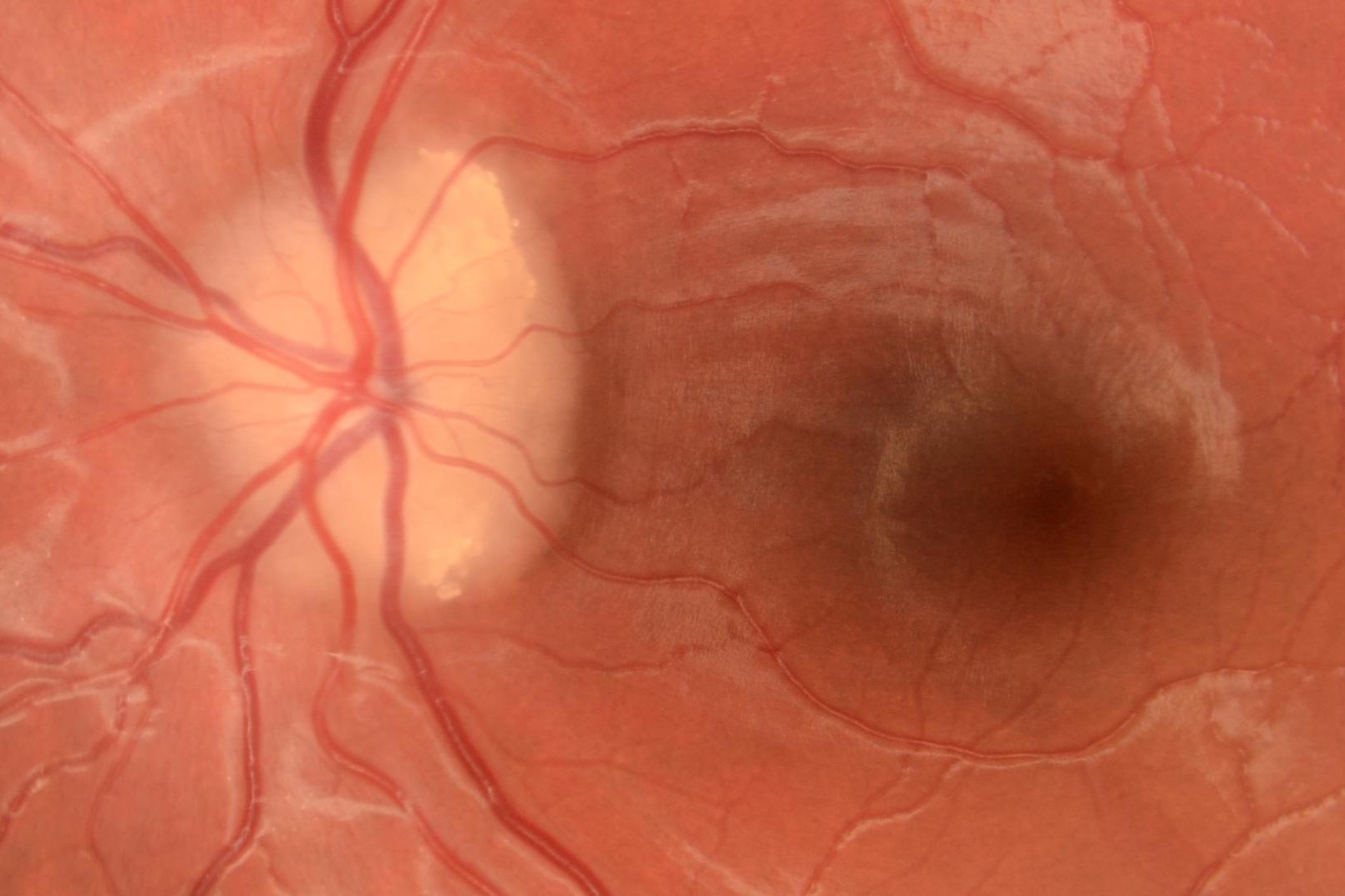
Optic Disc Drusen might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it is crucial for eye health. These tiny, calcified deposits can form in the optic nerve head, often without causing any symptoms. However, they can sometimes lead to vision problems or even mimic other eye conditions. What exactly causes Optic Disc Drusen? The exact cause remains unclear, but genetics play a significant role. People with a family history of this condition are more likely to develop it. While there's no cure, regular eye exams can help monitor and manage any potential complications. Stay informed to keep your eyes healthy!
Key Takeaways:
- Optic Disc Drusen are tiny deposits in the eye that can affect vision. They are often inherited and may not cause symptoms, so regular eye exams are important for early detection and management.
- Living with Optic Disc Drusen requires vigilance, healthy habits, and support. Patients should stay informed, seek emotional support, and take steps to protect their vision for a better quality of life.
What is Optic Disc Drusen?
Optic Disc Drusen (ODD) are tiny, rock-like deposits of protein and calcium salts that accumulate in the optic nerve head. These deposits can affect vision and are often discovered during routine eye exams. Here are some fascinating facts about this condition:
- ODD are usually inherited. If one family member has it, others might too.
- They can be found in both eyes. However, one eye might have more deposits than the other.
- ODD are more common in Caucasians. This condition is less frequently seen in other ethnic groups.
- They can be detected in childhood. Though symptoms might not appear until later in life.
- ODD are often asymptomatic. Many people don't realize they have them until an eye exam reveals their presence.
- They can cause peripheral vision loss. Central vision usually remains unaffected.
- ODD can mimic other eye conditions. This can make diagnosis tricky without proper imaging.
- Ultrasound is a common diagnostic tool. It helps to visualize the drusen clearly.
- ODD can lead to optic nerve damage. This is due to the pressure they exert on the nerve fibers.
- They are different from macular drusen. Macular drusen are associated with age-related macular degeneration.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how ODD is diagnosed can help in managing the condition effectively.
- ODD can cause transient visual obscurations. These are brief episodes of vision loss.
- They may lead to optic disc swelling. This can be mistaken for papilledema, a sign of increased intracranial pressure.
- Visual field tests are essential. They help in assessing the extent of vision loss.
- ODD can cause visual field defects. These defects are usually permanent.
- Fluorescein angiography can be used. This imaging test helps in differentiating ODD from other conditions.
- ODD can cause night vision problems. This is due to the damage to the optic nerve fibers.
- They can be associated with retinal hemorrhages. This is a rare but serious complication.
- ODD can cause color vision defects. This is less common but can occur in some cases.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is useful. It provides detailed images of the optic nerve head.
- ODD can cause blind spots. These are areas in the visual field where vision is lost.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for ODD, understanding treatment and management options can help in dealing with the condition.
- Regular eye exams are crucial. They help in monitoring the progression of the condition.
- There is no specific treatment for ODD. Management focuses on monitoring and addressing symptoms.
- Low vision aids can be helpful. These devices assist in maximizing remaining vision.
- Patients should avoid activities that increase intracranial pressure. This includes heavy lifting and straining.
- Managing underlying conditions is important. Conditions like hypertension can exacerbate ODD.
- Laser therapy is rarely used. It might be considered in cases with significant complications.
- Genetic counseling can be beneficial. It helps families understand the hereditary nature of ODD.
- Patients should be educated about the condition. Understanding ODD can help in managing expectations and reducing anxiety.
- Regular visual field testing is recommended. This helps in tracking any changes in vision.
- ODD can be associated with other eye conditions. Regular check-ups can help in early detection and management.
Living with Optic Disc Drusen
Living with ODD requires adjustments and awareness to maintain quality of life.
- Patients should be vigilant about changes in vision. Early detection of changes can help in managing complications.
- Wearing protective eyewear is advisable. This helps in preventing eye injuries that could worsen the condition.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is beneficial. Good nutrition and regular exercise support overall eye health.
- Stress management techniques can be helpful. Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so relaxation techniques are recommended.
- Joining support groups can provide emotional support. Sharing experiences with others can be comforting.
- Patients should inform their healthcare providers about ODD. This ensures comprehensive care and management.
- Using adaptive technologies can enhance daily living. Devices like screen readers and magnifiers can be useful.
- Patients should avoid smoking. Smoking can worsen eye health and exacerbate symptoms.
- Regular follow-ups with an ophthalmologist are essential. This helps in monitoring the condition and managing any complications.
- Staying informed about new research and treatments is important. Advances in medical research can offer new insights and options for managing ODD.
Final Glimpse at Optic Disc Drusen
Optic Disc Drusen (ODD) are tiny, calcified deposits in the optic nerve head. They can affect vision, often discovered during routine eye exams. While many people with ODD don't experience symptoms, some might notice vision changes like blind spots or peripheral vision loss. Regular check-ups are crucial for monitoring any progression.
ODD can be mistaken for other eye conditions, so accurate diagnosis is essential. Advanced imaging techniques like OCT and ultrasound help in identifying these deposits. Though there's no cure, managing symptoms and protecting overall eye health remain vital.
Understanding ODD helps in recognizing its impact on vision. Staying informed and proactive with eye care can make a significant difference. If you suspect any vision issues, consult an eye specialist promptly. Knowledge and vigilance are your best tools in maintaining eye health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
