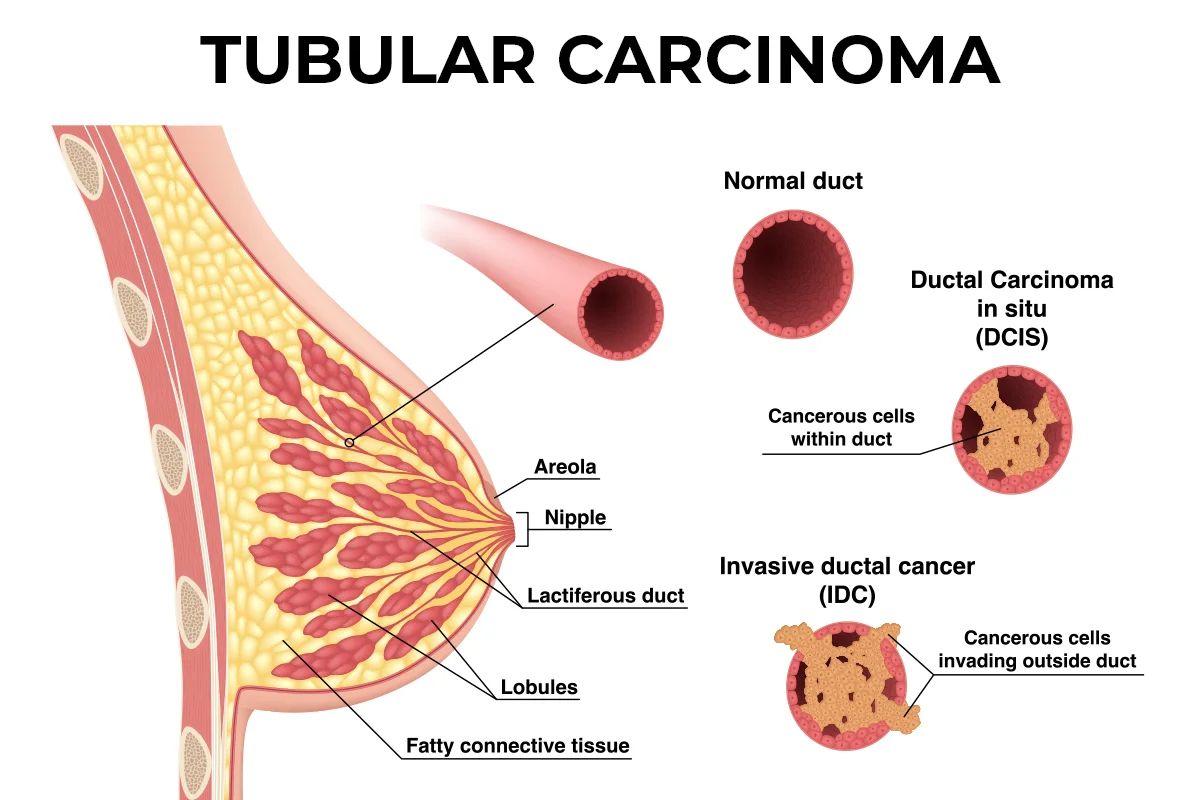
What is Tubular Carcinoma? Tubular carcinoma is a rare type of breast cancer that accounts for about 1-2% of all breast cancer cases. Unlike other forms, this cancer is often considered less aggressive. It typically affects women over 50, but younger women can also be diagnosed. The cancer cells form small, tube-like structures, which is how it gets its name. Most tubular carcinomas are hormone receptor-positive, meaning they grow in response to hormones like estrogen. This makes them more responsive to hormone therapy treatments. Early detection is crucial, as tubular carcinoma usually has a favorable prognosis when caught early. Regular mammograms and self-exams are key in identifying any unusual changes. Understanding this condition can help in making informed decisions about treatment options and lifestyle changes.
Key Takeaways:
- Tubular carcinoma is a rare, slow-growing type of breast cancer with a favorable prognosis. Early detection through mammograms and biopsy is crucial for effective treatment and management.
- Living with tubular carcinoma requires a strong support system, healthy lifestyle, regular check-ups, awareness, and a positive outlook. Ongoing research and global collaborations aim to improve understanding and treatment of this condition.
Understanding Tubular Carcinoma
Tubular carcinoma is a rare type of breast cancer. It's known for its unique tubular structure when viewed under a microscope. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Rare Occurrence
Tubular carcinoma accounts for only about 1-2% of all breast cancer cases. Its rarity makes it less known compared to other types. -
Distinctive Shape
The cancer cells form tube-like structures, which is how it got its name. This unique shape is visible during microscopic examination. -
Slow Growth
This type of cancer tends to grow slowly. Its indolent nature often leads to a better prognosis compared to more aggressive forms. -
Common in Older Women
It is more frequently diagnosed in women over the age of 50. Younger women are less likely to develop this type of cancer. -
Hormone Receptor Positive
Most tubular carcinomas are estrogen and progesterone receptor-positive. This means they may respond well to hormone therapy.
Diagnosis and Detection
Early detection is key in managing any cancer. Tubular carcinoma has specific characteristics that aid in its diagnosis.
-
Mammogram Detection
Mammograms can often detect tubular carcinoma. The cancer appears as a small, spiculated mass on the imaging. -
Biopsy Confirmation
A biopsy is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. It involves taking a small tissue sample for microscopic examination. -
Low Grade
Tubular carcinoma is usually classified as a low-grade cancer. This indicates that the cells look more like normal cells and tend to grow slowly. -
Favorable Prognosis
Due to its slow growth and low-grade nature, the prognosis for tubular carcinoma is generally favorable. -
Minimal Lymph Node Involvement
It rarely spreads to lymph nodes. This limited spread contributes to its better prognosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for tubular carcinoma often involves a combination of surgery, radiation, and hormone therapy.
-
Surgical Removal
Lumpectomy or mastectomy are common surgical options. The choice depends on the size and location of the tumor. -
Radiation Therapy
Radiation is often recommended after surgery. It helps eliminate any remaining cancer cells. -
Hormone Therapy
Since most tubular carcinomas are hormone receptor-positive, hormone therapy can be effective. Medications like tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors are commonly used. -
Chemotherapy Rarely Needed
Chemotherapy is not typically required. The slow-growing nature of the cancer often makes other treatments sufficient. -
Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up care is crucial. It helps monitor for any signs of recurrence and manage overall health.
Living with Tubular Carcinoma
Living with a cancer diagnosis can be challenging, but understanding the condition can help in managing it effectively.
-
Support Systems
Having a strong support system is vital. Family, friends, and support groups can provide emotional and practical assistance. -
Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can aid recovery. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management are beneficial. -
Regular Check-Ups
Regular medical check-ups are important. They help ensure any changes in health are promptly addressed. -
Awareness and Education
Being informed about the condition empowers patients. Understanding treatment options and potential side effects can aid in decision-making. -
Positive Outlook
A positive outlook can improve quality of life. Many people with tubular carcinoma lead fulfilling lives post-diagnosis.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research continues to improve understanding and treatment of tubular carcinoma.
-
Genetic Studies
Research into genetic factors is ongoing. Understanding genetic predispositions can aid in early detection and prevention. -
Improved Imaging Techniques
Advancements in imaging techniques are enhancing detection. More precise imaging helps in early and accurate diagnosis. -
Targeted Therapies
Development of targeted therapies is underway. These therapies aim to specifically attack cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells. -
Clinical Trials
Participation in clinical trials can provide access to new treatments. Trials help advance medical knowledge and improve patient outcomes. -
Patient Registries
Patient registries are being developed. They collect data to better understand the condition and improve care strategies.
Global Perspective
Understanding how tubular carcinoma is viewed and treated worldwide provides a broader perspective.
-
Varied Incidence Rates
Incidence rates vary globally. Factors like genetics, lifestyle, and healthcare access influence these rates. -
Access to Care
Access to care differs across regions. In some areas, limited resources can impact diagnosis and treatment options. -
Cultural Perceptions
Cultural perceptions of cancer can affect patient experiences. Awareness campaigns aim to reduce stigma and promote early detection. -
International Collaborations
International collaborations are enhancing research efforts. Sharing knowledge and resources helps improve global outcomes. -
Awareness Campaigns
Awareness campaigns play a crucial role. They educate the public about the importance of early detection and treatment.
Final Thoughts on Tubular Carcinoma
Tubular carcinoma, a rare form of breast cancer, often presents a more favorable prognosis compared to other types. Its slow growth and low likelihood of spreading make it less aggressive, which is a relief for many diagnosed with it. Early detection remains crucial, as it allows for more effective treatment options. Regular screenings and mammograms play a vital role in catching this cancer early.
Understanding the symptoms and risk factors can empower individuals to seek medical advice promptly. While the word "cancer" can be daunting, knowledge about tubular carcinoma's nature can provide some comfort. Advances in medical research and treatment continue to improve outcomes for those affected. Staying informed and proactive about breast health is key. Remember, if you or someone you know is facing this diagnosis, support and resources are available to help navigate the journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
