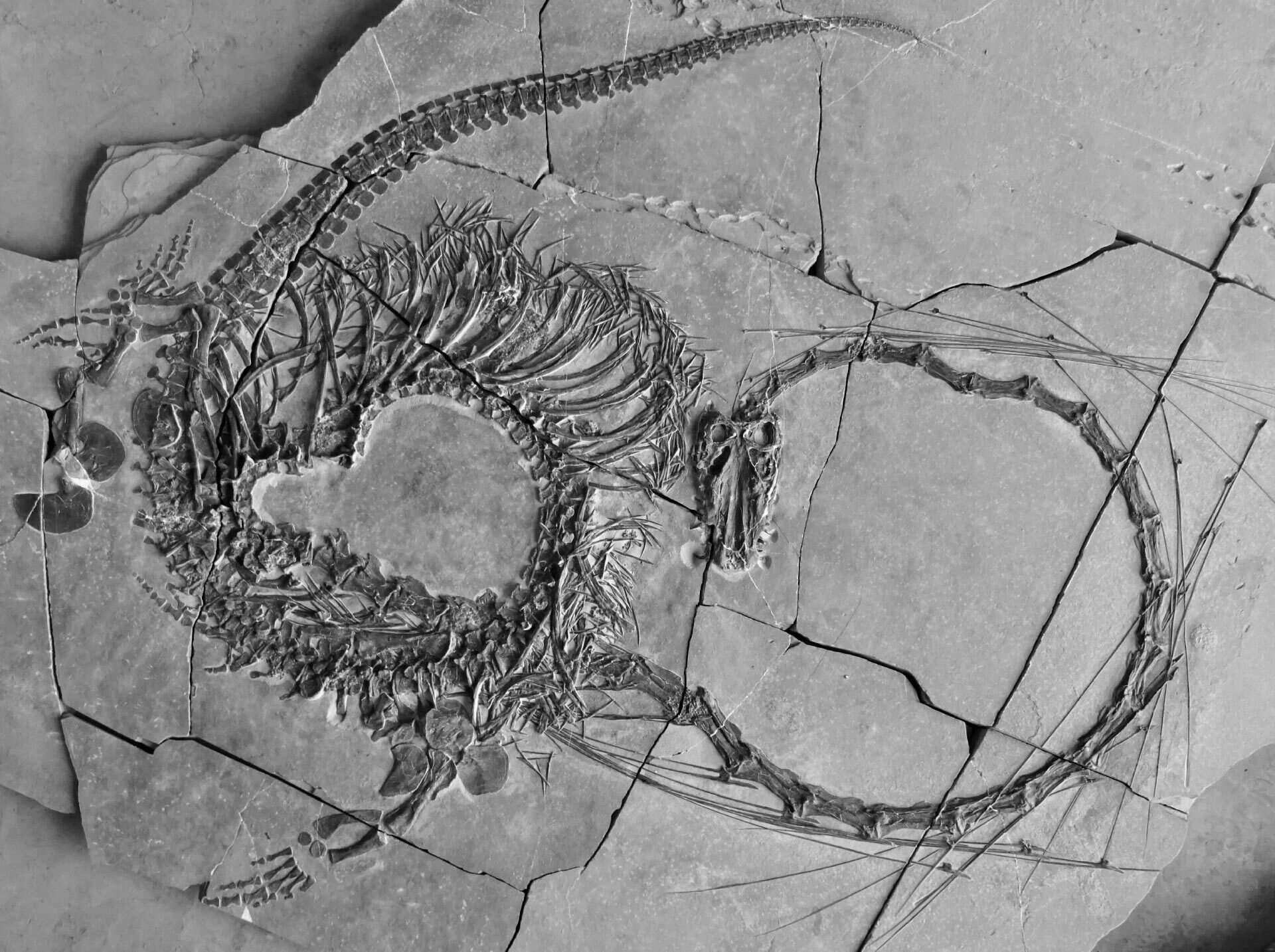
Dinocephalosaurus orientalis might sound like a mouthful, but this ancient marine reptile is anything but boring. Living around 245 million years ago, this creature roamed the seas during the Middle Triassic period. Unlike many of its contemporaries, Dinocephalosaurus had a long neck, which helped it snatch prey with surprising speed. Fossils of this fascinating reptile were first discovered in China, providing a glimpse into a world long gone. What makes it even more intriguing is its unique method of reproduction—giving birth to live young instead of laying eggs. This adaptation is rare among reptiles, making Dinocephalosaurus a subject of great interest for paleontologists. Dive into these 35 facts to learn more about this captivating creature!
Key Takeaways:
- Dinocephalosaurus orientalis, a prehistoric marine reptile, had a long neck, sharp teeth, and webbed feet, living around 245 million years ago. It was a solitary hunter, preying on fish and other marine creatures.
- Fossil discoveries of Dinocephalosaurus orientalis have provided valuable insights into its anatomy and evolutionary significance, shedding light on the evolution of marine reptiles and their transitional role in prehistoric times.
Dinocephalosaurus Orientalis: A Prehistoric Marvel
Dinocephalosaurus orientalis, a fascinating creature from the Triassic period, has intrigued scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike. This marine reptile, with its unique features and mysterious lifestyle, offers a glimpse into a world long gone.
Unique Physical Characteristics
Dinocephalosaurus orientalis had some truly remarkable physical traits that set it apart from other marine reptiles.
- Long Neck: This creature had an exceptionally long neck, which could reach up to 1.7 meters, making up almost half its body length.
- Flexible Vertebrae: The neck vertebrae were highly flexible, allowing it to move its head in various directions to catch prey.
- Sharp Teeth: Equipped with sharp, conical teeth, it was well-adapted to gripping slippery prey like fish.
- Streamlined Body: Its body was streamlined, aiding in swift movement through water.
- Webbed Feet: Webbed feet helped it navigate efficiently in its aquatic environment.
- Small Head: Despite its long neck, it had a relatively small head compared to its body size.
- Elongated Skull: The skull was elongated, contributing to its hydrodynamic shape.
Habitat and Lifestyle
Understanding the habitat and lifestyle of Dinocephalosaurus orientalis provides insight into how it lived and thrived.
- Marine Environment: This reptile lived in shallow marine environments, likely near the coast.
- Triassic Period: It existed during the Middle Triassic period, around 245 million years ago.
- Predatory Behavior: Dinocephalosaurus orientalis was a predator, hunting smaller marine animals.
- Ambush Predator: It likely used its long neck to ambush prey, striking quickly from a distance.
- Solitary Hunter: Evidence suggests it was a solitary hunter, relying on stealth and surprise.
- Diet: Its diet primarily consisted of fish and other small marine creatures.
- Breathing: Like other marine reptiles, it had to surface for air, indicating it was not fully aquatic.
Fossil Discoveries
Fossil evidence has provided much of what we know about Dinocephalosaurus orientalis.
- First Discovery: The first fossil was discovered in China in 2002.
- Well-Preserved Specimens: Some fossils are remarkably well-preserved, offering detailed insights into its anatomy.
- Egg Fossil: A fossilized egg found inside a specimen suggests it gave birth to live young.
- Multiple Sites: Fossils have been found in several locations, indicating a wide range.
- Soft Tissue Impressions: Some fossils include soft tissue impressions, a rare find in paleontology.
- Complete Skeletons: Several nearly complete skeletons have been unearthed, providing a comprehensive view of its structure.
- Museum Displays: Many fossils are displayed in museums, allowing the public to learn about this ancient creature.
Evolutionary Significance
Dinocephalosaurus orientalis holds a significant place in the evolutionary history of marine reptiles.
- Archosauromorph: It belongs to the Archosauromorpha group, which includes modern birds and crocodiles.
- Unique Adaptations: Its unique adaptations provide clues about the evolution of marine reptiles.
- Transitional Species: It is considered a transitional species, bridging the gap between early reptiles and more advanced marine reptiles.
- Neck Evolution: The evolution of its long neck is a subject of interest, shedding light on similar adaptations in other species.
- Phylogenetic Studies: Studies of its phylogeny help understand the relationships between different reptile groups.
- Adaptive Radiation: Its existence during the Triassic period highlights the adaptive radiation of reptiles following the Permian extinction.
Modern Comparisons
Comparing Dinocephalosaurus orientalis to modern animals can help us understand its behavior and lifestyle.
- Similar to Plesiosaurs: Its long neck and aquatic lifestyle are reminiscent of plesiosaurs, though they are not closely related.
- Bird-Like Features: Some features, like its flexible neck, are similar to modern birds.
- Crocodile Relatives: As an archosauromorph, it shares a distant ancestry with modern crocodiles.
- Convergent Evolution: Its adaptations show convergent evolution with other marine predators, like dolphins and ichthyosaurs.
- Modern Analogues: Studying modern analogues helps paleontologists infer its behavior and ecology.
Scientific Impact
The study of Dinocephalosaurus orientalis has had a significant impact on paleontology and our understanding of prehistoric life.
- New Insights: Its discovery provided new insights into the diversity of Triassic marine reptiles.
- Research Opportunities: It continues to be a subject of research, with new findings emerging regularly.
- Public Interest: Its unique appearance and intriguing lifestyle have captured the public's imagination, promoting interest in paleontology.
Final Thoughts on Dinocephalosaurus Orientalis
Dinocephalosaurus orientalis, a fascinating marine reptile, continues to captivate scientists and enthusiasts alike. Its unique features, like the elongated neck and live birth, set it apart from other prehistoric creatures. These adaptations hint at a complex and intriguing lifestyle, making it a subject of ongoing research and discovery.
Understanding this creature helps us appreciate the diversity and adaptability of life forms that existed millions of years ago. Each new finding about Dinocephalosaurus orientalis adds a piece to the puzzle of Earth's ancient past, offering insights into evolutionary biology and the dynamics of prehistoric ecosystems.
For those interested in paleontology, this reptile serves as a reminder of the endless wonders waiting to be uncovered beneath our feet. Keep an eye on future discoveries, as they promise to shed even more light on this remarkable species.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


