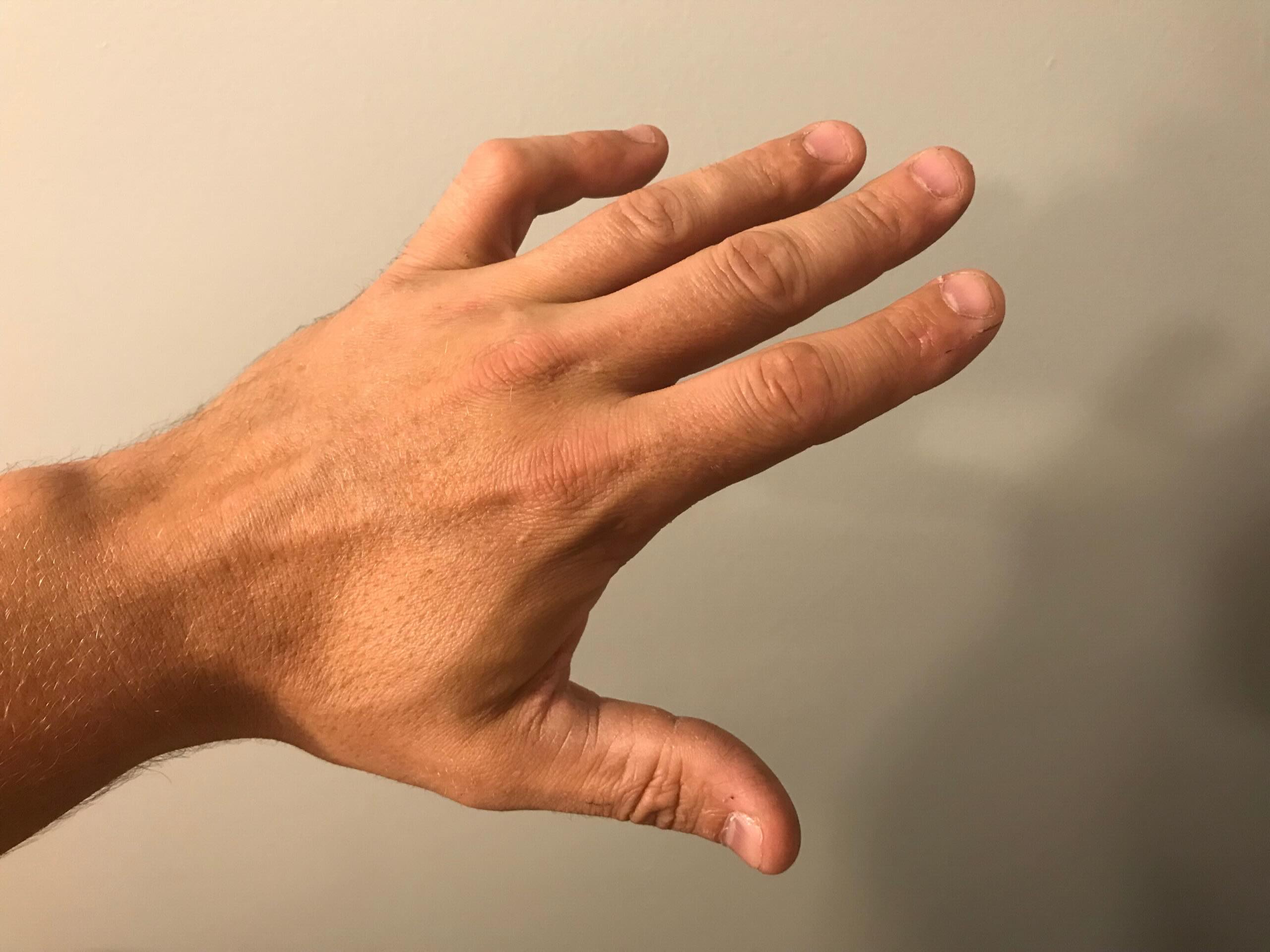
What is a boutonniere deformity? A boutonniere deformity is a finger condition where the middle joint bends down while the fingertip bends back. This happens when the central slip of the extensor tendon, which straightens the finger, gets damaged. Common causes include injuries like jamming a finger or chronic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Symptoms often include pain, swelling, and difficulty straightening the finger. Early treatment can prevent permanent damage. Options range from splinting to surgery, depending on severity. Understanding this condition helps in seeking timely medical advice and ensuring proper care.
Key Takeaways:
- Boutonniere Deformity causes finger bending and pain. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for better outcomes. Prevention includes protective gear and regular hand exercises.
- Surgical options like tendon repair and joint fusion can help severe cases. Research on stem cell therapy and gene therapy offers hope for future treatments.
What is Boutonniere Deformity?
Boutonniere deformity is a condition affecting the fingers, causing them to bend in an unusual way. This deformity can be painful and limit hand function. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
- Boutonniere deformity occurs when the central slip of the extensor tendon is damaged, leading to a bent middle joint and a hyperextended fingertip.
- The term "boutonniere" means "buttonhole" in French, describing the buttonhole-like appearance of the deformity.
- Common causes include trauma, rheumatoid arthritis, and severe finger injuries.
- Symptoms often involve pain, swelling, and difficulty straightening the finger.
- Early diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and preventing permanent damage.
Causes of Boutonniere Deformity
Understanding the causes helps in preventing and managing boutonniere deformity. Various factors can lead to this condition, each contributing differently to its development.
- Trauma is the most common cause, often resulting from sports injuries or accidents.
- Rheumatoid arthritis can weaken the tendons, making them more susceptible to damage.
- Burns or lacerations to the finger can also lead to this deformity.
- Infections affecting the tendons may cause inflammation and subsequent deformity.
- Genetic factors might play a role, especially in families with a history of tendon issues.
Symptoms of Boutonniere Deformity
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to prompt treatment and better outcomes. Symptoms vary but generally affect the finger's appearance and function.
- Pain and tenderness around the affected joint are common initial symptoms.
- Swelling may occur, making the finger appear larger than usual.
- Difficulty straightening the middle joint while the fingertip remains hyperextended.
- Stiffness in the finger, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Decreased grip strength due to the finger's inability to function normally.
Diagnosing Boutonniere Deformity
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Several methods help in diagnosing boutonniere deformity, each providing valuable information.
- Physical examination by a healthcare professional is the first step.
- X-rays can reveal any bone abnormalities or joint damage.
- MRI scans provide detailed images of the tendons and soft tissues.
- Ultrasound may be used to assess tendon damage.
- Patient history helps in understanding the cause and progression of the deformity.
Treatment Options for Boutonniere Deformity
Various treatments are available, ranging from non-surgical to surgical options. The choice depends on the severity and cause of the deformity.
- Splinting is often the first line of treatment, helping to straighten the finger.
- Physical therapy can improve flexibility and strength.
- Anti-inflammatory medications reduce pain and swelling.
- Steroid injections may be used to decrease inflammation.
- Surgical repair is considered when non-surgical treatments fail.
Surgical Treatments for Boutonniere Deformity
Surgery may be necessary for severe cases. Different surgical techniques aim to restore finger function and appearance.
- Tendon repair involves stitching the damaged tendon back together.
- Joint fusion may be performed to stabilize the finger.
- Tendon grafting uses a tendon from another part of the body to replace the damaged one.
- Arthroplasty replaces the damaged joint with an artificial one.
- Post-surgical rehabilitation is crucial for regaining full function.
Preventing Boutonniere Deformity
Prevention focuses on avoiding injuries and managing underlying conditions. Simple measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing this deformity.
- Protective gear during sports can prevent finger injuries.
- Proper technique in activities reduces the risk of trauma.
- Managing rheumatoid arthritis with medication and lifestyle changes.
- Regular hand exercises to maintain tendon strength and flexibility.
- Prompt treatment of finger injuries to prevent complications.
Living with Boutonniere Deformity
Living with this condition requires adjustments and ongoing care. Understanding how to manage daily activities can improve quality of life.
- Adaptive tools can make daily tasks easier.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor the condition.
- Support groups offer emotional and practical support.
- Education about the condition helps in managing symptoms.
- Healthy lifestyle choices, including a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Interesting Facts about Boutonniere Deformity
Some lesser-known facts about boutonniere deformity can provide a deeper understanding of this condition.
- Named by French surgeons, the term boutonniere deformity has been used for centuries.
- Not exclusive to humans, animals can also develop similar tendon injuries.
- Historical records show descriptions of this deformity in ancient medical texts.
- Modern technology has improved diagnosis and treatment significantly.
- Research continues to explore new treatment options and preventive measures.
Future Directions in Boutonniere Deformity Research
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of boutonniere deformity. Innovations in medical science hold promise for better outcomes.
- Stem cell therapy is being explored as a potential treatment.
- Gene therapy may offer solutions for genetic predispositions.
- Advanced imaging techniques provide more accurate diagnoses.
- Robotic surgery offers precision in tendon repair.
- Patient-specific treatments tailored to individual needs are on the horizon.
Understanding Boutonniere Deformity
Boutonniere deformity, a condition affecting the fingers, can significantly impact daily activities. Recognizing its symptoms early, like the inability to straighten the middle joint, helps in seeking timely treatment. Causes range from injuries to underlying conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment options vary from splinting to surgery, depending on severity.
Preventing boutonniere deformity involves protecting fingers during activities and managing health conditions that might contribute. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider ensure any signs are caught early.
Living with this condition requires adjustments, but with proper care and treatment, many regain significant function. Staying informed and proactive about hand health makes a big difference.
If you suspect you have boutonniere deformity, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Your hands are essential, so take steps to keep them healthy and functional.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
