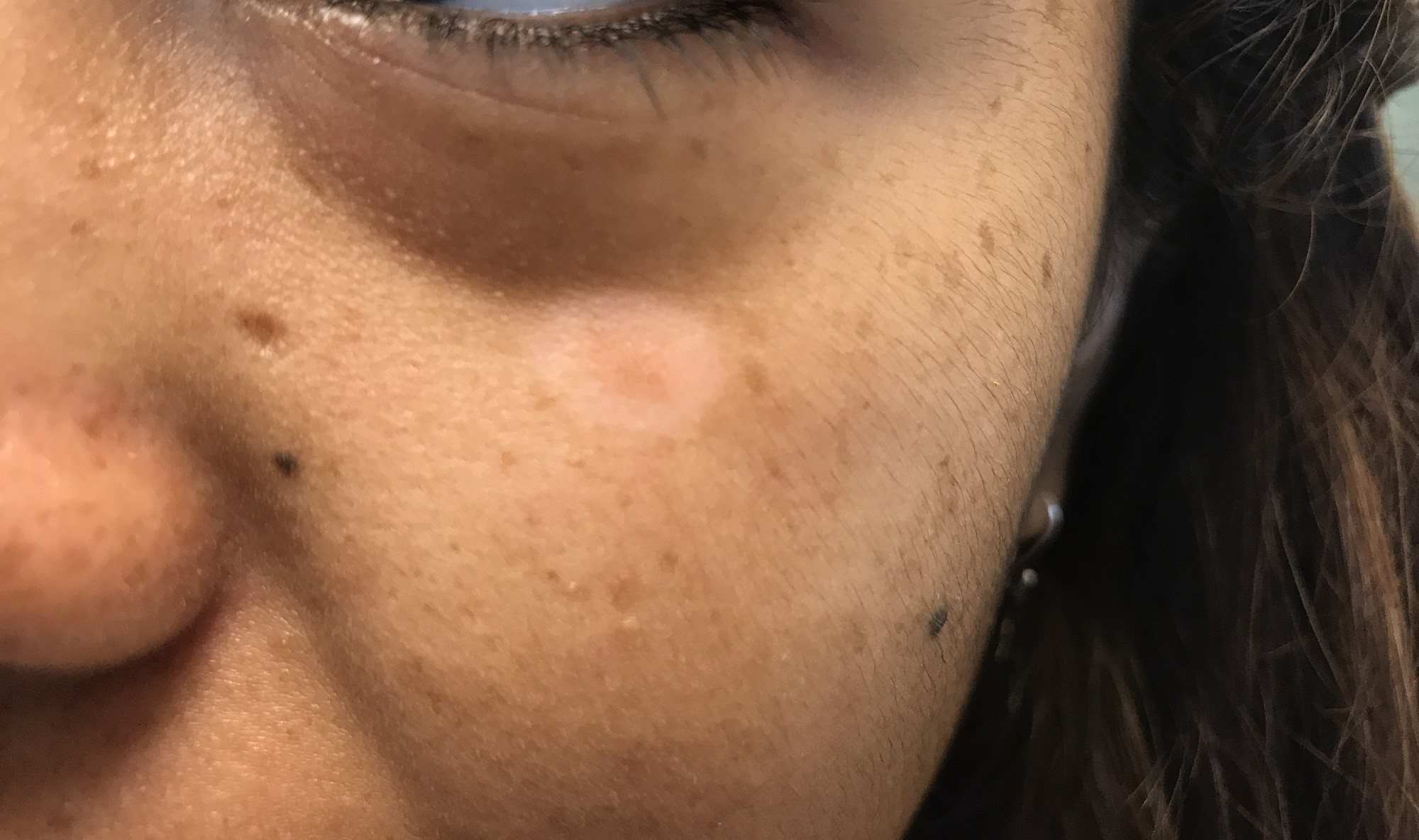
Hypopigmentation is a condition where patches of skin become lighter than the surrounding area. This happens when the skin produces less melanin, the pigment responsible for color. But what causes hypopigmentation? It can result from various factors like injuries, burns, infections, or certain medical conditions. Sometimes, it’s temporary and resolves on its own, while other times, it may require treatment. Understanding hypopigmentation helps in managing it better and knowing when to seek medical advice. This article will provide you with 22 facts about hypopigmentation, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and treatments. Get ready to learn more about this intriguing skin condition!
What is Hypopigmentation?
Hypopigmentation refers to patches of skin that are lighter than the surrounding area. This condition occurs when the skin produces less melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Let's dive into some interesting facts about hypopigmentation.
Causes of Hypopigmentation
Understanding what causes hypopigmentation can help in managing and treating it effectively.
- Genetic Factors: Some people inherit genes that make them more likely to develop hypopigmentation.
- Skin Injuries: Burns, blisters, or other injuries can damage the skin, leading to lighter patches.
- Inflammation: Conditions like eczema or psoriasis can cause inflammation, resulting in hypopigmentation.
- Infections: Fungal infections such as tinea versicolor can lead to lighter skin patches.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks melanocytes, causing hypopigmentation.
Types of Hypopigmentation
There are several types of hypopigmentation, each with unique characteristics.
- Vitiligo: This condition causes white patches on the skin due to the loss of melanocytes.
- Albinism: A genetic disorder where little or no melanin is produced, affecting skin, hair, and eyes.
- Pityriasis Alba: Common in children, this condition causes round or oval patches of lighter skin.
- Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation: Occurs after skin inflammation or injury, leaving lighter patches.
- Tinea Versicolor: A fungal infection that disrupts normal pigmentation, causing lighter or darker patches.
Symptoms of Hypopigmentation
Recognizing the symptoms can help in early diagnosis and treatment.
- White or Light Patches: The most noticeable symptom is patches of skin lighter than the surrounding area.
- Itching: Some types, like tinea versicolor, may cause itching.
- Dry Skin: Conditions like pityriasis alba often come with dry, scaly skin.
- Sensitivity to Sun: Hypopigmented areas may be more sensitive to sunlight.
Diagnosing Hypopigmentation
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
- Physical Examination: Doctors often start with a visual inspection of the affected areas.
- Wood's Lamp: This special light can help identify fungal infections and other causes of hypopigmentation.
- Skin Biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of skin is taken for laboratory analysis.
- Blood Tests: These can help identify underlying conditions like autoimmune diseases.
Treatment Options for Hypopigmentation
Various treatments can help manage hypopigmentation, depending on its cause.
- Topical Steroids: These can reduce inflammation and help restore normal pigmentation.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet light can stimulate melanin production in some cases.
- Antifungal Medications: Used to treat fungal infections like tinea versicolor.
- Cosmetic Solutions: Makeup or self-tanning products can temporarily cover lighter patches.
Final Thoughts on Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation, a condition marked by lighter skin patches, affects many people worldwide. Understanding its causes, from genetic factors to skin injuries, helps in managing it better. Treatments vary, including topical creams, laser therapy, and sometimes just patience as skin naturally heals. Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment plans.
Living with hypopigmentation can be challenging, but awareness and medical advancements offer hope. Support from loved ones and connecting with others facing similar issues can make a big difference. Remember, everyone’s skin is unique, and beauty comes in all shades.
Stay informed, seek professional advice, and embrace your skin’s journey. Hypopigmentation doesn’t define you; it’s just one part of your story. Keep learning and supporting each other in this shared experience.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


