesis of vital molecules, coenzymes are truly remarkable. They act as versatile helpers, assisting enzymes in their catalytic activities and ensuring the smooth running of biochemical reactions in our bodies.As we continue to explore the world of chemistry, it is evident that coenzymes are not just mere catalysts; they are the unsung heroes behind countless physiological processes. So, the next time you come across the term coenzyme, remember the vital role it plays in maintaining the delicate balance of life.
FAQs
Q: What is a coenzyme?
A: A coenzyme is a non-protein organic molecule that is required for the proper functioning of an enzyme. It acts as a cofactor, assisting enzymes in catalyzing biochemical reactions.
Q: How are coenzymes different from enzymes?
A: Enzymes are proteins that facilitate biochemical reactions, whereas coenzymes are non-protein molecules that work in conjunction with enzymes to enhance their activity.
Q: What are some examples of coenzymes?
A: Examples of coenzymes include NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide), and coenzyme Q10.
Q: What functions do coenzymes serve?
A: Coenzymes serve various functions, such as carrying electrons and protons, transferring chemical groups, and participating in metabolic pathways.
Q: Can coenzymes be synthesized by the body?
A: Some coenzymes can be synthesized by the body, while others are obtained from dietary sources, such as vitamins and minerals.
Q: Are coenzymes essential for human health?
A: Yes, coenzymes are essential for human health as they are involved in vital processes like energy production, DNA synthesis, and cellular metabolism.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
