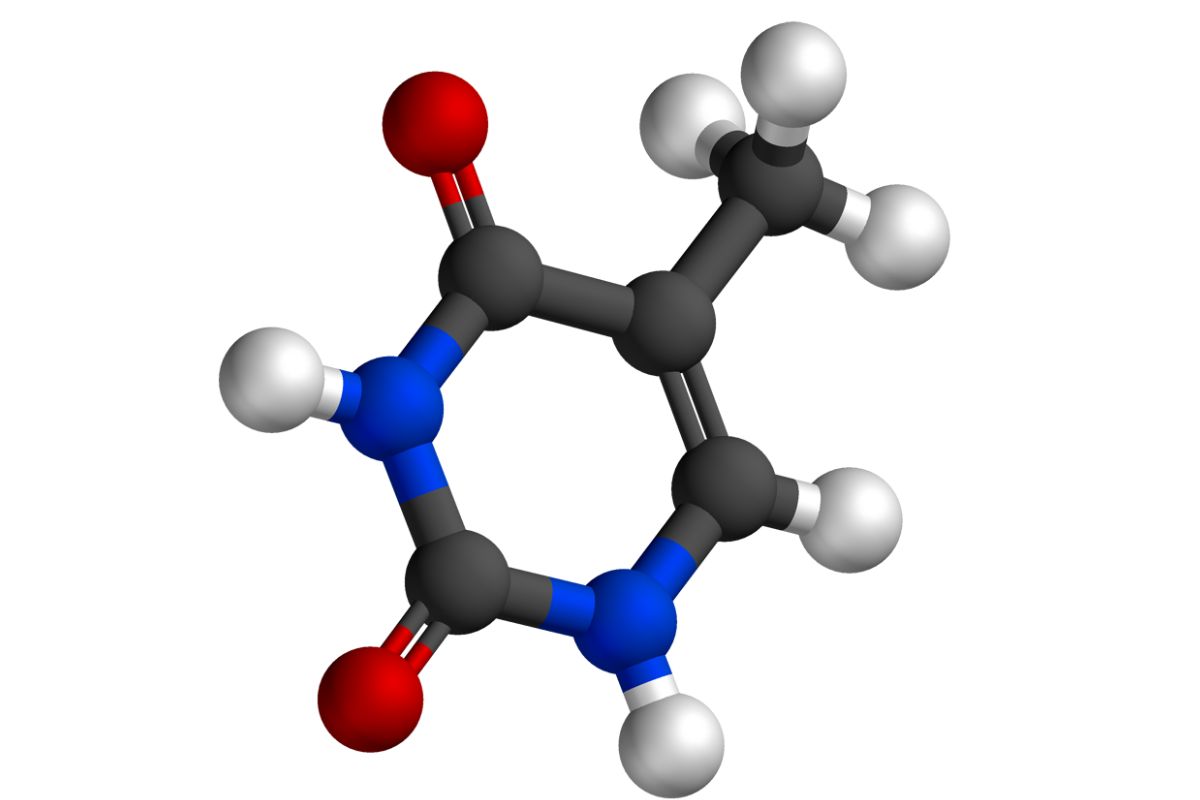
Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the DNA of cells, alongside adenine, cytosine, and guanine. This essential component plays a crucial role in the genetic code, pairing with adenine to help form the rungs of the DNA ladder. But what makes thymine so special? Thymine is unique to DNA, unlike uracil, which appears in RNA. Its structure includes a methyl group, distinguishing it from uracil and contributing to DNA's stability. Understanding thymine can provide insights into genetic mutations, DNA repair mechanisms, and even the development of certain diseases. Ready to dive into 50 fascinating facts about this vital molecule? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Thymine is a crucial part of DNA and helps protect it from damage. It plays a big role in genetic stability and can be used in cancer treatment and DNA sequencing.
- Thymine has unique chemical properties and is used in medicine and research. It's not just a boring compound; it's involved in fun things like DNA-based nanotechnology and ancient DNA studies!
What is Thymine?
Thymine is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA. It pairs with adenine through two hydrogen bonds, helping to stabilize the nucleic acid structures. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this essential component of our genetic code.
- Thymine is a pyrimidine base, which means it has a single-ring structure.
- It is represented by the letter 'T' in the DNA sequence.
- Thymine pairs exclusively with adenine (A) in DNA.
- It was first isolated from calf thymus glands, hence the name.
- Thymine is not found in RNA; instead, RNA contains uracil (U).
- The molecular formula of thymine is C5H6N2O2.
- Thymine has a melting point of 316-317°C.
- It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature.
- Thymine can be synthesized in the laboratory.
- It plays a crucial role in the replication of DNA.
Thymine's Role in DNA
Thymine is essential for the proper functioning of DNA. It ensures the stability and integrity of genetic information. Here are some more intriguing facts about thymine's role in DNA.
- Thymine helps to protect DNA from damage by ultraviolet (UV) light.
- It forms two hydrogen bonds with adenine, which helps to stabilize the DNA double helix.
- Thymine is involved in the process of DNA repair.
- Mutations in thymine can lead to genetic disorders.
- Thymine dimers, caused by UV light, can result in skin cancer.
- Thymine is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information.
- It is involved in the regulation of gene expression.
- Thymine is necessary for the proper functioning of DNA polymerase.
- It plays a role in the synthesis of new DNA strands.
- Thymine is crucial for the maintenance of genetic stability.
Chemical Properties of Thymine
Thymine has unique chemical properties that make it an essential component of DNA. These properties contribute to its stability and functionality. Let's explore some of these chemical properties.
- Thymine is a weak acid with a pKa of 9.9.
- It is soluble in water and ethanol.
- Thymine can form hydrogen bonds with other molecules.
- It is relatively stable under normal conditions.
- Thymine can undergo chemical modifications, such as methylation.
- It can be oxidized to form thymine glycol.
- Thymine can be deaminated to form uracil.
- It can participate in base-pairing interactions with other nucleobases.
- Thymine can be incorporated into synthetic DNA molecules.
- It is used in various biochemical assays and experiments.
Thymine in Medicine and Research
Thymine has significant applications in medicine and research. It is used in various diagnostic and therapeutic techniques. Here are some interesting facts about thymine's role in medicine and research.
- Thymine analogs are used in cancer treatment.
- It is used in the development of antiviral drugs.
- Thymine is involved in the study of genetic mutations.
- It is used in DNA sequencing techniques.
- Thymine is essential for the development of gene therapy.
- It is used in the study of DNA repair mechanisms.
- Thymine is involved in the development of diagnostic tests for genetic disorders.
- It is used in the study of DNA-protein interactions.
- Thymine is essential for the development of personalized medicine.
- It is used in the study of epigenetic modifications.
Fun Facts about Thymine
Thymine is not just a boring chemical compound; it has some fun and quirky aspects too. Let's take a look at some fun facts about thymine.
- Thymine was first discovered in 1893 by Albrecht Kossel.
- It is named after the thymus gland, where it was first isolated.
- Thymine is sometimes called 5-methyluracil.
- It is one of the few nucleobases that can be synthesized in the lab.
- Thymine is used in forensic science to analyze DNA samples.
- It is involved in the study of ancient DNA.
- Thymine is used in the development of DNA-based nanotechnology.
- It is essential for the study of evolutionary biology.
- Thymine is used in the development of DNA-based computing.
- It is involved in the study of DNA damage and repair mechanisms.
The Final Word on Thymine
Thymine, one of the four nucleobases in DNA, plays a crucial role in genetic coding. It pairs with adenine, ensuring the stability of the DNA structure. Without thymine, DNA replication and repair would be impossible, leading to genetic mutations. This small molecule has a big impact on life as we know it. Understanding thymine helps us grasp the complexities of genetics and molecular biology. From its discovery to its role in modern science, thymine remains a key player in the study of life. Whether you're a student, a scientist, or just curious, knowing about thymine enriches your appreciation of the intricate dance of molecules that make up our genetic code. So next time you think about DNA, remember the vital role thymine plays in keeping our genetic information intact and functional.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
