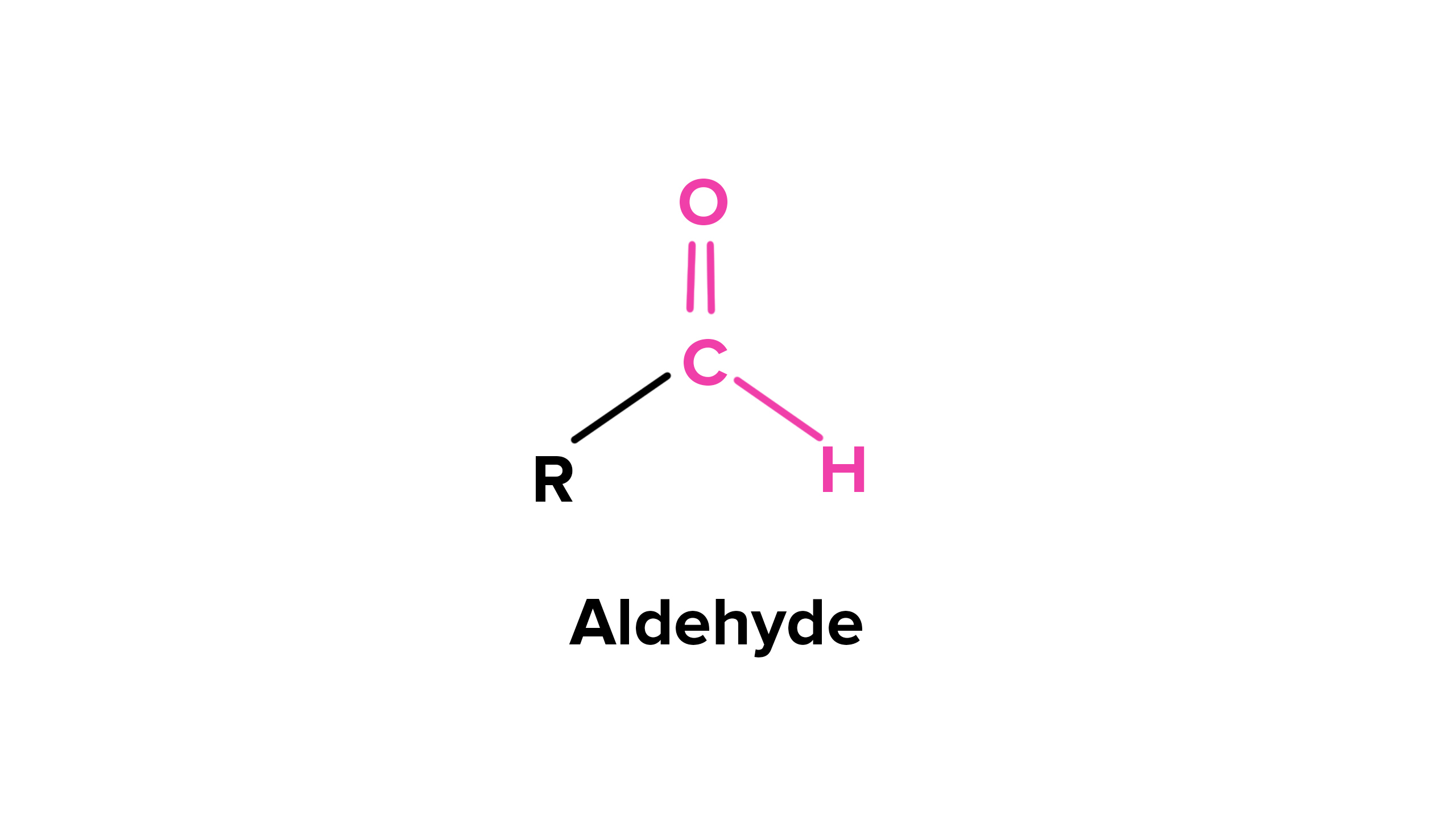
Aldehydes are a fascinating class of organic compounds that boast a wide range of applications and play a crucial role in various chemical reactions. Derived from the oxidation of primary alcohols, they are characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group, consisting of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and a hydrogen atom bonded to the same carbon atom.
In this article, we will delve into the world of aldehydes and uncover 13 astounding facts about these compounds. From their historical significance to their importance in industrial processes and their role in our everyday lives, these facts will shed light on the intriguing nature of aldehydes and showcase their diverse and vital functions.
Key Takeaways:
- Aldehydes are organic compounds with unique smells and play important roles in perfumes, flavors, and even medicine. They are versatile building blocks in chemistry and have wide industrial applications.
- Some aldehydes are found in fruits and flowers, contributing to their distinct aromas. However, high concentrations of aldehydes can be toxic, so proper precautions are necessary when handling them.
Aldehydes are organic compounds.
Aldehydes belong to a class of organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom) and a hydrogen atom. This unique structure gives aldehydes their distinct chemical properties.
Aldehydes are commonly used in perfumes and fragrances.
Due to their pleasant and distinctive smells, aldehydes are widely employed in the production of perfumes and fragrances. They add a unique character and longevity to the scents.
Formaldehyde is a well-known aldehyde.
Formaldehyde, a simple aldehyde with the chemical formula CH2O, is a familiar name to many. It is used in various industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and even as a preservative.
Aldehydes are important building blocks in organic synthesis.
Aldehydes serve as fundamental building blocks in the synthesis of various organic compounds. They can be further modified or transformed into other functional groups, allowing chemists to create a wide range of complex molecules.
Aldehydes play a crucial role in metabolic processes.
In living organisms, aldehydes are involved in vital metabolic pathways. For example, glucose is converted to glucose-6-phosphate through an oxidation process that forms an aldehyde intermediate.
Some aldehydes have medicinal properties.
Certain aldehydes exhibit medicinal properties and are used in pharmaceutical research and development. For instance, retinaldehyde is a precursor to vitamin A and is used in the treatment of skin conditions.
Aldehydes can be found naturally in fruits and flowers.
Many fruits and flowers contain naturally occurring aldehydes, which contribute to their distinctive aromas and flavors. Examples include benzaldehyde in almonds and citral in lemons.
Aldehydes are involved in the production of plastics and resins.
Due to their reactivity and ability to undergo polymerization, aldehydes are used in the production of plastics and resins. They contribute to the strength and durability of these materials.
Aldehydes can be toxic in high concentrations.
While aldehydes are generally safe in low concentrations, some aldehydes can be toxic and harmful to human health, especially when exposed to high levels. Proper precautions should be taken when handling or working with aldehydes.
Aldehydes have important roles in the flavor and aroma of food.
The presence of aldehydes in food contributes to the overall flavor and aroma profiles. They are responsible for the characteristic smells and tastes of various foods, ranging from fruity and floral to nutty and buttery.
Aldehydes can undergo oxidation reactions.
One of the key reactions of aldehydes is oxidation, where they are converted into carboxylic acids. This oxidation process is utilized in many chemical reactions and has significant industrial applications.
Aldehydes have unique chemical reactivity.
Aldehydes have distinct chemical reactivity due to their carbonyl group. They can undergo various reactions, including nucleophilic addition, reduction, and condensation reactions, which makes them versatile compounds in organic chemistry.
Aldehydes have a wide range of industrial applications.
Aldehydes find applications in diverse industries, including manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and agriculture. They are used as solvents, intermediates for chemical synthesis, and as ingredients in various products.
Conclusion
Aldehydes are fascinating compounds that play a significant role in various chemical processes and industries. From their distinctive odor to their involvement in reactions and applications, aldehydes have both practical and theoretical importance. Whether it’s in the field of organic chemistry, biochemistry, or even fragrance and flavor formulations, aldehydes have proven to be versatile and essential compounds.
Throughout this article, we have explored 13 astounding facts about aldehydes. We have learned about their chemical structure, naming conventions, sources, and diverse applications. From the creation of artificial flavors to their role in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, aldehydes continue to amaze us with their unique properties and contributions to various industries.
In conclusion, aldehydes are an intriguing class of compounds that have captivated chemists for centuries. As researchers continue to delve further into their properties and applications, we can expect even more astonishing discoveries surrounding these compounds in the future.
FAQs
Q: What is an aldehyde?
A: An aldehyde is a functional group characterized by a carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom and a double bond to an oxygen atom.
Q: Where are aldehydes found?
A: Aldehydes can be found in both natural and synthetic sources. They are present in essential oils, fruits, and many organic compounds.
Q: What is the distinctive odor of aldehydes?
A: Aldehydes are known for their pungent and often fruity odor, which can range from pleasant to overpowering, depending on the compound.
Q: How are aldehydes named?
A: Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e at the end of the corresponding parent alkane with -al.
Q: What are some applications of aldehydes?
A: Aldehydes have a wide range of applications, including their use as solvents, preservatives, fragrance ingredients, and in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and plastics.
Q: Are aldehydes toxic?
A: Certain aldehydes can be toxic if ingested or inhaled in high concentrations. However, many aldehydes are safe to use in controlled environments and at appropriate concentrations.
Q: What are some examples of aldehydes?
A: Some common examples of aldehydes include formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, benzaldehyde, and vanillin.
Q: Can aldehydes undergo reactions?
A: Yes, aldehydes are highly reactive and can undergo various chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and condensation reactions.
Q: Are aldehydes flammable?
A: Many aldehydes are highly flammable and should be handled with caution. They can easily ignite and should be stored and used in well-ventilated areas.
Q: Can aldehydes be used in food and fragrance compositions?
A: Yes, certain aldehydes, such as cinnamaldehyde and benzaldehyde, are commonly used in food and fragrance compositions to enhance aroma and flavor profiles.
Q: Are aldehydes used in the pharmaceutical industry?
A: Aldehydes are crucial in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds. They serve as building blocks for drug molecules and play a vital role in drug discovery and development.
Q: Can aldehydes be naturally produced by our bodies?
A: Yes, our bodies naturally produce certain aldehydes as byproducts of metabolic processes. However, excessive accumulation of certain aldehydes can be harmful and is associated with health issues.
Q: Are aldehydes stable compounds?
A: Aldehydes can be relatively stable under certain conditions. However, they are prone to oxidation and can quickly undergo reactions, especially in the presence of reactive substances.
Aldehydes' fascinating properties and applications make them a captivating subject for chemistry enthusiasts and curious minds alike. From their role in creating alluring scents to their importance in metabolic processes, aldehydes demonstrate a remarkable versatility that extends beyond the realm of organic compounds. For those eager to expand their knowledge of chemical concepts, exploring the intriguing world of functional groups promises to be an enlightening journey. So, why not continue your discovery of chemistry's hidden gems by delving into the surprising facts surrounding these fundamental building blocks of molecules?
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
