The human body is a complex and fascinating system, with various organs and tissues working together to maintain our health. When it comes to understanding the intricacies of our body, the study of human anatomy plays a crucial role. One such element of human anatomy is the arachnoid mater, a layer of the meninges that helps protect and support the brain and spinal cord.
In this article, we will delve into the wonders of the arachnoid mater and uncover 17 astonishing facts that highlight its importance and functions. From its structure and composition to its vital role in cerebrospinal fluid circulation, we will explore the fascinating world of the arachnoid mater, shedding light on its significance in our overall well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- The arachnoid mater is like a protective spider web for the brain and spinal cord, helping to cushion, support blood vessels, and regulate pressure. It also plays a role in conditions like arachnoid cysts and arachnoiditis.
- Abnormalities in the arachnoid mater can lead to serious neurological conditions, but diagnostic imaging and surgical interventions can help identify and address these issues to restore normal function and alleviate symptoms.
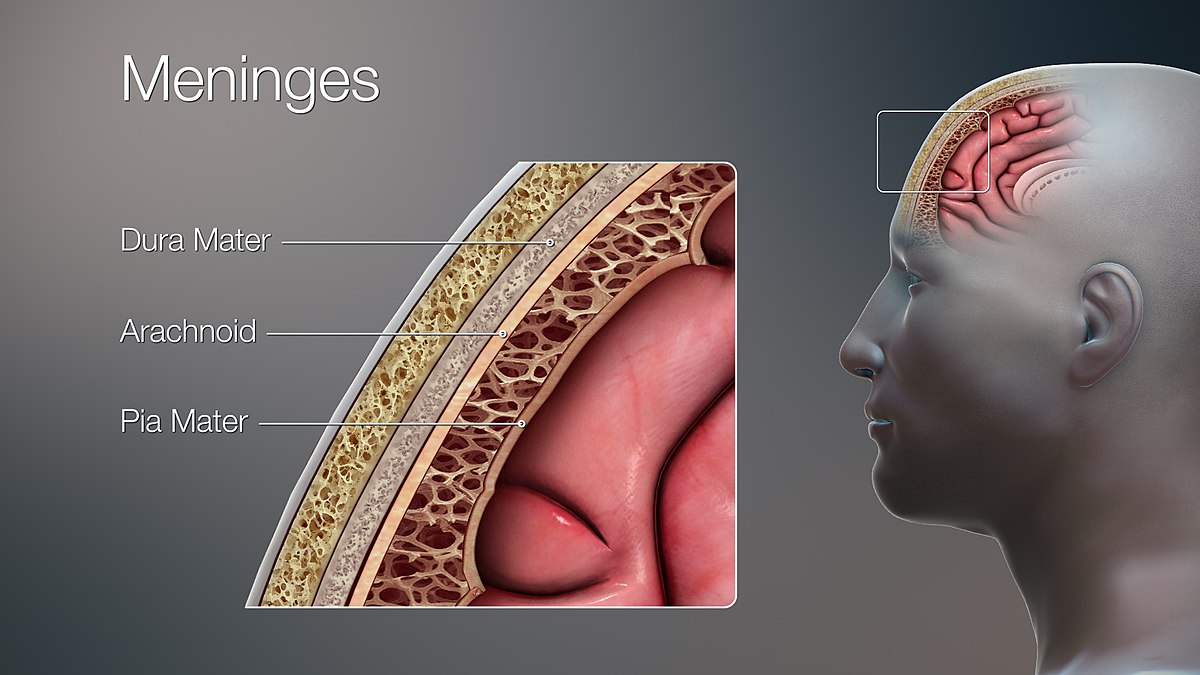
Arachnoid Mater: The Spider-Like Layer
The arachnoid mater is one of the three layers that make up the meninges, the protective coverings of the brain and spinal cord. Its name comes from its spider web-like appearance.
Location and Composition
The arachnoid mater is situated between the dura mater, the tough outer layer, and the pia mater, the delicate inner layer. It is composed of a thin, transparent membrane made up of connective tissue.
Cerebrospinal Fluid Transport
The arachnoid mater plays a crucial role in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) around the brain and spinal cord. It forms the “arachnoid granulations” which protrude into the venous sinuses, facilitating the absorption of CSF back into the bloodstream.
Protection and Cushioning
The arachnoid mater acts as a protective barrier, helping to cushion the brain and spinal cord from external shocks or trauma. It absorbs impact and distributes it evenly across the central nervous system.
Blood Vessel Support
It provides support and nutrients to the blood vessels that supply the brain and spinal cord. The arachnoid mater contains numerous blood vessels that help nourish the underlying neural tissue.
Sensory Function
The arachnoid mater is richly supplied with sensory nerve endings, allowing it to detect changes in pressure and temperature within the cranial and spinal cavities.
Role in Intracranial Pressure Regulation
Abnormalities within the arachnoid mater can lead to increased intracranial pressure, a condition that can have serious consequences. Maintaining the integrity and proper functioning of this layer is crucial for regulating pressure within the skull.
Arachnoid Cysts
Arachnoid cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop within the arachnoid mater. These cysts are usually benign but can cause symptoms such as headaches, seizures, and neurological deficits if they exert pressure on surrounding structures.
Spiderweb-like Appearance
The arachnoid mater gets its name from its resemblance to a spider web when viewed under a microscope. This unique appearance is due to its intricate network of connective tissue fibers.
Protection Against Pathogens
The arachnoid mater, along with the other layers of the meninges, acts as a physical barrier, preventing the entry of pathogens and foreign substances into the brain and spinal cord.
Collaboration with the Blood-Brain Barrier
The arachnoid mater works in conjunction with the blood-brain barrier, a specialized system that regulates the passage of molecules from the bloodstream into the brain. Together, they protect the central nervous system from potentially harmful substances.
Role in Neurological Disorders
Abnormalities in the arachnoid mater can contribute to the development of certain neurological conditions, such as arachnoiditis, a rare inflammatory disorder that affects the meninges and can cause chronic pain and neurological deficits.
Arachnoid Membrane Adhesions
Adhesions may develop between the arachnoid mater and other layers of the meninges or adjacent structures as a result of inflammation or trauma. These adhesions can restrict the movement of the underlying neural tissue and disrupt normal physiological functions.
Arachnoid Membrane Tears
Tears in the arachnoid mater can occur due to trauma, infections, or medical procedures. These tears can disrupt the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid and lead to complications such as hydrocephalus or meningitis.
Role in Diagnostic Imaging
The arachnoid mater can be visualized using various diagnostic imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans. These imaging modalities help identify structural abnormalities or pathologies associated with this layer.
Developmental Abnormalities
In some cases, abnormalities in the development of the arachnoid mater can occur during embryonic development, leading to conditions such as meningocele or arachnoid cysts.
Surgical Interventions
In certain medical conditions, surgical interventions may be required to address abnormalities or pathologies affecting the arachnoid mater. These procedures aim to restore normal function and alleviate symptoms associated with the condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the arachnoid mater is a crucial component of the meninges, which protects and supports the brain and spinal cord. It is a complex and fascinating structure that plays a significant role in maintaining the overall health and function of the central nervous system. Understanding the arachnoid mater and its functions can provide valuable insights into the intricate workings of the human body.With its delicate web-like structure and its ability to regulate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, the arachnoid mater is a vital part of our body’s defense system. Its protective barrier prevents harmful substances from entering the brain and spinal cord, ensuring their proper functioning. Furthermore, the arachnoid mater’s close association with the other meninges and its involvement in cerebrospinal fluid dynamics contribute to maintaining the stability and balance of our central nervous system.By delving into the astonishing facts about the arachnoid mater, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate design and functionality of our bodies. From its unique appearance to its involvement in various physiological processes, the arachnoid mater leaves us in awe of the wonders of human anatomy.
FAQs
1. What is the arachnoid mater?
The arachnoid mater is a delicate membrane that forms one of the three layers of the meninges, which surround and protect the brain and spinal cord.
2. What is the function of the arachnoid mater?
The arachnoid mater acts as a protective barrier, preventing harmful substances from entering the central nervous system. It also helps regulate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
3. How does the arachnoid mater contribute to the stability of the central nervous system?
The arachnoid mater, along with the other meninges, provides structural support and stability to the brain and spinal cord. It helps maintain a stable environment for the proper functioning of the central nervous system.
4. Can the arachnoid mater be affected by diseases or conditions?
Yes, certain conditions such as arachnoiditis or arachnoid cysts can affect the arachnoid mater. These conditions can cause inflammation or the development of abnormal fluid-filled sacs within the membrane.
5. How does the arachnoid mater look like?
The arachnoid mater has a web-like appearance, resembling a spider’s web, which gives it its name. It forms a delicate network of fibers that cover the brain and spinal cord.
6. Is the arachnoid mater present throughout the entire central nervous system?
Yes, the arachnoid mater covers the brain and spinal cord, extending down the entire length of the vertebral column.
Arachnoid mater, a fascinating layer of the meninges, plays a crucial role in protecting the brain and spinal cord. Its unique structure and functions make it an intriguing subject for exploration. If you're curious to learn more about the anatomy surrounding this spider-like membrane, consider delving into the mysterious realm of the subarachnoid space. This fluid-filled cavity holds secrets waiting to be uncovered, promising to enhance your understanding of the complex workings within our skulls.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
