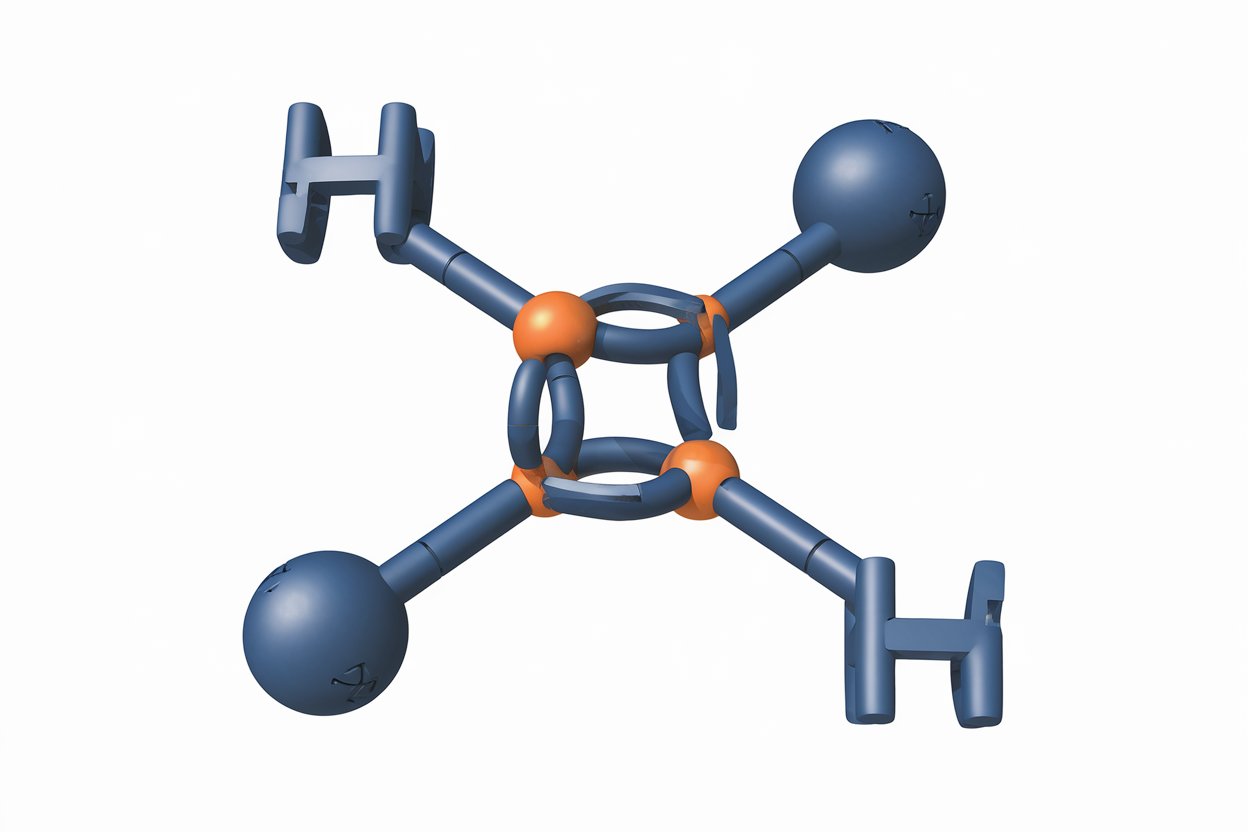
Borazine, often called "inorganic benzene," is a fascinating compound with a unique structure and properties. This molecule, composed of boron, nitrogen, and hydrogen, mimics the aromatic characteristics of benzene but with a twist. Why is borazine important? Its stability and reactivity make it a subject of interest in various fields, from materials science to chemistry. Understanding borazine can help in developing new materials, improving chemical processes, and even advancing nanotechnology. In this post, we'll explore 40 intriguing facts about borazine, shedding light on its composition, uses, and the science behind its remarkable properties. Get ready to dive into the world of this extraordinary compound!
Key Takeaways:
- Borazine, also known as "inorganic benzene," is a unique compound with a hexagonal ring structure. It has diverse uses, from high-temperature lubricants to potential energy storage materials.
- Despite its flammability and toxicity, borazine's aromatic properties and potential in advanced materials make it an intriguing subject for scientific research and future technological advancements.
What is Borazine?
Borazine, often called "inorganic benzene," is a fascinating compound with unique properties. It consists of boron, nitrogen, and hydrogen atoms arranged in a ring structure similar to benzene. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this compound.
-
Borazine's chemical formula is B3N3H6. This means it contains three boron atoms, three nitrogen atoms, and six hydrogen atoms.
-
It was first synthesized in 1926. German chemist Alfred Stock discovered borazine while studying boron-nitrogen compounds.
-
Borazine is colorless. In its pure form, it appears as a colorless liquid.
-
It has a boiling point of 53°C (127°F). This relatively low boiling point makes it volatile.
-
Borazine smells like ammonia. Its odor is quite pungent and similar to that of ammonia.
Borazine's Structure and Properties
Borazine's structure closely resembles benzene, but with some key differences. Here are some facts about its structure and properties.
-
The boron and nitrogen atoms alternate in the ring. This alternating pattern gives borazine its unique properties.
-
It has a planar structure. Like benzene, borazine is flat, with all atoms lying in the same plane.
-
Borazine is aromatic. This means it has a stable ring structure with delocalized electrons.
-
It is less stable than benzene. Despite its aromaticity, borazine is more reactive than benzene.
-
Borazine can polymerize. Under certain conditions, borazine molecules can link together to form polymers.
Uses of Borazine
Borazine's unique properties make it useful in various applications. Here are some ways it is used.
-
It is a precursor to boron nitride. Borazine can be used to produce boron nitride, a material with excellent thermal and electrical properties.
-
Used in high-temperature lubricants. Borazine-derived compounds can withstand high temperatures, making them ideal for lubricants.
-
It is used in ceramics. Borazine can be a starting material for producing advanced ceramics.
-
Borazine is used in coatings. Its derivatives can be used to create protective coatings for various surfaces.
-
It has potential in hydrogen storage. Borazine's ability to release hydrogen makes it a candidate for hydrogen storage materials.
Borazine in Research
Borazine continues to be a subject of scientific research. Here are some interesting research-related facts.
-
Studied for its electronic properties. Researchers are exploring borazine's potential in electronic applications.
-
Used in chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Borazine can be used in CVD processes to create thin films.
-
Investigated for its catalytic properties. Scientists are studying borazine's potential as a catalyst in chemical reactions.
-
Research on borazine-based polymers. Borazine's ability to polymerize has led to research on new polymer materials.
-
Explored for its optical properties. Borazine's unique structure gives it interesting optical properties.
Borazine and Safety
Handling borazine requires caution due to its reactivity and potential hazards. Here are some safety-related facts.
-
Borazine is flammable. It can catch fire easily, so it must be handled with care.
-
It is toxic if inhaled. Breathing in borazine vapors can be harmful.
-
Borazine can cause skin irritation. Direct contact with the skin should be avoided.
-
It should be stored in a cool, dry place. Proper storage conditions are essential to prevent accidents.
-
Use protective equipment when handling. Gloves, goggles, and lab coats are recommended when working with borazine.
Fun Facts About Borazine
Let's look at some fun and lesser-known facts about borazine.
-
Borazine is sometimes called "borazole." This alternative name is less common but still used.
-
It has a hexagonal ring structure. This hexagonal shape is similar to that of benzene.
-
Borazine can form adducts. It can react with other molecules to form stable adducts.
-
It is used in academic research. Borazine is a popular subject in chemistry research labs.
-
Borazine's discovery was accidental. Alfred Stock discovered it while investigating other boron compounds.
Borazine in Popular Culture
While not as famous as benzene, borazine has made its way into popular culture in some interesting ways.
-
Featured in scientific literature. Borazine is often mentioned in chemistry textbooks and research papers.
-
Used in educational demonstrations. Its unique properties make it a great example in chemistry classes.
-
Appears in science fiction. Some sci-fi stories feature borazine due to its futuristic-sounding name.
-
Inspired by benzene. Borazine's structure and properties are often compared to benzene in popular science discussions.
-
Mentioned in chemistry blogs. Many chemistry enthusiasts write about borazine and its fascinating properties.
Borazine's Future Potential
Borazine holds promise for future technological advancements. Here are some potential future applications.
-
Advanced materials. Borazine could be used to create new materials with unique properties.
-
Energy storage. Its hydrogen storage potential could play a role in future energy solutions.
-
Nanotechnology. Borazine-based compounds could be used in nanotechnology applications.
-
Environmental applications. Borazine's properties could be harnessed for environmental protection.
-
Medical research. Scientists are exploring borazine's potential in medical applications.
Borazine: A Unique Compound
Borazine, often called "inorganic benzene," stands out due to its fascinating properties and structure. This compound, with its alternating boron and nitrogen atoms, mimics benzene in many ways but also has distinct differences. Its ability to form stable bonds and its unique electronic configuration make it a subject of interest in both academic research and practical applications.
From its discovery to its potential uses in materials science and chemistry, borazine continues to intrigue scientists. Its role in creating new materials, such as boron nitride nanotubes, showcases its versatility. Understanding borazine not only broadens our knowledge of chemistry but also opens doors to innovative technologies.
In essence, borazine is more than just a chemical curiosity. It's a gateway to new possibilities in science and technology, proving that even the most niche compounds can have a significant impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
