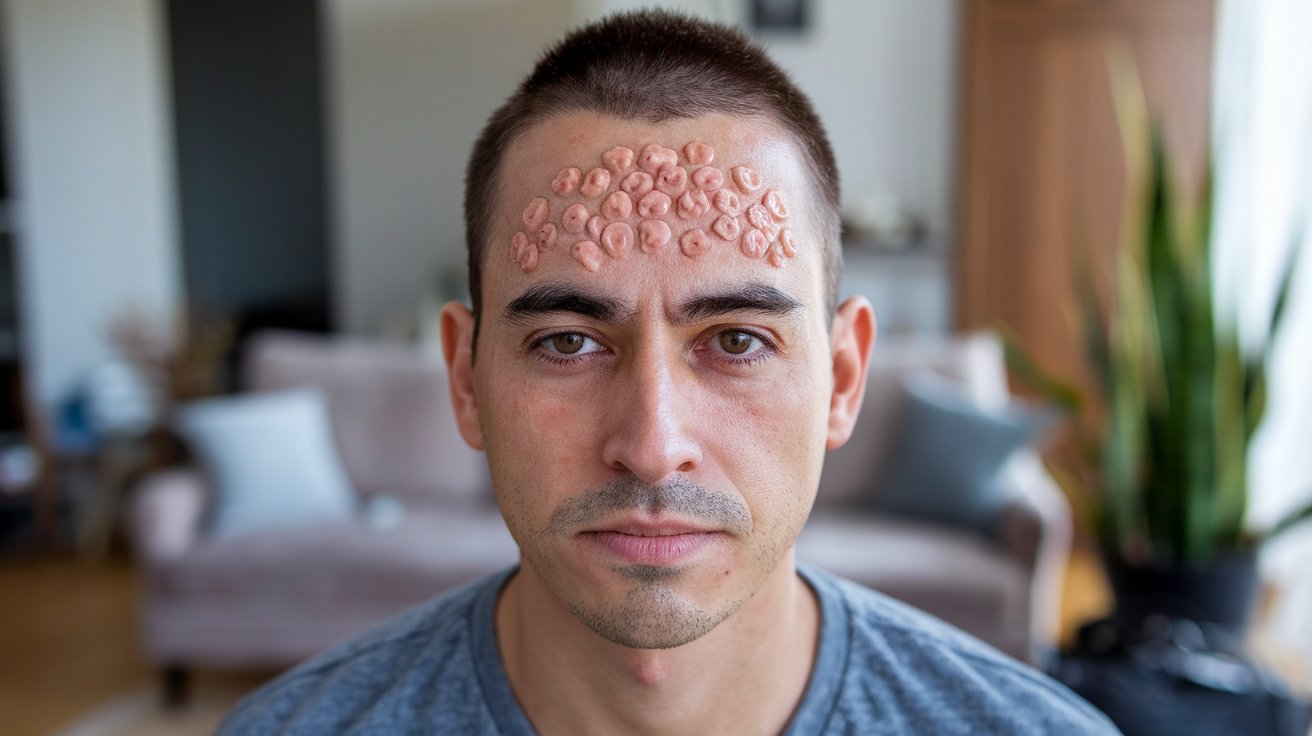
Trichoepithelioma is a rare skin condition that might sound like a tongue twister, but it's actually a benign tumor related to hair follicles. These small, firm bumps usually appear on the face, especially around the nose, cheeks, and forehead. They can be mistaken for other skin issues, like acne or basal cell carcinoma, which makes understanding them crucial. What causes trichoepithelioma? It's often linked to genetic factors, with some cases running in families. While these bumps are generally harmless, they can be bothersome due to their appearance. Treatment options range from surgical removal to laser therapy, depending on the size and location of the tumors. Learning about trichoepithelioma helps in recognizing and managing this condition effectively. Whether you're curious about its causes or treatment, this guide will provide essential insights into this unique skin condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Trichoepithelioma is a non-cancerous skin condition that often appears as small bumps on the face. It's more common in females and can be managed with various treatment options.
- While trichoepithelioma is generally benign, regular check-ups and early detection are important. Support groups and genetic counseling can provide valuable assistance for those affected.
What is Trichoepithelioma?
Trichoepithelioma is a rare skin condition that often puzzles many. It's a benign tumor that originates from hair follicles. While it might sound alarming, understanding it can help ease concerns.
-
Trichoepithelioma is a benign tumor, meaning it is non-cancerous and generally not life-threatening.
-
These tumors originate from hair follicles, the tiny structures in the skin that produce hair.
-
They often appear as small, flesh-colored bumps on the skin, typically on the face.
-
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of trichoepithelioma, with some cases being inherited.
-
The condition is more common in females than in males.
How is Trichoepithelioma Diagnosed?
Diagnosing trichoepithelioma involves a combination of clinical examination and sometimes more detailed tests. Knowing the process can help in early detection and management.
-
A dermatologist usually performs the initial examination to identify trichoepithelioma.
-
A biopsy may be conducted, where a small sample of the skin is taken for further analysis.
-
Histopathological examination helps differentiate trichoepithelioma from other similar skin conditions.
-
Imaging tests are rarely needed but can be used in complex cases.
-
Family history is often reviewed to check for any genetic links.
Treatment Options for Trichoepithelioma
While trichoepithelioma is benign, treatment may be sought for cosmetic reasons or if the tumors cause discomfort. Various options are available depending on individual needs.
-
Surgical excision is a common method to remove the tumors.
-
Laser therapy can be used to target and reduce the appearance of the bumps.
-
Cryotherapy involves freezing the tumors to remove them.
-
Electrosurgery uses electric currents to destroy the tumor tissue.
-
Topical treatments may be prescribed to manage symptoms or reduce tumor size.
Can Trichoepithelioma Become Cancerous?
Understanding the potential risks associated with trichoepithelioma is crucial for those diagnosed with the condition. While generally benign, there are rare cases to be aware of.
-
Trichoepithelioma is typically non-cancerous and does not spread to other parts of the body.
-
In very rare instances, it can transform into a malignant tumor known as basal cell carcinoma.
-
Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is recommended to catch any changes early.
-
Genetic counseling might be suggested for families with a history of the condition.
-
Early detection and treatment can prevent complications.
Living with Trichoepithelioma
Living with trichoepithelioma involves managing symptoms and maintaining a positive outlook. Support and information can make a significant difference.
-
Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can help manage the condition effectively.
-
Sun protection is important, as UV exposure can worsen skin conditions.
-
Cosmetic camouflage techniques can help cover the bumps if desired.
-
Support groups and online communities offer a space to share experiences and advice.
-
Mental health support is beneficial for coping with any emotional impact.
Genetic Aspects of Trichoepithelioma
The genetic component of trichoepithelioma is a key area of interest for researchers. Understanding these aspects can provide insights into prevention and management.
-
Trichoepithelioma can be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning only one parent needs to pass on the gene.
-
Mutations in specific genes, such as CYLD, are linked to the condition.
-
Genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis and help assess the risk for family members.
-
Research is ongoing to better understand the genetic mechanisms involved.
-
Family planning discussions may be advised for those with a genetic predisposition.
Trichoepithelioma vs. Other Skin Conditions
Differentiating trichoepithelioma from other skin conditions is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Here's how it compares to similar conditions.
-
Basal cell carcinoma is a malignant tumor that can resemble trichoepithelioma but requires different treatment.
-
Sebaceous hyperplasia presents as yellowish bumps and is often confused with trichoepithelioma.
-
Milia are small white cysts that can appear similar but are unrelated.
-
Dermatofibromas are firm nodules that differ in texture and color.
-
Neurofibromas are nerve-related tumors that can be mistaken for trichoepithelioma.
Historical Context of Trichoepithelioma
The history of trichoepithelioma provides context for its understanding and treatment today. Knowing its past can illuminate its present.
-
The condition was first described in the 19th century by dermatologists.
-
Early treatments were limited to surgical removal.
-
Advancements in dermatology have improved diagnosis and treatment options.
-
Public awareness of the condition has increased over time.
-
Research continues to evolve, offering hope for better management.
Future Directions in Trichoepithelioma Research
Research into trichoepithelioma is ongoing, with scientists exploring new treatments and genetic insights. The future holds promise for those affected.
-
Gene therapy is being investigated as a potential treatment option.
-
Targeted therapies aim to address the specific genetic mutations involved.
-
Clinical trials are testing new medications and approaches.
-
Collaboration between researchers worldwide is advancing understanding.
-
Patient advocacy groups are pushing for more research funding.
Common Myths About Trichoepithelioma
Misconceptions about trichoepithelioma can lead to unnecessary worry. Clearing up these myths can provide clarity and peace of mind.
-
Trichoepithelioma is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
-
It does not result from poor hygiene or lifestyle choices.
-
The condition is not exclusive to any particular age group, though it often appears in young adults.
-
Diet does not directly influence the development of trichoepithelioma.
-
Alternative therapies have not been proven effective in treating the condition.
Final Thoughts on Trichoepithelioma Facts
Trichoepithelioma, a rare skin condition, often leaves folks with more questions than answers. Understanding its genetic roots and benign nature can ease concerns. While these tumors are usually harmless, they can affect one's appearance and self-esteem. Treatments like surgical removal or laser therapy offer options for those seeking cosmetic improvements. It's crucial to consult with a dermatologist for personalized advice. Awareness and early detection play key roles in managing this condition effectively.
Remember, knowledge empowers. By learning about trichoepithelioma, individuals can make informed decisions about their health. Sharing this information can also help others who might be dealing with similar issues. Stay curious and proactive in your health journey. If you or someone you know is affected, seek support and guidance from medical professionals. Understanding trichoepithelioma is the first step towards managing it confidently.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
