Lymphocytic colitis might sound like a complex medical term, but understanding it can be straightforward. This condition involves inflammation of the colon, leading to chronic diarrhea and abdominal pain. Unlike other forms of colitis, lymphocytic colitis is microscopic, meaning it can only be seen under a microscope. Symptoms often include watery diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue. The exact cause remains unknown, but factors like autoimmune disorders, infections, and medications might play a role. Diagnosing lymphocytic colitis typically requires a colonoscopy and biopsy. Treatment options range from dietary changes to medications. Ready to dive into 50 intriguing facts about this condition? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Lymphocytic colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes chronic diarrhea and abdominal pain. It is more common in older adults, especially women, and can be managed with medications and lifestyle adjustments.
- Factors like smoking, NSAID use, and genetic predisposition can increase the risk of developing lymphocytic colitis. Accurate diagnosis through colonoscopy and biopsies is crucial for effective treatment. Treatment options include medications, dietary changes, and stress management techniques.
What is Lymphocytic Colitis?
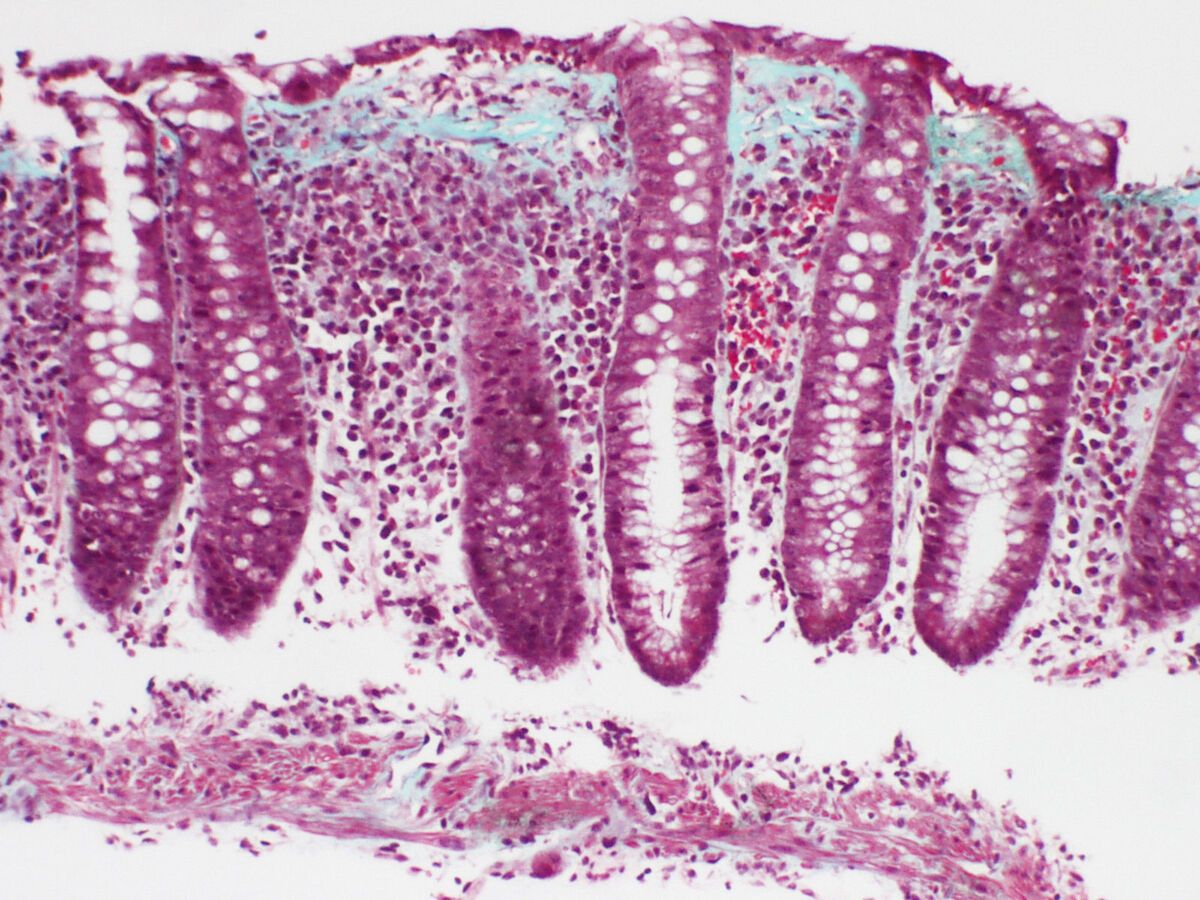
Lymphocytic colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease. It affects the colon and causes chronic diarrhea. Here are some interesting facts about this condition.
- Lymphocytic colitis is characterized by an increase in lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, in the lining of the colon.
- It is a form of microscopic colitis, meaning inflammation is only visible under a microscope.
- The exact cause of lymphocytic colitis remains unknown.
- Symptoms often include chronic, watery diarrhea without blood.
- Abdominal pain and cramping are common symptoms.
- Weight loss and fatigue can also occur.
- The condition is more common in older adults, typically over 50.
- Women are more likely to develop lymphocytic colitis than men.
- Diagnosis usually involves a colonoscopy and biopsy of the colon tissue.
- Treatment often includes medications like anti-inflammatory drugs and antidiarrheal agents.
Risk Factors and Triggers
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing lymphocytic colitis. Understanding these can help manage the condition better.
- Smoking has been linked to a higher risk of lymphocytic colitis.
- Use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may trigger symptoms.
- Some studies suggest a genetic predisposition to the disease.
- Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, are often associated with lymphocytic colitis.
- Infections, particularly gastrointestinal infections, can trigger the condition.
- Certain medications, like proton pump inhibitors, have been implicated.
- Stress and anxiety may exacerbate symptoms.
- A family history of inflammatory bowel disease increases risk.
- Hormonal changes, especially in women, can influence the onset.
- Diet does not cause lymphocytic colitis but can affect symptom severity.
Diagnosis and Testing
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here’s how doctors diagnose lymphocytic colitis.
- A colonoscopy is the primary diagnostic tool.
- Biopsies taken during colonoscopy reveal increased lymphocytes.
- Blood tests can help rule out other conditions.
- Stool tests check for infections and other causes of diarrhea.
- Imaging tests like CT scans may be used to examine the abdomen.
- A detailed medical history is essential for diagnosis.
- Physical examination often reveals no abnormalities.
- Endoscopy can sometimes be used for diagnosis.
- Capsule endoscopy, where a patient swallows a small camera, may be used in rare cases.
- Differential diagnosis is important to distinguish from other forms of colitis.
Treatment Options
Managing lymphocytic colitis involves various treatment strategies. Here are some common approaches.
- Anti-inflammatory medications like budesonide are often prescribed.
- Antidiarrheal agents, such as loperamide, help manage symptoms.
- Immunosuppressive drugs may be used in severe cases.
- Dietary changes, like a low-fat diet, can help reduce symptoms.
- Avoiding trigger foods, such as caffeine and lactose, is recommended.
- Probiotics may improve gut health and reduce symptoms.
- Stress management techniques, like yoga and meditation, can be beneficial.
- Regular follow-up with a gastroenterologist is crucial.
- In rare cases, surgery may be considered if other treatments fail.
- Hydration is important to prevent dehydration from chronic diarrhea.
Living with Lymphocytic Colitis
Living with this condition requires lifestyle adjustments. Here are some tips for managing daily life.
- Keeping a symptom diary can help identify triggers.
- Joining a support group provides emotional support.
- Regular exercise can improve overall health and reduce stress.
- Adequate sleep is essential for managing symptoms.
- Avoiding alcohol and smoking can reduce flare-ups.
- Staying informed about the condition helps in better management.
- Communicating openly with healthcare providers ensures effective treatment.
- Planning meals and snacks helps maintain a balanced diet.
- Wearing comfortable clothing can reduce abdominal discomfort.
- Staying positive and proactive improves quality of life.
Final Thoughts on Lymphocytic Colitis
Lymphocytic colitis, though not as well-known as other gastrointestinal conditions, significantly impacts those who suffer from it. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help manage this condition better. Key symptoms include chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Causes range from autoimmune responses to infections. Treatments often involve dietary changes, medications, and sometimes probiotics.
Early diagnosis and proper management can greatly improve quality of life. If you suspect you might have lymphocytic colitis, consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment. Staying informed and proactive is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Remember, you're not alone; many resources and support systems are available to help you navigate this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
