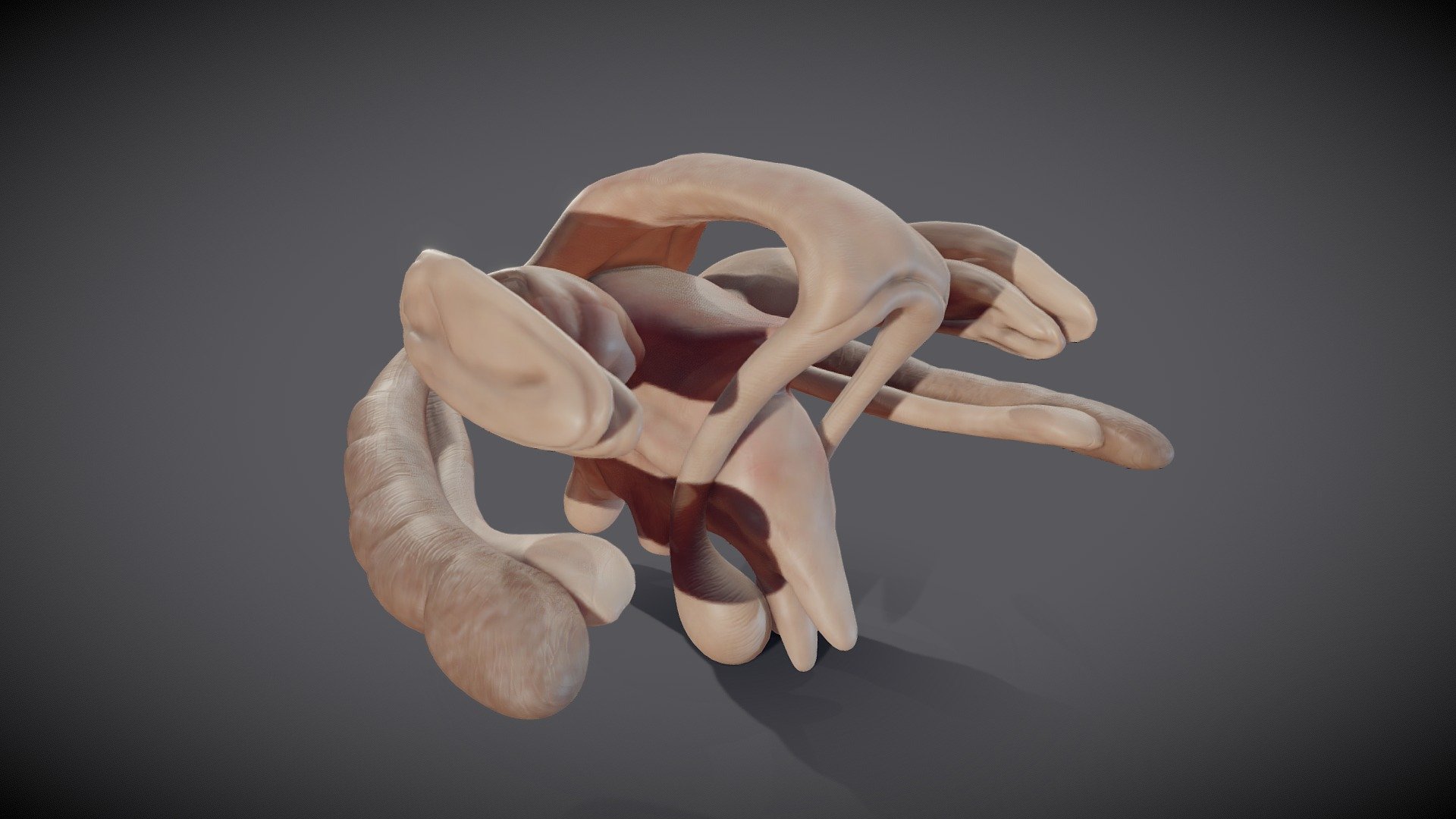
The fornix is an essential component of the human brain, playing a crucial role in various cognitive functions and processes. This intriguing structure connects different regions within the brain and is involved in memory formation, learning, and emotional regulation. Understanding the fornix can provide valuable insights into how the brain functions and processes information.
In this article, we will dive into the fascinating world of the fornix and uncover 15 intriguing facts about this unique brain structure. From its anatomy and functions to its role in certain neurological conditions, we will explore everything you need to know about the fornix. So, grab a cup of coffee and get ready to embark on a journey through the depths of the human brain.
Key Takeaways:
- The fornix is like a memory superhighway in your brain, helping you form and recall memories. Damage to it can cause memory problems, but stimulating it may boost memory performance.
- The fornix is a brain superstar, connecting memory and emotions. Scientists are exploring its potential to treat memory-related disorders like Alzheimer’s disease.
The fornix is an important structure in the human brain.
The fornix is a bundle of nerve fibers that plays a crucial role in memory formation and retrieval. It is part of the limbic system, which is responsible for emotions, learning, and memory.
The fornix connects the hippocampus to other areas of the brain.
The hippocampus, a region involved in memory processing, sends information to different parts of the brain via the fornix. This allows for the integration of new memories and the retrieval of stored memories.
The fornix is named after its arched shape.
The term “fornix” comes from the Latin word for arch. This is due to the curved structure of the fornix as it extends from the hippocampus to the diencephalon.
Damage to the fornix can lead to memory impairments.
Lesions or damage to the fornix can result in memory difficulties, such as the inability to form new memories or recall past events. This highlights the importance of the fornix in memory functioning.
The fornix is composed of fibers called axons.
Axons are elongated projections of nerve cells that transmit signals between different parts of the brain. In the fornix, these axons form a compact bundle that facilitates efficient communication within the limbic system.
The fornix is part of the Papez circuit.
The Papez circuit is a neural pathway involved in the processing of emotions and memory. The fornix serves as a major component of this circuit, connecting various structures such as the hippocampus, cingulate gyrus, and mammillary bodies.
Stimulation of the fornix can enhance memory performance.
Studies have shown that electrical stimulation of the fornix can improve memory functions in both animals and humans. This finding has implications for potential therapeutic approaches in memory-related disorders.
Damage to the fornix can occur in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder, often affects the fornix. As a result, memory deficits are prevalent in individuals with this condition.
The fornix is involved in spatial memory.
Research has demonstrated that the fornix plays a key role in spatial navigation and memory. It helps individuals remember their surroundings and find their way in different environments.
The fornix is a bilateral structure.
The fornix is present on both sides of the brain, connecting the right and left hemispheres. This bilateral arrangement facilitates efficient communication and coordination between the two hemispheres.
Studies have explored the therapeutic potential of fornix deep brain stimulation.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves the implantation of electrodes to modulate neural activity. Researchers have investigated the use of DBS targeted at the fornix to improve memory in conditions like epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease.
The fornix is primarily composed of myelinated fibers.
Myelin is a fatty substance that surrounds axons and acts as an insulating layer. In the fornix, myelin enhances the speed and efficiency of signal transmission between different brain regions.
Brain imaging techniques can visualize the fornix.
Advances in brain imaging technologies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), allow researchers to visualize the fornix and study its structure and connectivity in living individuals.
Research on the fornix continues to uncover its role in various cognitive functions.
Scientists are actively investigating the fornix to gain a deeper understanding of its involvement in memory, emotions, and other cognitive processes. Ongoing research may lead to further insights into neurological disorders and potential therapeutic interventions.
The fornix is an intricate and fascinating structure in the human brain.
Understanding its functions and complexities contributes to our knowledge of the brain’s remarkable capabilities and the intricate interplay between different regions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fornix is a fascinating and important structure in the human anatomy. Its role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, and the regulation of various bodily functions makes it an integral part of our brain’s functionality. From its unique shape and connections to its involvement in diseases and disorders, the fornix continues to captivate researchers and healthcare professionals alike.
Understanding the intricacies of the fornix helps us gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of the human brain and its impact on our overall well-being. As research in the field of neuroanatomy progresses, we can expect to uncover even more secrets about this enigmatic structure.
FAQs
1. What is the fornix?
The fornix is a C-shaped bundle of nerve fibers in the brain that plays a crucial role in memory consolidation and emotional processing.
2. What is the function of the fornix?
The primary function of the fornix is to transmit information between various regions of the brain, especially those involved in memory and emotional regulation.
3. How does the fornix contribute to memory consolidation?
The fornix connects the hippocampus, a key region for memory formation, to other regions involved in memory storage and retrieval. It facilitates the transfer of information, aiding in the consolidation of memories.
4. Can damage to the fornix affect memory?
Yes, damage or dysfunction of the fornix can lead to memory impairments, such as difficulty in forming new memories or problems with recalling previously learned information.
5. Are there any disorders associated with the fornix?
Yes, conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, and schizophrenia have been linked to abnormalities in the fornix.
6. Can the fornix be visualized in medical imaging?
Yes, advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI, allow for the visualization of the fornix and its associated structures in the brain.
7. Are there any ongoing research studies on the fornix?
Yes, scientists and researchers continue to investigate the role of the fornix in various neurological disorders, as well as its potential as a therapeutic target.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
