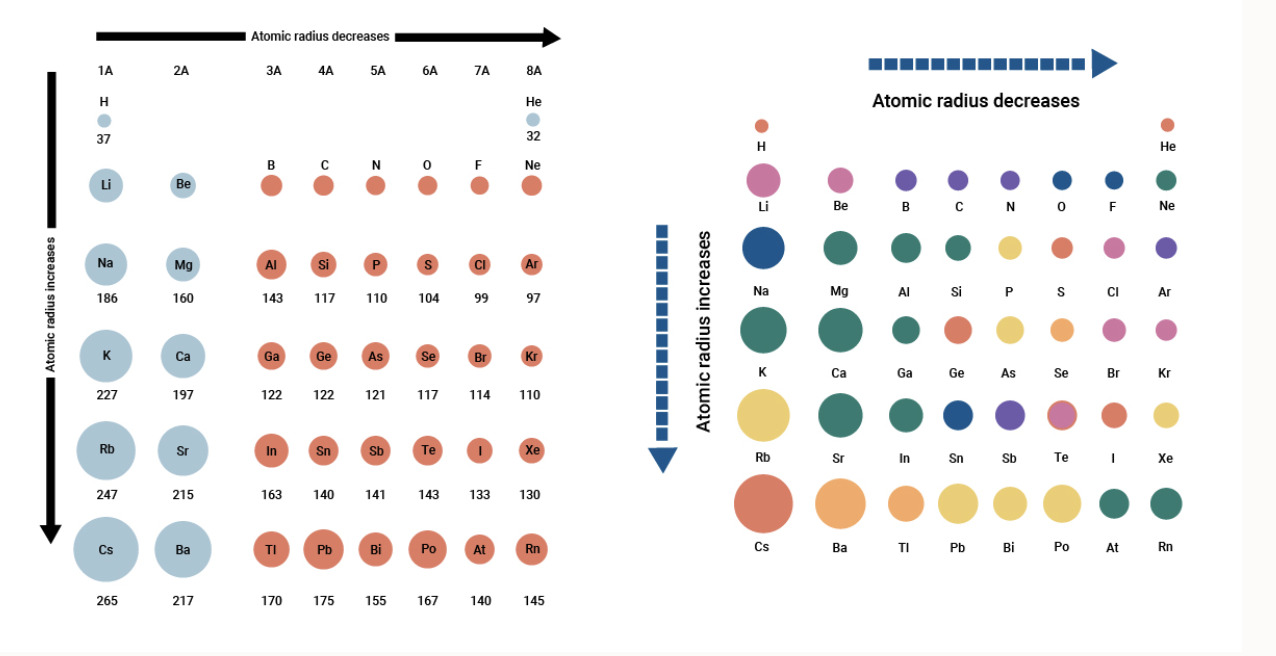
The concept of atomic radius is a fundamental principle in the field of chemistry. It refers to the size of an atom, which plays a crucial role in determining various properties and behaviors of elements. Understanding atomic radius helps us comprehend trends within the periodic table, predict bonding patterns, and comprehend the arrangement of electrons within an atom. In this article, we will dive into 15 captivating facts about atomic radius that will broaden our understanding of this essential concept. From the influences of atomic number and electron configuration to the impact of various factors on atomic size, we will explore the fascinating world of atomic radius. So, get ready for an informative journey as we uncover intriguing insights about atomic radius in the realm of chemistry.
Key Takeaways:
- Atomic radius determines how big an atom is and affects how it behaves. It can change based on the element and its position on the periodic table.
- The size of an atom can impact its ability to bond with other atoms and form ions. Understanding atomic radius helps us understand the behavior of elements in chemistry.
The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost energy level of an atom.
Knowing the atomic radius helps us understand how atoms interact and bond with each other. It varies depending on the element and its electronic configuration.
Periodic Trend
The atomic radius generally decreases across a period and increases down a group in the periodic table.
This trend can be attributed to the increasing number of protons in the nucleus and the addition of electron shells as you move along a period or down a group.
Relationship with Electronegativity
The atomic radius is inversely related to electronegativity.
Elements with smaller atomic radii tend to have higher electronegativity, meaning they have a greater attraction for electrons.
Relationship with Ionization Energy
The atomic radius is inversely related to ionization energy.
Elements with smaller atomic radii require more energy to remove an electron since the electrons are closer to the nucleus and experience a stronger attraction.
Factors Affecting Atomic Radius
Multiple factors can influence the atomic radius, including the number of electron shells, nuclear charge, and the shielding effect of inner electrons.
These factors determine the overall size of an atom and its ability to interact with other atoms.
Trend in Metallic Character
Elements with larger atomic radii tend to exhibit more metallic character.
Larger atomic radii allow for easier delocalization of electrons, leading to enhanced metallic properties such as electrical conductivity and malleability.
Comparison of Covalent and Metallic Radii
The covalent radius is typically smaller than the metallic radius for the same element.
This is because covalent radius measures the bond length between two atoms, whereas metallic radius considers the size of the individual atom within a metallic lattice.
Trend in Ionic Radii
When atoms lose electrons to form cations, the resulting ions have smaller atomic radii compared to their neutral counterparts.
This is because the removal of electrons reduces the electron-electron repulsion, causing the remaining electrons to be drawn closer to the nucleus.
Exceptions to the Trend
There are exceptions to the periodic trend of atomic radius, often occurring in transition elements due to intricate electron configurations.
Factors such as the presence of partially filled d or f orbitals can influence atomic size.
Variation in Across Isotopes
Isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, which can affect atomic radius.
With additional neutrons, the atomic radius increases slightly due to increased nuclear mass but remains relatively unchanged due to similar electronic configurations.
Comparison of Main Group Elements with Transition Metals
Main group elements generally have larger atomic radii compared to transition metals.
This difference arises from the different orbital structures and electron arrangements in the two groups of elements.
Periodic Table: Alkali Metals and Halogens
Alkali metals have the largest atomic radii in their respective periods, while halogens have the smallest.
This trend reflects the increased number of electron shells in alkali metals and the high electronegativity of halogens.
Rare Gases and Atomic Radius
Among the noble gases, atomic radius increases with increasing atomic number.
These elements have complete electron shells, resulting in larger atomic radii and minimal reactivity.
Atomic Radius and Chemical Reactions
Atomic radius influences the ease at which atoms can form chemical bonds with other atoms.
Atoms with larger atomic radii are more likely to lose electrons and form positive ions, while atoms with smaller atomic radii tend to gain electrons and form negative ions.
Experimental Determination of Atomic Radius
Various experimental techniques, such as X-ray crystallography and spectroscopy, are used to determine atomic radius.
These methods allow scientists to measure the distances between atomic nuclei in a solid or study the behavior of atoms in a gaseous state.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the atomic radius is a crucial concept in the field of chemistry. Understanding the atomic radius helps us grasp the physical and chemical properties of elements, as well as their behavior during reactions and bonding. Through this article, we have explored 15 captivating facts about atomic radius, diving into its definition, trends across the periodic table, and its influence on various chemical phenomena.From discovering how the atomic radius changes along a period and down a group to understanding its impact on atomic bonds and reactivity, we have gained a deeper appreciation for this fundamental concept. The atomic radius greatly influences an element’s behavior, from determining its size and density to affecting its ability to form compounds and participate in chemical reactions.By delving into these fascinating facts, we have come to appreciate the immense importance of the atomic radius in explaining the behavior and properties of the elements that make up our world.
FAQs
1. What is atomic radius?
Atomic radius refers to the size of an atom. It is measured as the distance between the nucleus and the outermost shell of electrons.
2. How does atomic radius change across a period?
The atomic radius generally decreases from left to right across a period. This is due to an increase in the effective nuclear charge, which pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus.
3. How does atomic radius change down a group?
Atomic radius generally increases as you move down a group. This is because each subsequent energy level is further from the nucleus, resulting in an increase in atomic size.
4. Does atomic radius influence chemical reactivity?
Yes, atomic radius does influence chemical reactivity. Generally, larger atoms have greater tendencies to lose electrons, while smaller atoms have a higher affinity to gain electrons.
5. How does atomic radius affect the formation of atomic bonds?
The atomic radius plays a key role in determining the distance between atoms in a bond. Smaller atomic radii usually lead to stronger bonds, while larger atomic radii result in weaker bonds.
6. Can atomic radius be measured experimentally?
Yes, atomic radius can be estimated experimentally using techniques such as X-ray crystallography or spectroscopy.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
