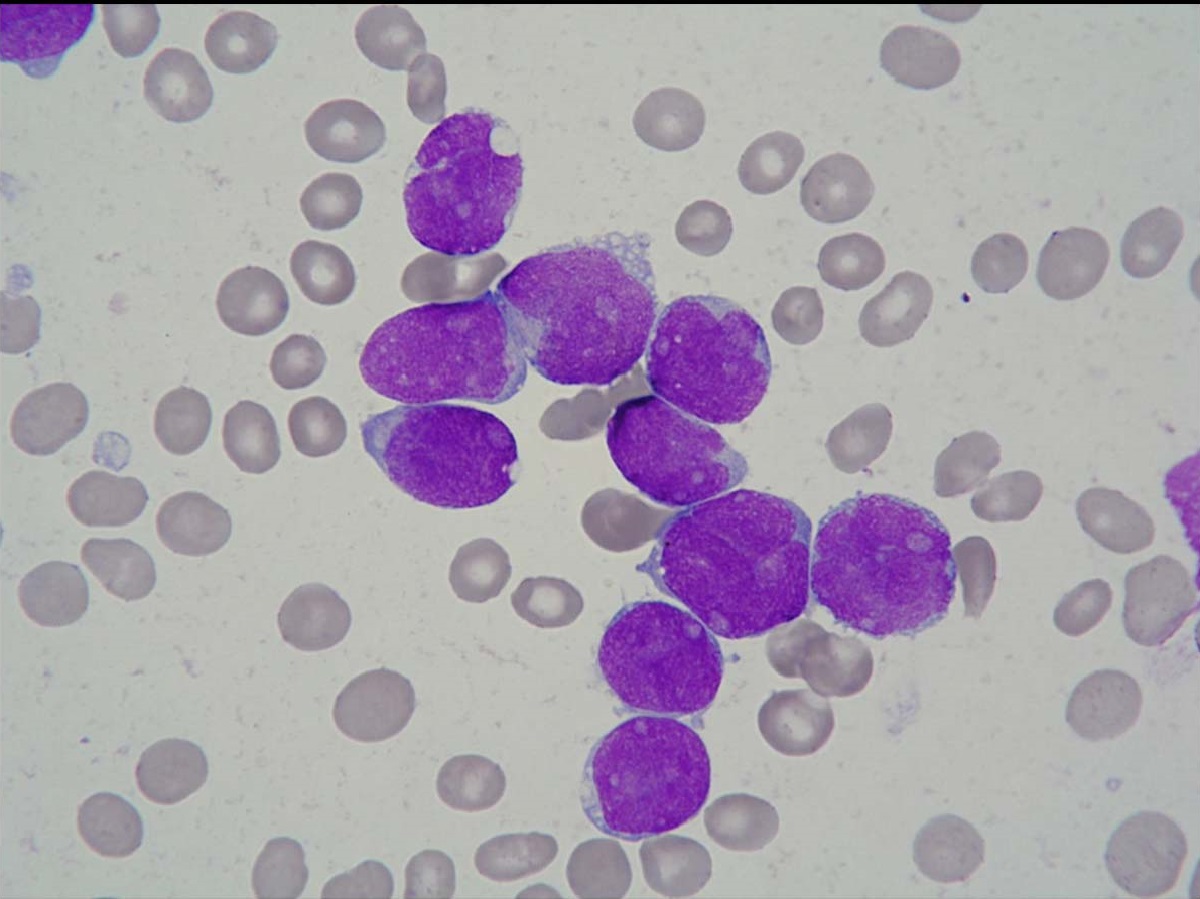
Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia is a type of cancer that starts in the bone marrow and affects white blood cells. Did you know that this disease is most common in children but can also occur in adults? Understanding the basics of this illness can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking timely treatment. From its causes to treatment options, there are many aspects to consider. In this post, we will share 30 essential facts about Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Whether you're a student, a parent, or just curious, these facts will provide valuable insights into this serious condition. Let's dive in and learn more about this critical health topic.
Key Takeaways:
- Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia is a fast-progressing cancer that mainly affects children, but can also occur in adults. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better prognosis and survival.
- Common symptoms of Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia include fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising, and bone/joint pain. Understanding the risk factors and seeking early diagnosis can improve survival rates.
What is Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia?
Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL) is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. It primarily impacts children but can also occur in adults. Understanding this disease is crucial for early detection and treatment.
-
B-ALL is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. It starts in immature white blood cells called lymphoblasts.
-
Most common in children. B-ALL is the most frequent type of leukemia in children, accounting for about 75% of childhood leukemia cases.
-
Affects B cells. This leukemia specifically targets B cells, which are a type of white blood cell responsible for producing antibodies.
-
Rapid progression. B-ALL progresses quickly, requiring immediate medical attention and treatment.
Symptoms of Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to a better prognosis. Here are some common signs to watch for.
-
Fatigue and weakness. Patients often feel extremely tired and weak due to a lack of healthy blood cells.
-
Frequent infections. The immune system is compromised, making it easier to get infections.
-
Easy bruising and bleeding. Low platelet counts can cause frequent bruising and bleeding, even from minor injuries.
-
Bone and joint pain. The buildup of leukemia cells in the bone marrow can cause significant pain.
Diagnosis of Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Early and accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment. Here are some methods used to diagnose B-ALL.
-
Blood tests. A complete blood count (CBC) can reveal abnormal levels of white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets.
-
Bone marrow biopsy. This procedure involves taking a sample of bone marrow to look for leukemia cells.
-
Imaging tests. X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs can help determine the extent of the disease.
-
Genetic tests. Identifying specific genetic mutations can help tailor treatment plans.
Treatment Options for Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Treatment varies depending on the patient's age, overall health, and the stage of the disease. Here are some common treatment options.
-
Chemotherapy. The primary treatment for B-ALL, chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
-
Radiation therapy. This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and kill leukemia cells.
-
Stem cell transplant. Replacing diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells can be an effective treatment.
-
Targeted therapy. Drugs that specifically target cancer cells without harming normal cells are increasingly used.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
The outlook for B-ALL patients has improved significantly over the years. Here are some key points about prognosis and survival.
-
High survival rates in children. With modern treatments, the five-year survival rate for children with B-ALL is about 90%.
-
Lower survival rates in adults. Adults have a lower five-year survival rate, around 40-50%, due to various factors.
-
Importance of early detection. Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve survival rates.
-
Ongoing research. Continuous research is leading to new treatments and better outcomes for patients.
Risk Factors for Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Understanding the risk factors can help in early detection and prevention. Here are some known risk factors.
-
Genetic predisposition. Certain genetic conditions, like Down syndrome, increase the risk of developing B-ALL.
-
Exposure to radiation. High levels of radiation exposure can increase the risk.
-
Previous cancer treatment. Chemotherapy or radiation therapy for other cancers can elevate the risk of developing B-ALL.
-
Family history. A family history of leukemia can be a risk factor.
Complications of Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Complications can arise from both the disease and its treatment. Here are some potential issues.
-
Infections. Due to a weakened immune system, patients are more susceptible to infections.
-
Bleeding problems. Low platelet counts can lead to severe bleeding issues.
-
Organ damage. Both the disease and its treatment can cause damage to organs like the liver and heart.
-
Secondary cancers. Some treatments can increase the risk of developing other types of cancer later in life.
Living with Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Living with B-ALL involves ongoing care and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some tips for managing life with this disease.
-
Regular follow-ups. Continuous monitoring and follow-up appointments are crucial for managing the disease.
-
Support systems. Emotional and psychological support from family, friends, and support groups can make a significant difference.
Final Thoughts on Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL) is a complex disease that affects many lives. Understanding its symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options can make a huge difference. Early detection often leads to better outcomes. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and bone marrow transplants are common treatments. Research continues to improve survival rates and quality of life for patients.
Support systems like family, friends, and healthcare teams play a crucial role in the journey. Staying informed and proactive can empower patients and their loved ones. Remember, knowledge is power. By spreading awareness, we can help others recognize the signs and seek timely medical advice.
Stay hopeful and keep fighting. Advances in medicine bring new hope every day. Let's continue to support research and each other in the battle against B-ALL.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
