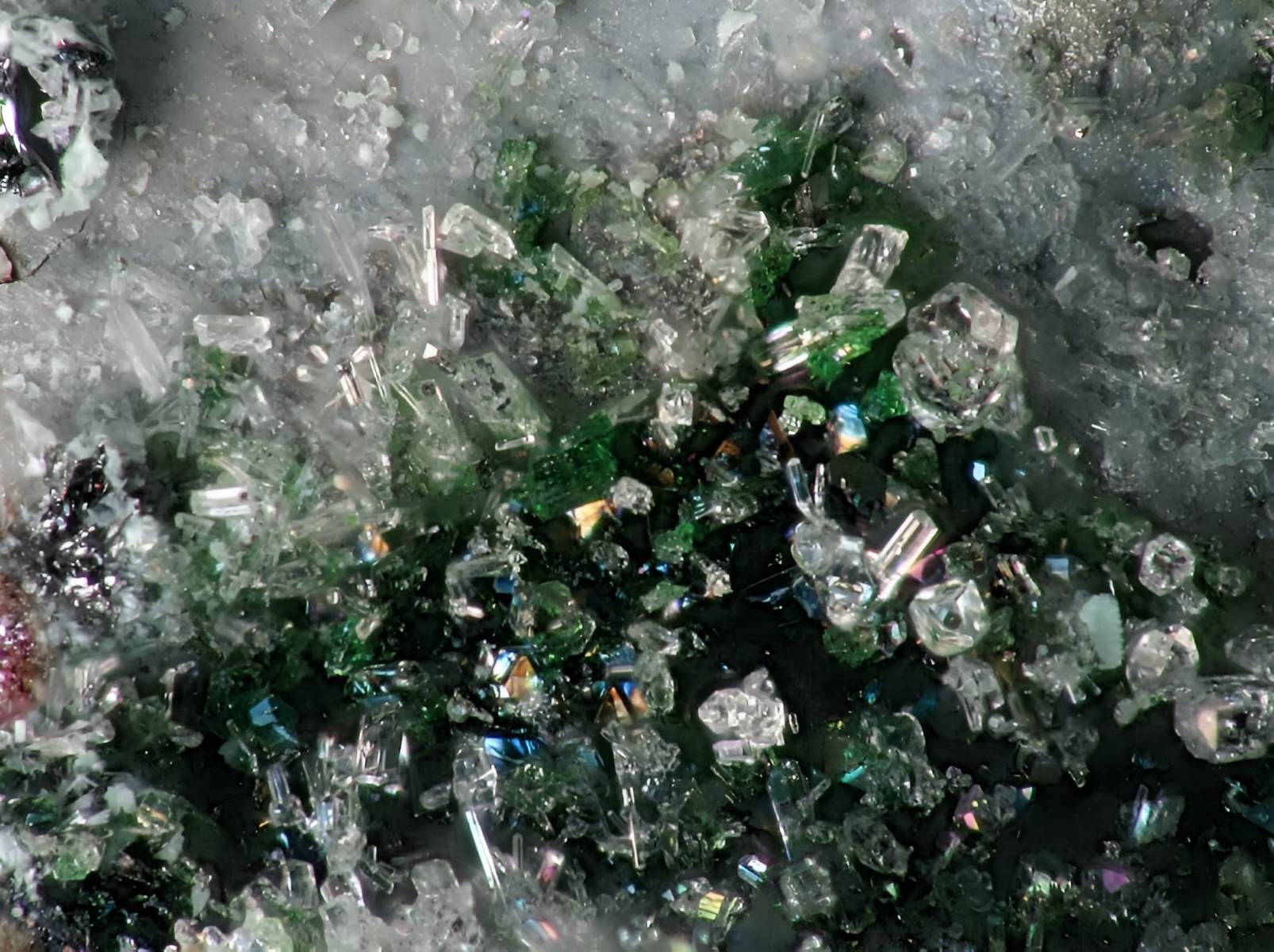
Bunsenite might sound like a quirky name, but this mineral holds some serious scientific weight. Named after the famous German chemist Robert Bunsen, it's a rare form of nickel oxide. Bunsenite is typically found in meteorites, making it a cosmic traveler of sorts. Its striking green color and unique crystal structure make it a fascinating subject for geologists and mineral enthusiasts alike. Ever wondered what makes Bunsenite so special? From its formation in outer space to its applications in modern technology, this mineral has a story worth telling. Ready to dive into 40 intriguing facts about Bunsenite? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Bunsenite is a rare, greenish-yellow mineral composed of nickel oxide, named after chemist Robert Bunsen. It has industrial uses in stainless steel, batteries, and catalysts, and can be found in specific locations worldwide.
- Mineral collectors prize Bunsenite for its rarity and unique properties. It's important to handle it with care, store it properly, and verify its authenticity. Joining mineral collecting clubs can help enthusiasts share information and connect with others.
What is Bunsenite?
Bunsenite is a rare mineral with a unique greenish-yellow hue. Named after the famous German chemist Robert Bunsen, it has some fascinating properties and uses. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this mineral.
-
Bunsenite is composed of nickel oxide (NiO), making it one of the few minerals with this composition.
-
It was first discovered in 1868 by Carl Christian Friedrich Glenck in the Harz Mountains of Germany.
-
The mineral is named in honor of Robert Bunsen, who is also known for inventing the Bunsen burner.
-
Bunsenite typically forms in hydrothermal veins, which are cracks in the Earth's crust filled with hot, mineral-rich water.
-
It is often found in association with other nickel minerals like millerite and pentlandite.
-
The mineral has a distinctive greenish-yellow color, which makes it easily recognizable.
Physical Properties of Bunsenite
Understanding the physical properties of Bunsenite can help in identifying and studying this mineral. Here are some key characteristics.
-
Bunsenite has a Mohs hardness of 5.5, which means it is relatively hard but can still be scratched by harder substances.
-
It has an isometric crystal system, meaning its crystals are shaped like cubes or other symmetrical forms.
-
The mineral has a specific gravity of 6.67, making it quite dense compared to many other minerals.
-
Bunsenite is opaque, meaning light does not pass through it.
-
It has a metallic luster, giving it a shiny, reflective surface.
-
The streak of Bunsenite, which is the color of its powdered form, is green.
Chemical Properties of Bunsenite
Bunsenite's chemical properties are just as fascinating as its physical ones. These properties make it unique among minerals.
-
The chemical formula for Bunsenite is NiO, indicating it is composed of nickel and oxygen.
-
It is a member of the oxide mineral group, which includes minerals composed of oxygen and one or more metals.
-
Bunsenite is stable at high temperatures, which is why it forms in hydrothermal veins.
-
The mineral can react with acids, dissolving to form nickel salts.
-
It is often used in the production of nickel alloys due to its high nickel content.
Uses of Bunsenite
Bunsenite has several practical applications, particularly in industrial settings. Here are some of its uses.
-
It is used in the production of stainless steel, where nickel is a key component.
-
Bunsenite is also used in the manufacture of batteries, particularly nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries.
-
The mineral is utilized in the production of catalysts, which speed up chemical reactions in industrial processes.
-
It is sometimes used in the ceramics industry to produce green pigments.
-
Bunsenite can also be used in the production of glass, where it acts as a colorant.
Where to Find Bunsenite
Bunsenite is a rare mineral, but it can be found in specific locations around the world. Here are some notable places.
-
The Harz Mountains in Germany, where it was first discovered, remain a key location for finding Bunsenite.
-
It has also been found in the Sudbury Basin in Ontario, Canada, which is known for its rich nickel deposits.
-
Bunsenite can be found in the Kambalda nickel mines in Western Australia.
-
The mineral has been discovered in the Norilsk-Talnakh region of Russia, another area rich in nickel.
-
It is sometimes found in meteorites, which can contain nickel-rich minerals.
Interesting Facts about Bunsenite
Beyond its scientific and industrial significance, Bunsenite has some interesting trivia associated with it.
-
Robert Bunsen, after whom the mineral is named, was a pioneer in the field of spectroscopy.
-
Bunsenite is one of the few minerals that contain only nickel and oxygen, making it unique.
-
The mineral's greenish-yellow color is due to the presence of nickel ions.
-
Bunsenite is often studied by mineralogists to understand the formation of nickel deposits.
-
It can sometimes be found in old mining dumps, where it was discarded as waste.
Collecting Bunsenite
For mineral collectors, Bunsenite is a prized specimen due to its rarity and unique properties. Here are some tips for collectors.
-
Always verify the authenticity of Bunsenite specimens, as they can be easily confused with other nickel minerals.
-
Handle Bunsenite with care, as its hardness means it can be scratched by harder minerals.
-
Store Bunsenite in a dry, stable environment to prevent any chemical reactions that could damage the mineral.
-
Use a magnifying glass or microscope to examine the crystal structure of Bunsenite specimens.
-
Join mineral collecting clubs or online forums to connect with other collectors and share information about Bunsenite.
Fun Facts about Bunsenite
Let's wrap up with some fun and lesser-known facts about Bunsenite that you might find intriguing.
-
Bunsenite's unique color makes it a popular choice for educational mineral kits.
-
The mineral's name is often a conversation starter among geology enthusiasts.
-
Bunsenite's association with Robert Bunsen adds a historical element to its appeal.
The Final Word on Bunsenite
Bunsenite, a rare mineral, holds a unique place in geology. Its striking green color and cubic crystals make it a standout. Discovered in 1868, this nickel oxide mineral has intrigued scientists and collectors alike. Found mainly in hydrothermal veins, it often appears alongside other nickel minerals. Despite its rarity, bunsenite's properties have practical applications, particularly in catalysis and electronics. Understanding bunsenite not only enriches our knowledge of mineralogy but also highlights the fascinating ways Earth's processes create such unique substances. Whether you're a geology enthusiast or just curious, bunsenite offers a glimpse into the intricate world of minerals. Keep exploring, and who knows what other hidden gems you'll uncover!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.