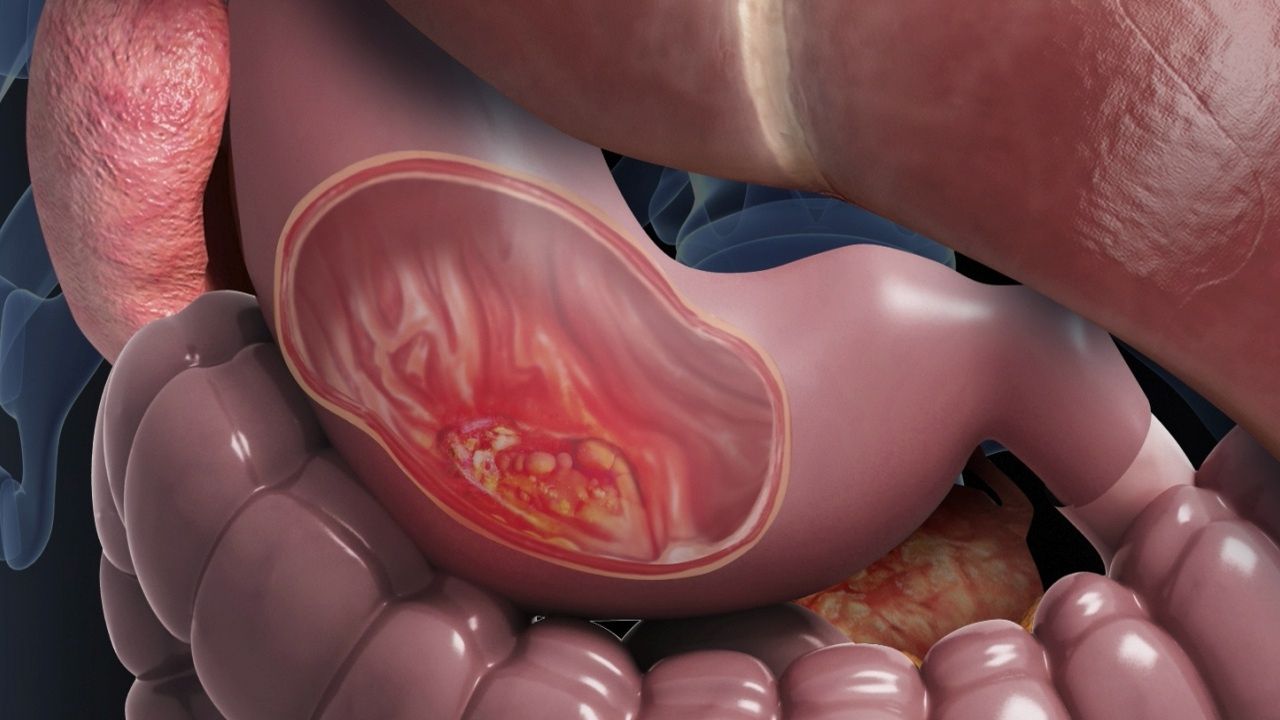
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a serious disease that begins in the stomach lining. It's not as common as other cancers, but it can be quite dangerous if not caught early. Understanding this illness is crucial for prevention and early detection. Did you know that stomach cancer is more prevalent in older adults, particularly those over 60? Factors like diet, smoking, and family history can increase risk. Symptoms might include indigestion, stomach pain, or feeling full quickly. However, these signs often appear in advanced stages, making regular check-ups vital. Treatment options vary, from surgery to chemotherapy, depending on the cancer's stage. Learning about stomach cancer can empower individuals to make informed health choices and seek timely medical advice. Stay informed and proactive about your health!
Key Takeaways:
- Stomach cancer is common, especially in East Asia, and more prevalent in men. Early detection through regular screenings and a healthy lifestyle can improve survival rates.
- Risk factors for stomach cancer include smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, and certain occupations. Understanding these factors and seeking regular medical check-ups can help in prevention and early detection.
Understanding Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, begins when cells in the stomach grow uncontrollably. This type of cancer can develop in any part of the stomach and may spread to other organs. Let's explore some interesting facts about this disease.
-
Common Worldwide: Stomach cancer ranks as the fifth most common cancer globally. It's particularly prevalent in East Asia, including countries like Japan and South Korea.
-
More Common in Men: Men are twice as likely to develop stomach cancer compared to women. The reasons for this gender disparity remain under investigation.
-
Age Factor: Most cases occur in individuals over 60 years old. The risk increases significantly with age.
-
Helicobacter pylori Connection: Infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria is a major risk factor. This bacterium can cause chronic inflammation and ulcers, leading to cancer.
-
Dietary Influences: Diets high in smoked, salted, or pickled foods can increase risk. Conversely, diets rich in fresh fruits and vegetables may lower it.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Family history plays a role. Those with close relatives who have had stomach cancer face a higher risk.
-
Early Symptoms Are Subtle: Early-stage symptoms can be vague, like indigestion or stomach discomfort, making early detection challenging.
-
Advanced Symptoms: As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include weight loss, vomiting, and difficulty swallowing.
-
Screening Practices: In countries with high incidence rates, regular screening is common. This helps in early detection and treatment.
-
Types of Stomach Cancer: The most common type is adenocarcinoma, which starts in the glandular cells of the stomach lining.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Understanding the risk factors can help in prevention and early detection. Here are some key points to consider.
-
Smoking Increases Risk: Smokers have a higher chance of developing stomach cancer. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce this risk.
-
Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is linked to a higher risk. Moderation is advised for better health.
-
Obesity Concerns: Being overweight is another risk factor. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is beneficial.
-
Occupational Hazards: Certain jobs, like those involving rubber manufacturing, may expose workers to carcinogens.
-
Previous Stomach Surgery: Individuals who have had stomach surgery for ulcers or other conditions may face an increased risk.
-
Blood Type A: People with blood type A have a slightly higher risk, though the reasons are not fully understood.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups can help in early detection, especially for those with risk factors.
-
Vaccination: Vaccines against Helicobacter pylori are being researched as a preventive measure.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol can lower risk.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Public health campaigns aim to educate people about risk factors and symptoms.
Treatment and Survival
Treatment options and survival rates vary depending on the stage of cancer and other factors. Here are some insights.
-
Surgery as a Primary Treatment: Surgery is often the main treatment, especially if the cancer is detected early.
-
Chemotherapy and Radiation: These treatments may be used before or after surgery to shrink tumors or kill remaining cancer cells.
-
Targeted Therapy: Newer treatments target specific cancer cell changes, offering hope for improved outcomes.
-
Immunotherapy Advances: Immunotherapy helps the immune system fight cancer and is showing promise in clinical trials.
-
Survival Rates: The five-year survival rate varies widely, from 70% for early-stage to less than 30% for advanced cases.
-
Importance of Early Detection: Early detection significantly improves survival rates, highlighting the need for awareness and screening.
-
Supportive Care: Palliative care focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life for patients.
-
Research and Innovation: Ongoing research is crucial for developing better treatments and understanding the disease.
-
Patient Advocacy: Patient support groups and advocacy organizations provide resources and support for those affected.
-
Hope for the Future: Advances in medical research and technology continue to improve the outlook for stomach cancer patients.
Understanding Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a serious health issue affecting many worldwide. Knowing the symptoms like persistent indigestion, unexplained weight loss, and stomach pain can lead to early detection, which is crucial for better outcomes. Risk factors include diet, genetics, and infection with Helicobacter pylori. Treatments range from surgery and chemotherapy to targeted therapies, depending on the stage and location of the cancer.
Prevention plays a key role. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol intake can reduce risk. Regular check-ups and being aware of family history are also important steps.
Staying informed and proactive about health can make a significant difference. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Early action can save lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
