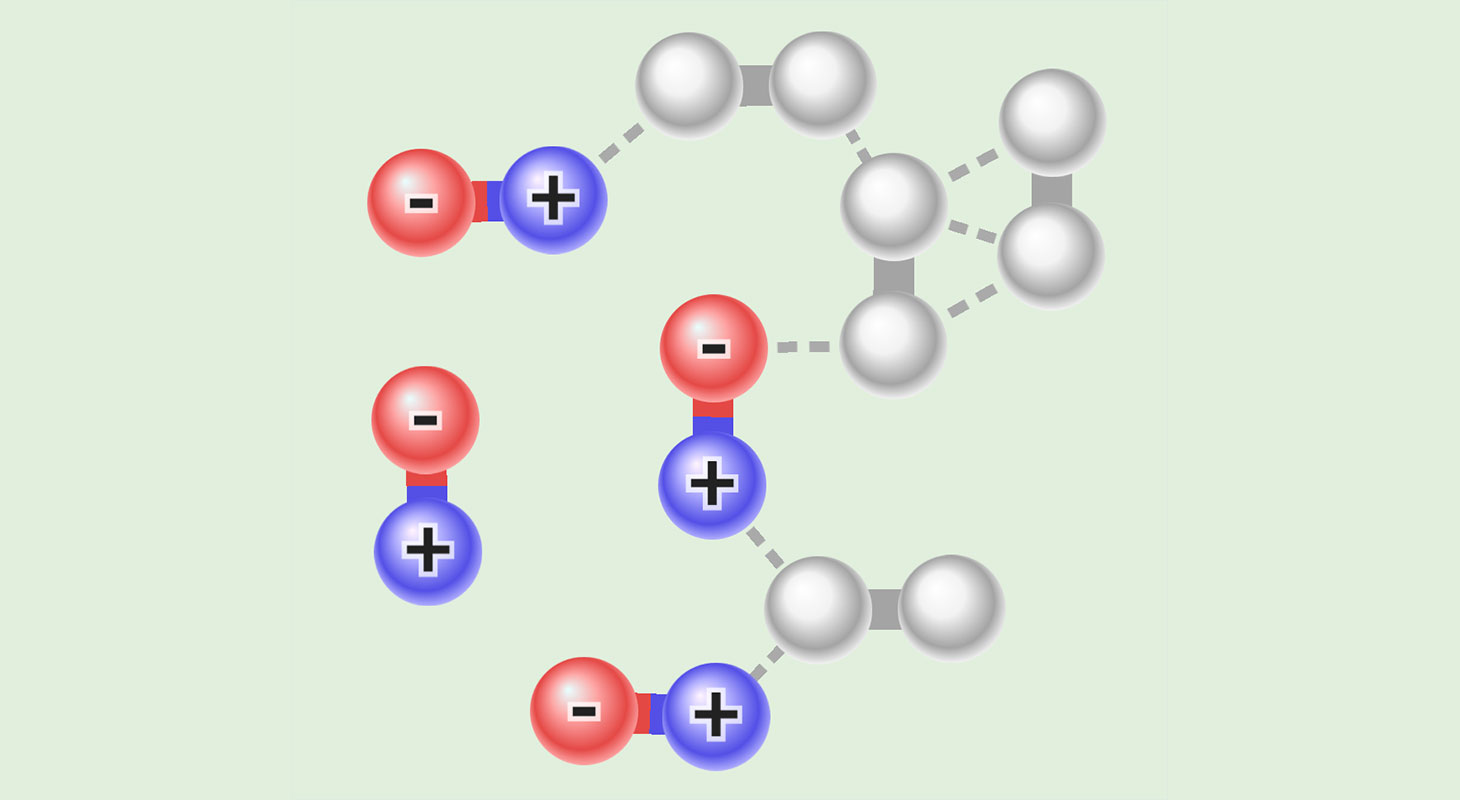
Intermolecular attractions are fascinating forces that play a crucial role in the interaction between different molecules. These forces are responsible for various phenomena and behaviors exhibited by substances, including the formation of liquids and solids, as well as unique chemical reactions. Understanding the nature of intermolecular attractions is essential for chemists to explain and predict the properties and behavior of different substances.
In this article, we will explore 12 mind-blowing facts about intermolecular attractions. From the different types of forces involved to their impact on physical and chemical properties, we will dive into the intriguing world of intermolecular attractions. So, get ready to be amazed as we unravel the secrets behind these captivating forces.
Key Takeaways:
- Intermolecular attractions determine how substances behave, like why water boils and why rubber stretches. They’re like tiny forces that shape the world of chemistry!
- These attractions affect everything from how things dissolve to the creation of new drugs and materials. They’re like secret codes that scientists use to unlock amazing discoveries!
Intermolecular attractions play a crucial role in determining the physical properties of substances.
These attractions are responsible for phenomena such as boiling points, melting points, and solubility.
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular attraction that occurs between hydrogen and a highly electronegative atom such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
This type of bonding is responsible for the unique properties of water and the structure of DNA.
London dispersion forces, also known as Van der Waals forces, are the weakest type of intermolecular attractions.
They arise from temporary fluctuations in electron density and are present in all molecules, regardless of their polarity.
Dipole-dipole interactions occur between molecules that have permanent dipoles.
This attraction arises from the positive end of one molecule being attracted to the negative end of another molecule.
The strength of an intermolecular attraction is influenced by the size, shape, and polarity of the molecules involved.
For example, larger molecules tend to have stronger London dispersion forces.
Intermolecular attractions can affect the viscosity of a liquid.
Substances with stronger intermolecular attractions tend to have higher viscosity, as the molecules have more difficulty moving past each other.
The boiling and melting points of substances can be explained by the strength of the intermolecular attractions.
Substances with stronger intermolecular attractions require more energy to overcome these forces and change from a solid to a liquid or from a liquid to a gas.
The concept of intermolecular attractions is used to explain the phenomenon of surface tension.
Surface tension is the result of the cohesive forces between the molecules at the surface of a liquid.
Intermolecular attractions can influence the solubility of substances.
Polar substances tend to dissolve in polar solvents, while nonpolar substances dissolve in nonpolar solvents.
Intermolecular attractions are responsible for the unique properties of certain substances, such as the elasticity of rubber.
The intermolecular attractions between polymer chains give rise to the stretchiness of rubber.
Intermolecular attractions can affect the volatility of a substance.
Substances with weaker intermolecular attractions tend to be more volatile, as they can more easily escape into the vapor phase.
Understanding intermolecular attractions is essential in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental chemistry.
Scientists study these attractions to develop new drugs, design innovative materials, and understand the behavior of pollutants in the environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, intermolecular attractions play a fundamental role in the behavior and properties of substances. Understanding these forces is crucial for comprehending various chemical phenomena and applications. The twelve mind-blowing facts outlined in this article shed light on the fascinating world of intermolecular attractions. From the complex interactions between molecules to the impact of these forces on physical and chemical properties, it is clear that intermolecular attractions are a key aspect of the molecular realm.Whether it’s the formation of hydrogen bonds, the role of dipole-dipole interactions, or the influence of London dispersion forces, intermolecular attractions govern a wide range of chemical processes and phenomena. By delving deep into the intricacies of intermolecular attractions, scientists can uncover new insights, develop innovative materials, and make advancements in various fields, including medicine, materials science, and environmental conservation.By recognizing the importance and diversity of intermolecular attractions, we come to appreciate the intricacy and beauty of the molecular world. The knowledge we gain from studying these forces allows us to better understand and manipulate the substances that surround us, paving the way for new discoveries and applications in the ever-evolving field of chemistry.
FAQs
1. What are intermolecular attractions?
Intermolecular attractions are the forces of attraction between different molecules or compounds. These forces arise due to the fluctuations in electron distributions and can include hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces.
2. How do intermolecular attractions affect the properties of substances?
Intermolecular attractions determine various physical and chemical properties of substances, such as boiling and melting points, solubility, viscosity, and surface tension. The strength and type of intermolecular attractions greatly influence how molecules interact and behave in different situations.
3. What is the importance of hydrogen bonding in intermolecular attractions?
Hydrogen bonding is a strong intermolecular attraction that occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to an electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. It plays a crucial role in numerous biological processes, influencing the structures and properties of molecules like DNA, proteins, and water.
4. How do dipole-dipole interactions contribute to intermolecular attractions?
Dipole-dipole interactions occur between polar molecules with permanent dipole moments. These forces arise due to the attraction between the positive end of one molecule and the negative end of another molecule. Dipole-dipole interactions play a significant role in determining the properties of polar substances.
5. What are London dispersion forces?
London dispersion forces, also known as van der Waals forces, are the weakest type of intermolecular attractions. They arise due to temporary fluctuations in electron distribution, creating temporary dipoles. Although individually weak, these forces can have a significant cumulative effect on the properties of substances.
6. Can intermolecular attractions be stronger than intramolecular forces?
No, intramolecular forces, such as covalent bonds, are generally much stronger than intermolecular attractions. While intermolecular forces govern the interactions between separate molecules, intramolecular forces hold the atoms within a molecule together.
7. How are intermolecular attractions relevant to real-life applications?
Intermolecular attractions are crucial in various fields. In pharmaceuticals, understanding these forces helps in drug design and interaction with target molecules. In materials science, it enables the development of materials with desired properties. In environmental science, intermolecular attractions play a role in the behavior and transport of pollutants and contaminants.
8. Can intermolecular attractions be altered or manipulated?
Yes, intermolecular attractions can be altered or manipulated by changing the molecular structure or introducing external factors. For example, increasing the temperature can weaken intermolecular attractions, causing substances to change from a solid to a liquid or gas phase.
9. Are intermolecular attractions the same as chemical bonding?
No, intermolecular attractions are different from chemical bonding. Chemical bonding refers to the strong forces that hold atoms together within a molecule, such as covalent or ionic bonds. Intermolecular attractions, on the other hand, occur between separate molecules or compounds.
10. Can intermolecular attractions be observed directly?
Intermolecular attractions cannot be observed directly, as they are molecular-level forces. However, their effects can be observed through various phenomena, such as boiling and freezing points, surface tension, and solubility.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
