Valence Bond Theory is a fundamental concept in the field of chemistry that helps us understand how atoms come together to form chemical bonds. It provides a fascinating glimpse into the interactions between individual atoms and the forces that hold them together. This theory, developed by Linus Pauling in the 1930s, revolutionized our understanding of chemical bonding and paved the way for advancements in molecular structure and reactivity.
In this article, we will explore 16 intriguing facts about Valence Bond Theory that will not only deepen your understanding of this important concept but also spark your curiosity about the intricate world of chemical bonds. From the basic principles to its practical applications, Valence Bond Theory continues to be a cornerstone in the study of chemistry. So, let’s dive in and uncover some captivating facts about this fundamental theory!
Key Takeaways:
- Valence Bond Theory explains how atoms form bonds by sharing electrons, determining bond strength and shape of molecules. It’s like a secret code that unlocks the mysteries of chemical bonding!
- Valence Bond Theory bridges the gap between different branches of chemistry, helps predict reactivity of molecules, and is used in designing new substances. It’s like a superhero power for chemists!
The Origins of Valence Bond Theory
Valence Bond Theory was developed in the early 20th century by chemists Walter Heitler and Fritz London, based on the work of Linus Pauling. It revolutionized our understanding of chemical bonding.
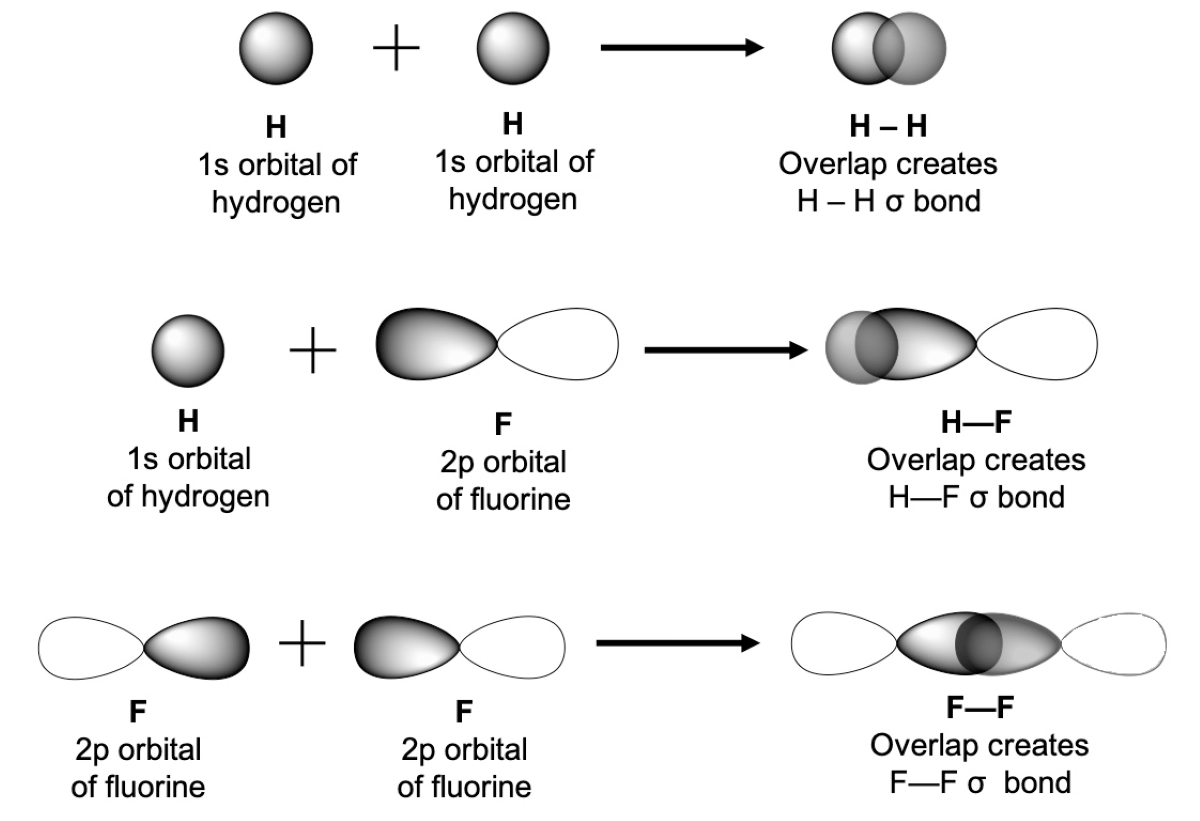
Valence Bond Theory Explains Covalent Bonds
Valence Bond Theory offers a detailed explanation of covalent bonding, which involves the sharing of electrons between atoms. It describes how the overlapping orbitals of atoms form the bonds.
Overlapping Orbitals Determine Bond Strength
In Valence Bond Theory, the strength of a covalent bond is determined by the extent of overlap between the bonding orbitals of the atoms involved. The greater the overlap, the stronger the bond.
Hybridization is an Important Concept
Valence Bond Theory introduces the concept of hybridization, which explains the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. This concept is crucial in understanding the geometry of molecules.
Sigma and Pi Bonds
Valence Bond Theory distinguishes between sigma (?) and pi (?) bonds. Sigma bonds are formed by the overlap of orbitals along the internuclear axis, while pi bonds are formed by the lateral overlap of p orbitals.
Delocalized Electrons and Resonance
Valence Bond Theory explains the phenomenon of resonance, where multiple Lewis structures can be drawn for a molecule. It involves the delocalization of electrons and contributes to the stability of certain compounds.
Orbital Overlap and Bond Length
The extent of orbital overlap, as predicted by Valence Bond Theory, directly influences the bond length. Stronger overlap leads to shorter bond lengths and stronger bonds.
Valence Bond Theory and Quantum Mechanics
Valence Bond Theory was one of the first successful attempts to combine quantum mechanics with chemistry. It provides a bridge between the macroscopic world of chemical reactions and the microscopic world of atomic and molecular orbitals.
Application to Molecular Orbital Theory
Valence Bond Theory serves as a foundation for the development of Molecular Orbital Theory, which provides a more comprehensive understanding of the electronic structure and properties of molecules.
Limitations of Valence Bond Theory
While Valence Bond Theory is a powerful tool, it has limitations. It does not fully explain the bonding in transition metals, the energy levels of molecular orbitals, or the interaction of molecular orbitals in larger molecules.
The Concept of Spin and Magnetic Properties
Valence Bond Theory introduces the concept of electron spin, where electrons in a bond can have opposite spins. This concept is critical in understanding the magnetic properties of materials.
Explaining Bonding and Anti-Bonding Orbitals
Valence Bond Theory provides insight into the formation of bonding and anti-bonding orbitals. Bonding orbitals stabilize the molecule, while anti-bonding orbitals destabilize it.
Clarifying Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
Valence Bond Theory helps explain the principles of Electron Pair Repulsion Theory, which determines the geometrical arrangements of atoms within molecules.
Contributing to the Development of Chemical Reactivity Theory
Valence Bond Theory has contributed to the development of Chemical Reactivity Theory, providing a framework for understanding and predicting the reactivity of molecules.
Bridging the Gap Between Organic and Inorganic Chemistry
Valence Bond Theory plays a significant role in bridging the gap between organic and inorganic chemistry. It helps explain the bonding and properties of both organic and inorganic compounds.
Valence Bond Theory and Computational Chemistry
Valence Bond Theory continues to be used in computational chemistry to understand molecular structures and properties, aiding the design of new substances and materials.
Overall, Valence Bond Theory is a fundamental concept in chemistry that provides a deep understanding of chemical bonding and the behavior of molecules. Its applications and impact on various branches of chemistry make it a fascinating field of study.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Valence Bond Theory is a fundamental concept in chemistry that provides insights into the nature of chemical bonding. It helps us understand how atoms form stable molecules by sharing or transferring electrons. By considering the overlapping orbitals of atoms, this theory explains the formation of covalent bonds and the strength of these bonds. Valence Bond Theory has been instrumental in predicting and explaining molecular shapes, reactivity, and properties.Through its development and application, scientists have gained a deeper understanding of chemical bonding and have been able to make advancements in various fields, including organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and materials science. Valence Bond Theory continues to be a cornerstone of modern chemistry and serves as the foundation for further research and discoveries.By studying Valence Bond Theory, chemists can unlock the mysteries of how atoms come together to form the incredible array of compounds and materials that make up our world.
FAQs
1. What is Valence Bond Theory?
Valence Bond Theory is a concept in chemistry that explains how atoms form stable molecules by sharing or transferring electrons. It considers the overlapping orbitals of atoms to explain the formation and strength of covalent bonds.
2. Who developed Valence Bond Theory?
Valence Bond Theory was developed by Linus Pauling in the 1930s. His work laid the foundation for our understanding of chemical bonding and earned him the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954.
3. How does Valence Bond Theory explain molecular shapes?
Valence Bond Theory explains molecular shapes based on the hybridization of atomic orbitals. By considering the types and number of orbitals that hybridize, the theory can predict the geometry of molecules.
4. What is the significance of Valence Bond Theory in modern chemistry?
Valence Bond Theory is of great significance in modern chemistry as it provides a framework for understanding chemical bonding, molecular structure, reactivity, and properties. It has enabled advancements in various fields, including organic chemistry and materials science.
5. Are there any limitations to Valence Bond Theory?
While Valence Bond Theory is a powerful tool in understanding chemical bonding, it has some limitations. It does not fully explain the bonding in molecules with delocalized electrons or complex bonding situations. Other theories, such as Molecular Orbital Theory, are required to address these cases.
Valence Bond Theory offers a fascinating glimpse into the world of chemical bonding, but there's so much more to explore. Dive deeper into the intricacies of Covalent Bonds and uncover 13 mind-blowing facts that will change your perception. For a comprehensive understanding of the forces that hold molecules together, check out our article on 20 incredible facts about Chemical Bonding. If you're ready to take your knowledge to the next level, embark on a journey through the enigmatic realm of Quantum Chemistry and prepare to be amazed by 20 astounding facts that will reshape your understanding of the subatomic world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
