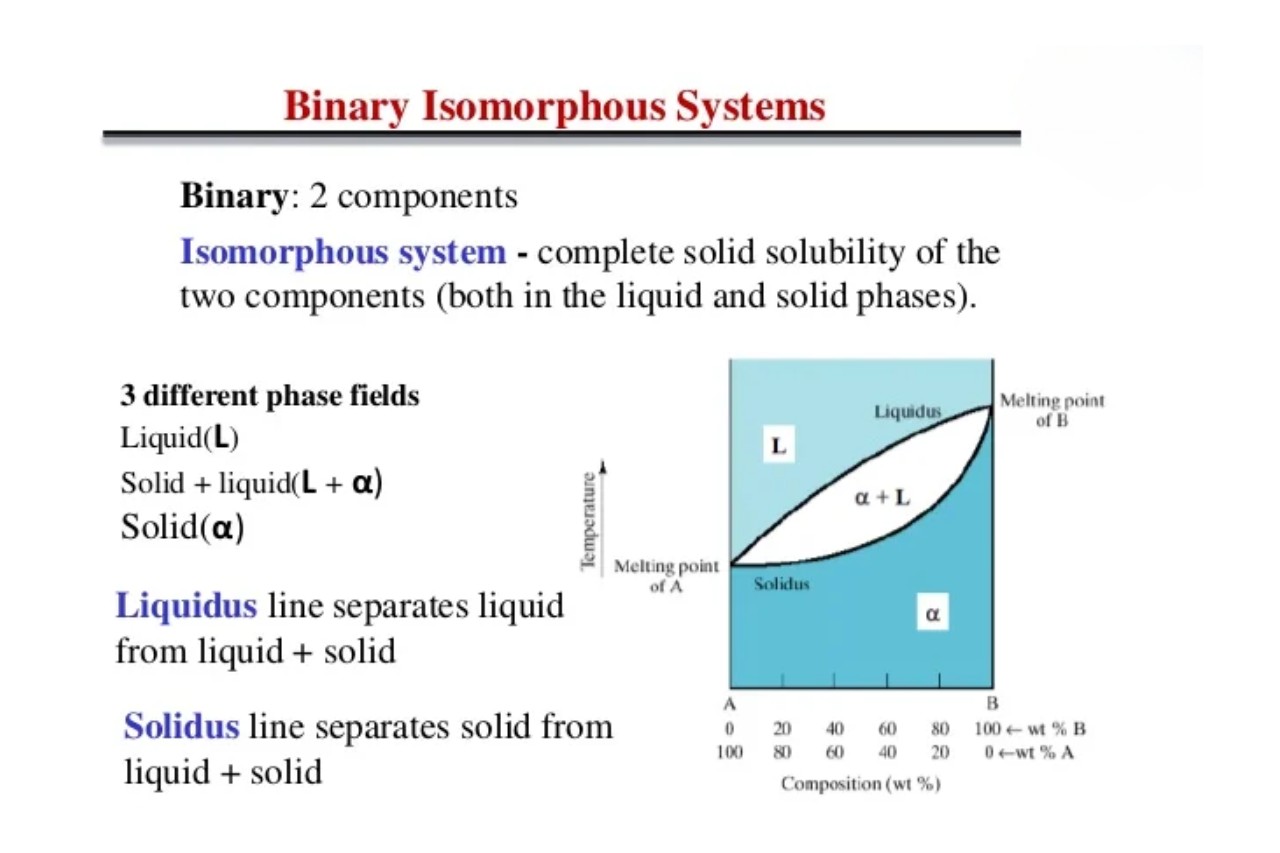
The world of chemistry is filled with fascinating phenomena and complex systems. One such system that never fails to amaze scientists and researchers is the isomorphous system. Isomorphous systems are a captivating subject of study as they exhibit unique properties and behaviors that defy our conventional understanding of materials.
In this article, we will explore 14 mind-blowing facts about the isomorphous system. From the intriguing concept of isomorphism to the practical applications in various fields, such as metallurgy and mineralogy, these facts will shed light on the remarkable nature of isomorphous systems. Prepare to be astounded as we delve into the intricacies of this remarkable phenomenon.
Key Takeaways:
- Isomorphous systems are like secret twins in the world of chemistry, sharing the same crystal structure but with different chemical compositions, leading to similar physical properties and exciting applications in drug development and materials science.
- The isomorphous system is like a magical puzzle that scientists use to create new materials and understand minerals. It’s all about matching crystal structures and uncovering the secrets of compounds to unlock endless possibilities for innovation in chemistry.
Isomorphous systems exhibit identical crystal structures.
Isomorphous systems consist of different compounds that share the same crystal structure, despite having different chemical compositions.
They have similar physical properties.
Compounds in an isomorphous system often have similar physical properties such as melting points, boiling points, and solubilities, making them difficult to differentiate based on these characteristics alone.
Isomorphous systems can form solid solutions.
Due to the similarities in crystal structures, compounds in an isomorphous system can mix together to form solid solutions, resulting in a wide range of materials with varying properties.
Isomorphous systems are commonly found in alloys.
Many metallic alloys exhibit the isomorphous system, allowing engineers to manipulate their properties by adjusting the composition of different elements.
The concept of isomorphous systems originated in the 19th century.
It was first introduced by the German chemist Eilhard Mitscherlich in the early 1800s, who observed the similarities in crystal structures of certain compounds.
Isomorphous systems have important applications in drug development.
By understanding the isomorphous behavior of different compounds, scientists can design more effective pharmaceutical drugs with desirable properties.
Isomorphous systems can exhibit different colors.
Compounds in an isomorphous system may display varying colors due to the presence of different transition metals or other chromophores.
The study of isomorphous systems involves X-ray crystallography.
X-ray crystallography is a powerful technique used to determine the atomic arrangement within crystals, providing insights into the isomorphous relationships between compounds.
Isomorphous systems can undergo phase transitions.
Changes in temperature or pressure can cause isomorphous systems to undergo phase transitions, resulting in different crystal structures and properties.
The formation of isomorphous systems depends on lattice matching.
Lattice matching is a critical factor in the formation of isomorphous systems, as it determines the compatibility of crystal structures between different compounds.
Isomorphous systems are used in the field of materials science.
Researchers utilize isomorphous systems to study the relationship between crystal structure and material properties, leading to advancements in various technological applications.
Isomorphous systems can exhibit solid-state transformations.
Under certain conditions, compounds in an isomorphous system can undergo solid-state transformations, resulting in changes in their crystal structure and properties.
Isomorphous systems play a role in mineralogy.
Many minerals exhibit isomorphous behavior, allowing geologists to identify and classify them based on their crystal structures.
Understanding isomorphous systems can aid in the development of new materials.
By gaining insights into the isomorphous relationships between compounds, scientists can design and synthesize new materials with enhanced properties and functionalities.
These 14 mind-blowing facts about isomorphous systems highlight the intriguing nature of this phenomenon in the field of chemistry. The isomorphous system continues to pave the way for advancements in various scientific disciplines, offering endless possibilities for innovation and discovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the isomorphous system is truly fascinating and offers a plethora of mind-blowing facts. From its unique characteristics to its wide-ranging applications, this system has captivated the attention of chemists and scientists worldwide. The ability of isomorphous compounds to form solid solutions opens up endless possibilities for creating new materials with enhanced properties for various industries. The concept of isomorphous substitution, where different atoms seamlessly replace each other in a crystal lattice, has revolutionized the field of materials science.Understanding the isomorphous system has significant implications not only in chemistry but also in fields like metallurgy, geology, and even pharmaceuticals. The knowledge gained from studying isomorphous compounds contributes to the development of improved alloys, geological studies, and the synthesis of new drugs.Exploring the intricacies of isomorphous systems will continue to push the boundaries of scientific knowledge and lead to exciting discoveries. Its potential for creating revolutionary materials and solutions to complex problems makes it a subject of ongoing research and exploration. The insights gained from studying isomorphous compounds will undoubtedly shape the future of various industries and pave the way for innovation.
FAQs
Q: What does the term “isomorphous system” mean?
A: The term “isomorphous system” refers to a phenomenon where two or more substances have similar crystal structures and can substitute for one another without affecting the overall structure.
Q: What are some examples of isomorphous systems?
A: One of the most well-known examples of an isomorphous system is the copper-nickel alloy. Both copper and nickel have the same crystal structure, allowing them to seamlessly substitute for one another in the alloy.
Q: What are the practical applications of isomorphous systems?
A: Isomorphous systems find applications in various industries. For example, in metallurgy, isomorphous alloys are used to create materials with enhanced properties, such as high strength and corrosion resistance. In geology, isomorphous minerals help in the identification and classification of rocks. Isomorphous substitution is also crucial in drug design, where similar molecules can be substituted to improve a drug’s efficacy or minimize side effects.
Q: How is the isomorphous system studied?
A: The isomorphous system is studied through various techniques, including X-ray crystallography, spectroscopy, and thermal analysis. These methods help determine the crystal structure, composition, and properties of isomorphous compounds.
Q: Are isomorphous systems limited to only two substances?
A: No, isomorphous systems can involve more than two substances. In fact, some systems can have multiple substances with similar crystal structures, allowing for extensive substitution possibilities.
Isomorphous systems' fascinating properties captivate scientists and enthusiasts alike. Beyond their crystal structures, solid solutions formed by these systems offer even more intriguing characteristics to explore. Metallurgy benefits greatly from understanding isomorphous systems, as they play a crucial role in alloy development and behavior. Delving deeper into the world of materials science reveals countless surprises and applications that isomorphous systems contribute to, making this field an exciting area of study for those curious about the building blocks of our world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
