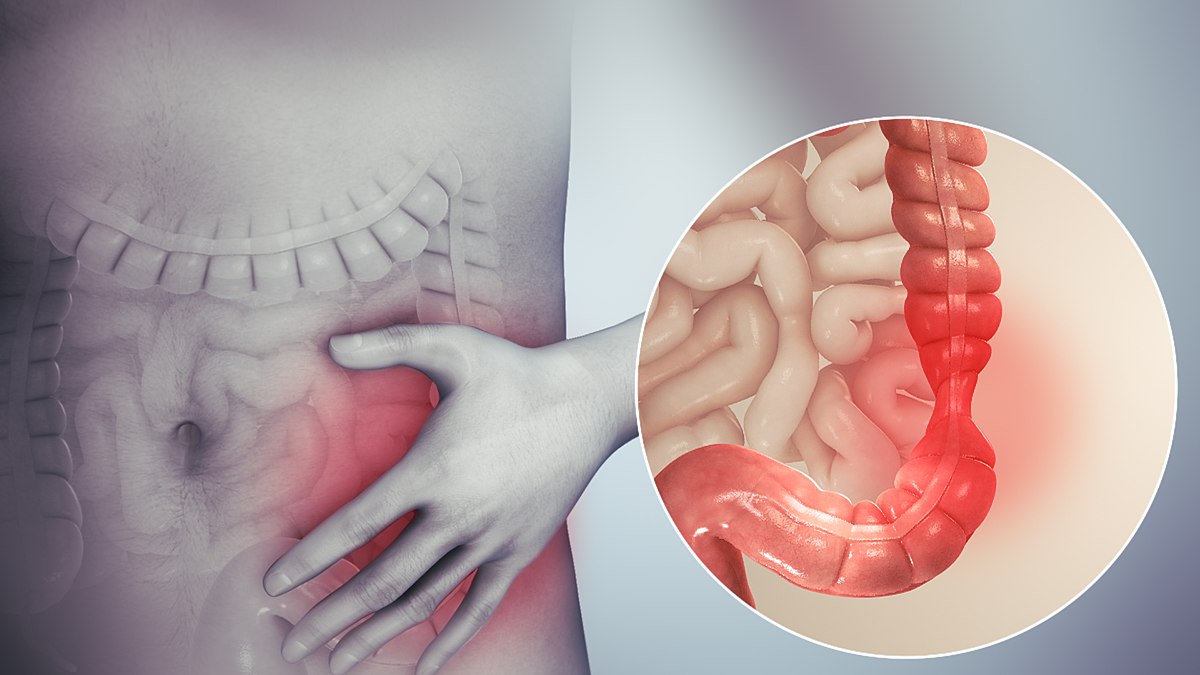
The transverse colon is a fascinating component of the human digestive system. Positioned between the ascending and descending colon, it plays a crucial role in the absorption of water and nutrients from the food we consume. While it may not be as widely known as other organs in the body, the transverse colon has some truly unbelievable facts that highlight its importance. From its distinct anatomy to its involvement in the development of certain medical conditions, understanding the transverse colon can provide valuable insights into our overall well-being. In this article, we will explore 12 remarkable facts about the transverse colon that will leave you amazed and eager to learn. So, let’s delve deeper into the world of human anatomy and uncover the secrets of this remarkable organ.
Key Takeaways:
- The transverse colon is like a curved bridge in your belly, helping to absorb nutrients and water from food. It’s super long and can change shape to keep things moving smoothly!
- Just like a superhero, the transverse colon fights off bad bacteria and helps your body absorb important nutrients. Taking care of it with regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle is key!
The Transverse Colon: A Vital Component of the Digestive System
The transverse colon is a major part of the large intestine, forming a bridge between the ascending colon and the descending colon. It plays a crucial role in the absorption of water and nutrients from digested food.
Curved Structure for Optimal Function
The transverse colon has a distinct curved shape, resembling an upside-down “U” in the abdominal cavity. This unique structure allows it to efficiently store and process waste material before it travels into the descending colon.
Location and Position
The transverse colon is positioned horizontally across the upper abdomen, just below the liver and the stomach. It passes in front of several organs, including the pancreas and the gallbladder, making it a crucial anatomical landmark for medical professionals.
Impressive Length
The transverse colon is the longest segment of the large intestine, stretching approximately 18-24 inches in length. This considerable size allows it to adequately process and transport the fecal matter before it reaches the descending colon.
Flexibility and Adaptability
The transverse colon has a remarkable ability to adapt and change its shape depending on the volume of content passing through it. This flexibility helps in smooth digestion and prevents any obstruction or blockages from occurring.
Blood Supply
The transverse colon receives its blood supply from multiple sources, including the middle colic artery, which branches off from the superior mesenteric artery. This rich blood supply ensures the proper nourishment and function of the colon.
Vulnerability to Diseases
Despite its essential role in digestion, the transverse colon is also susceptible to various diseases and conditions. These can include diverticulitis, colitis, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and even colon cancer. Regular screenings and a healthy lifestyle are crucial in maintaining its well-being.
Role in Nutrient Absorption
The transverse colon is responsible for the absorption of water, electrolytes, and some vitamins produced by gut bacteria. This absorption process is vital for maintaining proper hydration, electrolyte balance, and overall nutrient absorption in the body.
Connection with the Nervous System
The transverse colon is innervated by nerves from the autonomic nervous system, which helps regulate its contraction and movement. This intricate nerve supply ensures the efficient propulsion of waste material through the colon.
Importance in Colonic Transit Time
The transverse colon significantly influences colonic transit time, which refers to the duration it takes for food to pass through the entire large intestine. Any disturbances in the transverse colon can alter the overall transit time, leading to digestive issues such as diarrhea or constipation.
Connection with the Immune System
The transverse colon houses a significant number of immune cells, known as lymphoid follicles, which play a crucial role in immune defense. These cells help protect against harmful bacteria and pathogens that may enter the digestive system.
Surgical Procedures Involving the Transverse Colon
The transverse colon can be involved in various surgical procedures, such as colectomy or colostomy, where a portion of the colon needs to be removed or redirected for medical reasons. These procedures aim to treat conditions like colon cancer or diverticular disease.
In conclusion, the transverse colon is an essential part of the digestive system, responsible for the absorption of nutrients and effectively processing waste material. Its position, length, and unique features make it a key component in maintaining digestive health. Regular screenings and a healthy lifestyle are crucial in preserving the well-being of the transverse colon and preventing potential diseases or disorders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the transverse colon is an essential part of the digestive system, playing a crucial role in the absorption of nutrients and the removal of waste products from the body. It spans across the abdomen, connecting the ascending and descending colon, and is responsible for the proper movement and processing of food. Understanding the anatomy and function of the transverse colon helps us appreciate its importance in maintaining a healthy digestive system. So next time you hear about the transverse colon, remember these unbelievable facts!
FAQs
Q: What is the transverse colon?
A: The transverse colon is a part of the large intestine located between the ascending and descending colon. It plays a vital role in digestion and nutrient absorption.
Q: How long is the transverse colon?
A: On average, the transverse colon measures about 45-50 cm in length. However, it can vary depending on an individual’s anatomy.
Q: What is the function of the transverse colon?
A: The transverse colon helps in the digestion and absorption of food by mixing it with digestive juices and absorbing nutrients into the bloodstream.
Q: Are there any common disorders associated with the transverse colon?
A: Yes, some common disorders related to the transverse colon include diverticulosis, inflammation (colitis), and the formation of polyps or tumors.
Q: How can I keep my transverse colon healthy?
A: Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fiber, drinking plenty of water, and regular exercise can help keep your transverse colon healthy. It is also essential to undergo regular screenings and check-ups to detect any potential issues early on.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
