Lipoproteins are essential molecules in our bodies, playing a crucial role in transporting fats through the bloodstream. These complex particles consist of fats and proteins, ensuring that cholesterol and triglycerides reach the cells that need them. Without lipoproteins, our bodies would struggle to manage fat levels, leading to various health issues. Understanding lipoproteins can help us make better lifestyle choices and improve heart health. This article will explore 50 fascinating facts about lipoproteins, shedding light on their types, functions, and impact on our well-being. Get ready to dive into the world of lipoproteins and discover how they keep our bodies running smoothly!
Key Takeaways:
- Lipoproteins are like tiny fat taxis in our body, carrying cholesterol and triglycerides. Good ones (HDL) help our heart, while bad ones (LDL) can cause trouble.
- Eating healthy, exercising, and avoiding smoking can help keep our fat taxis in balance. As we grow older, it's important to monitor our levels to stay heart-healthy.
What is Lipoprotein?
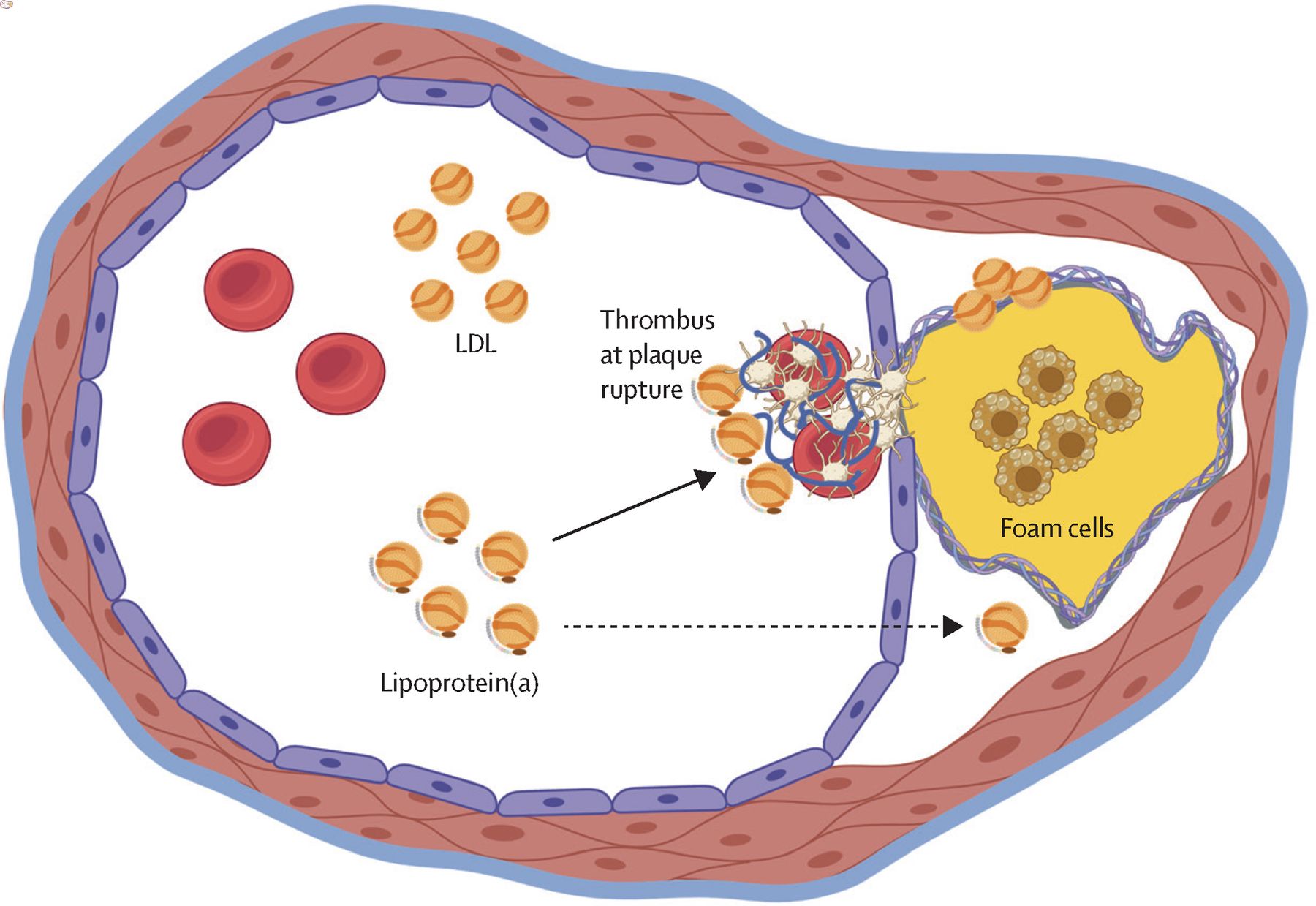
Lipoproteins are complex particles made of fat and protein. They transport fats like cholesterol and triglycerides through the bloodstream. Understanding lipoproteins is crucial for grasping how the body manages fat and maintains heart health.
- Lipoproteins consist of a core of lipids surrounded by a shell of proteins.
- They help transport cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood.
- Lipoproteins are categorized by their density: high-density (HDL), low-density (LDL), very low-density (VLDL), and intermediate-density (IDL).
Types of Lipoproteins
Different types of lipoproteins have unique roles in the body. Knowing these types helps in understanding their impact on health.
- HDL is often called "good cholesterol" because it helps remove cholesterol from arteries.
- LDL is known as "bad cholesterol" because high levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries.
- VLDL primarily carries triglycerides, another type of fat, to tissues.
- IDL is a transitional form between VLDL and LDL.
Functions of Lipoproteins
Lipoproteins play various roles in the body, from transporting fats to influencing heart health.
- HDL helps transport cholesterol to the liver for excretion.
- LDL delivers cholesterol to cells, which can lead to plaque formation if levels are too high.
- VLDL delivers triglycerides to tissues for energy or storage.
- IDL is converted into LDL in the bloodstream.
Lipoproteins and Heart Health
The balance of different lipoproteins is crucial for maintaining heart health. Imbalances can lead to cardiovascular diseases.
- High levels of LDL can increase the risk of heart disease.
- High HDL levels are associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
- VLDL levels can also contribute to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Managing lipoprotein levels is essential for preventing heart attacks and strokes.
Measuring Lipoprotein Levels
Regularly measuring lipoprotein levels helps monitor and manage heart health.
- A lipid panel test measures HDL, LDL, VLDL, and total cholesterol levels.
- Fasting before a lipid panel test ensures accurate results.
- Doctors use lipid panel results to assess cardiovascular risk.
- High LDL and low HDL levels indicate a higher risk of heart disease.
Factors Affecting Lipoprotein Levels
Various factors influence lipoprotein levels, including diet, lifestyle, and genetics.
- Diets high in saturated fats can increase LDL levels.
- Regular exercise can raise HDL levels.
- Smoking lowers HDL levels and raises LDL levels.
- Genetics play a role in determining baseline lipoprotein levels.
Managing Lipoprotein Levels
Adopting healthy habits can help manage lipoprotein levels and reduce cardiovascular risk.
- Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve lipoprotein levels.
- Regular physical activity helps maintain healthy HDL and LDL levels.
- Medications like statins can lower LDL levels.
- Quitting smoking can improve HDL levels.
Lipoproteins and Diet
Diet has a significant impact on lipoprotein levels. Making informed food choices can help maintain a healthy balance.
- Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish, can raise HDL levels.
- Trans fats, found in processed foods, can increase LDL levels.
- Soluble fiber, found in oats and beans, can lower LDL levels.
- Reducing sugar intake can help manage VLDL levels.
Lipoproteins and Exercise
Exercise is a powerful tool for managing lipoprotein levels and promoting heart health.
- Aerobic exercise, like running, can raise HDL levels.
- Strength training can also improve lipoprotein profiles.
- Consistent exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, which influences lipoprotein levels.
- Even moderate physical activity, like walking, can positively impact lipoprotein levels.
Lipoproteins and Medication
Medications can be necessary for managing lipoprotein levels, especially when lifestyle changes aren't enough.
- Statins are commonly prescribed to lower LDL levels.
- Niacin can raise HDL levels and lower LDL levels.
- Fibrates help reduce VLDL levels and raise HDL levels.
- PCSK9 inhibitors are a newer class of drugs that lower LDL levels.
Lipoproteins and Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in determining lipoprotein levels and cardiovascular risk.
- Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic disorder that causes high LDL levels.
- Some people have genetic variations that result in higher HDL levels.
- Genetic testing can help identify individuals at risk for high cholesterol.
- Understanding genetic predispositions can guide personalized treatment plans.
Lipoproteins and Age
Age affects lipoprotein levels and cardiovascular risk, making regular monitoring important.
- LDL levels tend to increase with age.
- HDL levels may decrease as people get older.
- Postmenopausal women often experience higher LDL levels.
- Regular lipid panel tests become more important with age.
Lipoproteins and Gender
Gender differences can influence lipoprotein levels and cardiovascular risk.
- Men typically have higher LDL levels than women before age 50.
- Women generally have higher HDL levels than men.
- After menopause, women's LDL levels often increase, raising cardiovascular risk.
Final Thoughts on Lipoproteins
Lipoproteins play a crucial role in our bodies by transporting fats through the bloodstream. They come in different types like LDL, HDL, and VLDL, each with its own function. LDL is often called "bad cholesterol" because high levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, while HDL is known as "good cholesterol" for helping remove LDL from the bloodstream. VLDL primarily carries triglycerides. Maintaining a balance between these lipoproteins is essential for heart health. Diet, exercise, and sometimes medication can help manage their levels. Understanding these facts about lipoproteins can empower you to make better health choices. So, next time you hear about cholesterol, you'll know there's more to the story. Keep these insights in mind for a healthier lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
