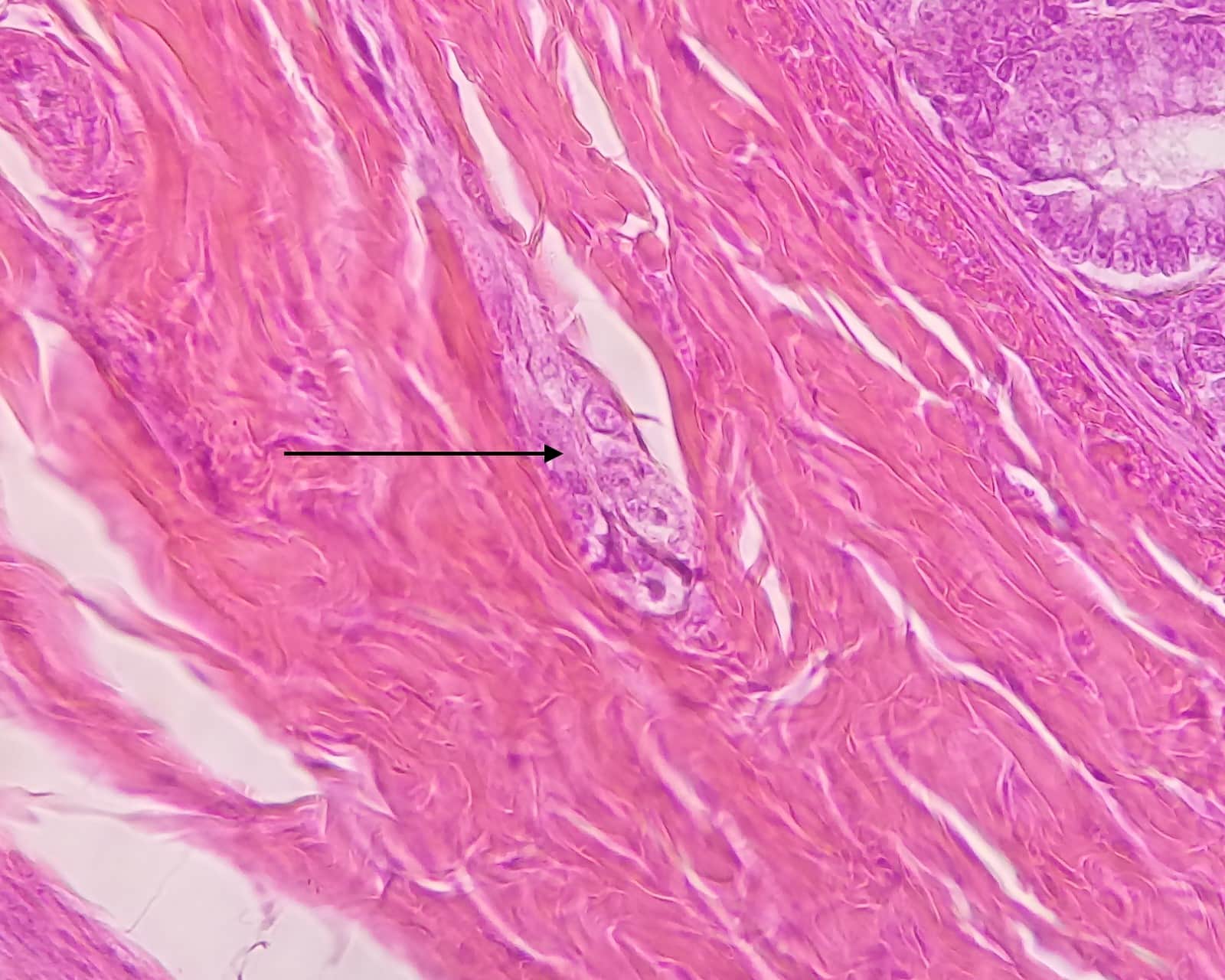
When it comes to the intricate world of human anatomy, Meissner’s plexus is an extraordinary network of nerves that holds a plethora of fascinating facts waiting to be discovered. Named after Georg Meissner, the German physiologist who first described it, Meissner’s plexus is found within the gastrointestinal system. This intricate web of nerve fibers is responsible for regulating various critical functions such as sensory perception, movement, and digestion. In this article, we will delve into the depths of Meissner’s plexus, exploring ten captivating facts that will give you a deeper understanding of this remarkable anatomical structure. From its unique histological features to its essential role in the human body, get ready to unravel the secrets of Meissner’s plexus and gain a new appreciation for the wonders of human anatomy.
Key Takeaways:
- Meissner’s Plexus, discovered by Georg Meissner, helps us feel textures and recognize objects through rapid adaptation and enhanced sensitivity in areas like fingertips.
- This network of mechanoreceptors in our skin plays a crucial role in our sense of touch, including reading Braille and contributing to reflexive responses.
The Discovery of Meissner’s Plexus
Meissner’s Plexus, also known as the tactile corpuscles, was first identified by the German anatomist and physiologist Georg Meissner in the mid-19th century. It was named after him to honor his significant contribution to the understanding of the nervous system.
Location and Composition
Meissner’s Plexus is located in the dermal papillae of the skin, particularly in areas of heightened sensitivity such as the fingertips, palms, soles of the feet, and lips. It is composed of specialized nerve endings called mechanoreceptors, which are responsible for detecting light touch and texture.
Role in Tactile Sensation
Meissner’s Plexus plays a crucial role in our sense of touch. These mechanoreceptors have the ability to detect vibrations, changes in texture, and fine tactile discrimination. They send signals to the brain, allowing us to recognize objects, feel textures, and experience physical sensations.
Rapid Adaptation
One remarkable characteristic of Meissner’s Plexus is its rapid adaptation. This means that the receptors quickly adapt to a continuous stimulus and stop responding, allowing our perception of touch to be focused on changes in stimuli rather than constant pressure.
Enhanced Sensitivity
The presence of Meissner’s Plexus in certain areas of the body, like the fingertips, gives us enhanced tactile sensitivity. This is why these areas are more adept at detecting fine details, such as distinguishing between different textures or feeling subtle vibrations.
Meissner’s Plexus and Braille
Meissner’s Plexus plays a crucial role in the reading and interpretation of Braille. The mechanoreceptors in the fingertips detect the raised dots on a Braille page, allowing individuals who are blind or visually impaired to read through touch.
Vulnerability to Age and Disease
As we age, Meissner’s Plexus may undergo degeneration, leading to a gradual decline in tactile sensitivity. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, can damage the nerves associated with the plexus, resulting in diminished tactile perception.
Interplay with Other Sensory Nerves
Meissner’s Plexus works in conjunction with other sensory nerves, including Merkel cells, to provide a comprehensive tactile experience. These sensory nerves work together to transmit signals to the brain, enabling us to perceive and interpret different aspects of touch.
Connection to Reflexive Responses
Meissner’s Plexus also has connections to reflexive responses in the body. When combined with other sensory information and processing centers, these nerve endings contribute to reflex arcs, which can lead to rapid involuntary movements or protective behaviors.
Clinical Significance
The study of Meissner’s Plexus and its functioning has significant clinical implications. Understanding its role and response mechanisms helps in diagnosing and treating conditions related to touch sensation, such as neuropathies, sensory perception disorders, and certain neurological disorders.
Overall, Meissner’s Plexus is a fascinating part of our nervous system, allowing us to experience the world through the sense of touch. Its intricate network of mechanoreceptors and its role in tactile perception make it an essential component of our sensory experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Meissner’s plexus is a fascinating and important component of the human anatomy. Its intricate network of nerves plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, particularly in sensory perception and motor control. Understanding and studying Meissner’s plexus can provide valuable insights into the complexities of the nervous system and help improve treatments for conditions such as gastrointestinal disorders and chronic pain. Its sensitivity to touch and pressure makes it a vital part of our ability to experience the world around us. As we continue to explore the wonders of the human body, Meissner’s plexus remains an intriguing area of study that enhances our understanding of the intricate mechanisms that govern our everyday experiences.
FAQs
Q: What is Meissner’s plexus?
A: Meissner’s plexus is a complex network of nerves located in the submucosa layer of the gastrointestinal tract.
Q: What is the function of Meissner’s plexus?
A: Meissner’s plexus is primarily responsible for regulating sensory perception, particularly in the sense of touch and pressure, in the gastrointestinal tract.
Q: How does Meissner’s plexus contribute to sensory perception?
A: Meissner’s plexus contains specialized nerve fibers that detect changes in pressure and transmit signals related to touch and texture from the digestive system to the brain.
Q: Can Meissner’s plexus be affected by medical conditions?
A: Yes, certain medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can impact the functionality of Meissner’s plexus and disrupt normal sensory perception in the gastrointestinal tract.
Q: Are there any treatments available for Meissner’s plexus-related disorders?
A: While there is no specific treatment for Meissner’s plexus disorders, managing the underlying medical condition, such as IBS or IBD, can help alleviate symptoms and improve the overall function of Meissner’s plexus.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
