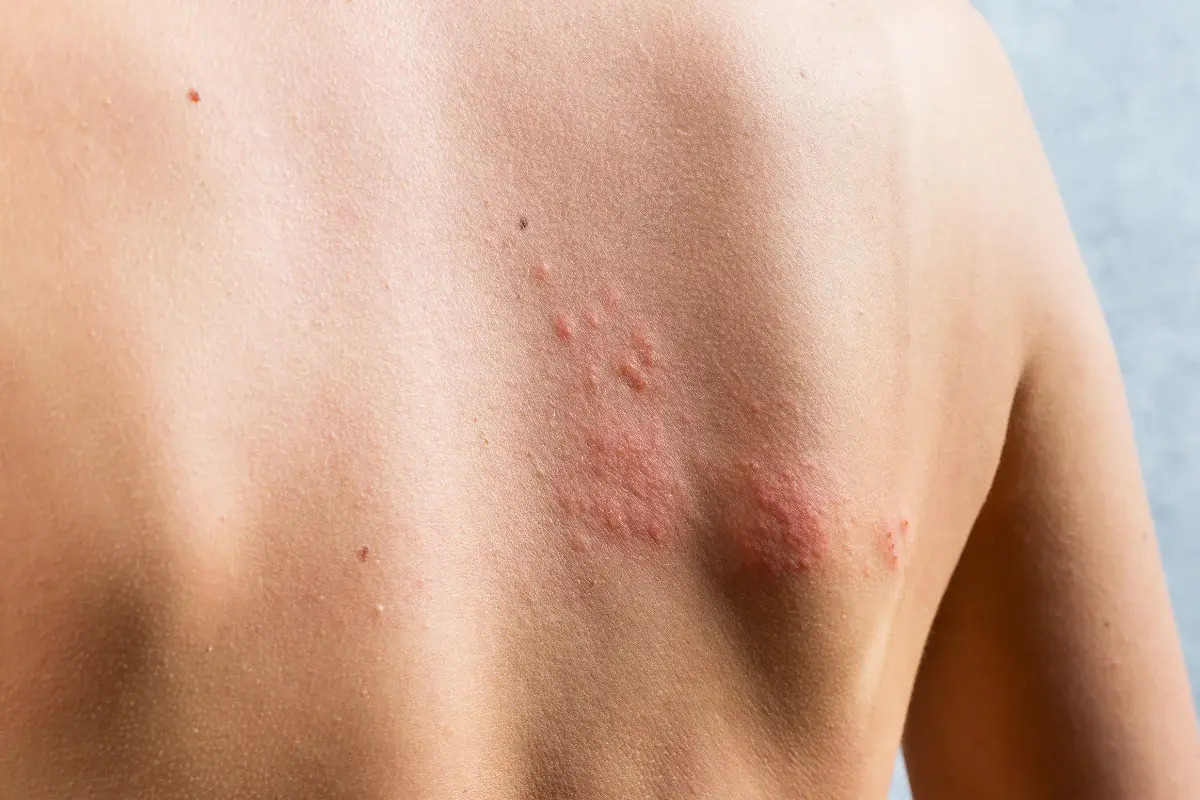
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT) is a rare disorder that affects the skin and liver. PCT occurs due to a deficiency in an enzyme called uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, leading to a buildup of porphyrins. These compounds cause sensitivity to sunlight, resulting in blisters, itching, and swelling on sun-exposed areas. PCT can be triggered by factors like alcohol consumption, smoking, estrogen use, and certain infections. Managing PCT involves avoiding triggers and sometimes undergoing treatments like phlebotomy or medication. Understanding this condition helps in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate care. Let's dive into 50 intriguing facts about Porphyria Cutanea Tarda to better grasp this unique condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT) is a rare skin and liver disorder caused by enzyme deficiency. It leads to extreme sunlight sensitivity and can be managed with lifestyle adjustments and medical treatments.
- Genetic mutations, alcohol consumption, and certain medications can trigger or worsen PCT symptoms. Avoiding triggers, seeking early diagnosis, and staying informed about the condition are crucial for managing PCT effectively.
What is Porphyria Cutanea Tarda?
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT) is a rare disorder that affects the skin and liver. It results from a deficiency in the enzyme uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, which leads to a buildup of porphyrins in the body. These porphyrins cause the skin to become extremely sensitive to sunlight.
- PCT is the most common type of porphyria.
- The disorder primarily affects adults, usually between the ages of 30 and 50.
- PCT can be inherited or acquired through environmental factors.
- Symptoms often include blistering, itching, and swelling of the skin when exposed to sunlight.
- Liver abnormalities are common in individuals with PCT.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of PCT can help in managing and preventing the condition. Various genetic and environmental factors contribute to the development of PCT.
- Genetic mutations can lead to a deficiency in the enzyme uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase.
- Alcohol consumption is a significant risk factor for developing PCT.
- Hepatitis C infection is commonly associated with PCT.
- Iron overload in the liver can exacerbate the condition.
- Estrogen therapy, including birth control pills, can trigger PCT in some individuals.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and getting a proper diagnosis is crucial for managing PCT effectively. The symptoms can vary but often involve skin and liver issues.
- Blisters on sun-exposed areas like the hands and face are common.
- Hyperpigmentation or darkening of the skin can occur.
- Increased hair growth on the face, particularly in women, is a symptom.
- Liver function tests may show abnormalities.
- A 24-hour urine test can detect elevated levels of porphyrins.
Treatment Options
Various treatment options are available to manage PCT. These treatments aim to reduce symptoms and prevent complications.
- Phlebotomy, or blood removal, helps reduce iron levels in the body.
- Low-dose hydroxychloroquine can be used to remove excess porphyrins.
- Avoiding alcohol and estrogen can prevent flare-ups.
- Sunscreen and protective clothing are essential for managing skin sensitivity.
- Regular monitoring of liver function is necessary.
Lifestyle and Management
Living with PCT requires lifestyle adjustments and ongoing management to keep symptoms under control. Here are some tips for managing the condition.
- Avoiding direct sunlight can prevent skin damage.
- Using broad-spectrum sunscreen with high SPF is crucial.
- Wearing protective clothing, including hats and long sleeves, helps shield the skin.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are important.
- Maintaining a healthy diet can support liver function.
Complications and Prognosis
PCT can lead to various complications if not managed properly. Understanding these complications can help in taking preventive measures.
- Chronic liver disease is a potential complication.
- There is an increased risk of liver cancer in individuals with PCT.
- Scarring and thickening of the skin can occur over time.
- Secondary infections can develop in blistered areas.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the prognosis significantly.
Genetic Aspects
The genetic aspects of PCT play a crucial role in understanding the condition. Knowing your genetic predisposition can help in early detection and management.
- PCT can be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
- Genetic testing can identify mutations in the UROD gene.
- Family history of PCT increases the risk of developing the condition.
- Carriers of the genetic mutation may not show symptoms but can pass it on.
- Genetic counseling can provide valuable information for affected families.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors can trigger or worsen PCT symptoms. Being aware of these triggers can help in avoiding flare-ups.
- Exposure to certain chemicals, like hexachlorobenzene, can trigger PCT.
- Smoking is a known risk factor for PCT.
- Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to symptom flare-ups.
- Certain medications, including some antibiotics, can exacerbate PCT.
- Avoiding these triggers can help manage the condition effectively.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for understanding PCT better and developing new treatments. Here are some recent advancements and future directions in PCT research.
- New genetic studies are identifying additional mutations linked to PCT.
- Research is exploring the role of gut microbiota in PCT.
- Advances in liver imaging techniques are improving diagnosis.
- Clinical trials are testing new drugs to reduce porphyrin levels.
- Future research aims to develop gene therapy for PCT.
Support and Resources
Living with PCT can be challenging, but various support and resources are available to help individuals manage the condition.
- Support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences and advice.
- Online forums offer a space for discussing symptoms and treatments.
- Educational resources can help individuals understand PCT better.
- Healthcare providers can offer personalized management plans.
- Patient advocacy organizations work to raise awareness and support research.
Final Thoughts on Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT) is a rare but fascinating condition. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can make a big difference for those affected. PCT often presents with skin sensitivity to sunlight, leading to blisters and scarring. It’s usually triggered by factors like alcohol consumption, iron overload, or certain medications. Early diagnosis and lifestyle changes can help manage the condition effectively. Treatments like phlebotomy and low-dose antimalarial drugs have shown promise in reducing symptoms. Awareness and education about PCT are crucial for better management and support. If you or someone you know shows signs of PCT, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Knowledge is power, and being informed can lead to better health outcomes. Stay curious, stay informed, and take care of your skin.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
