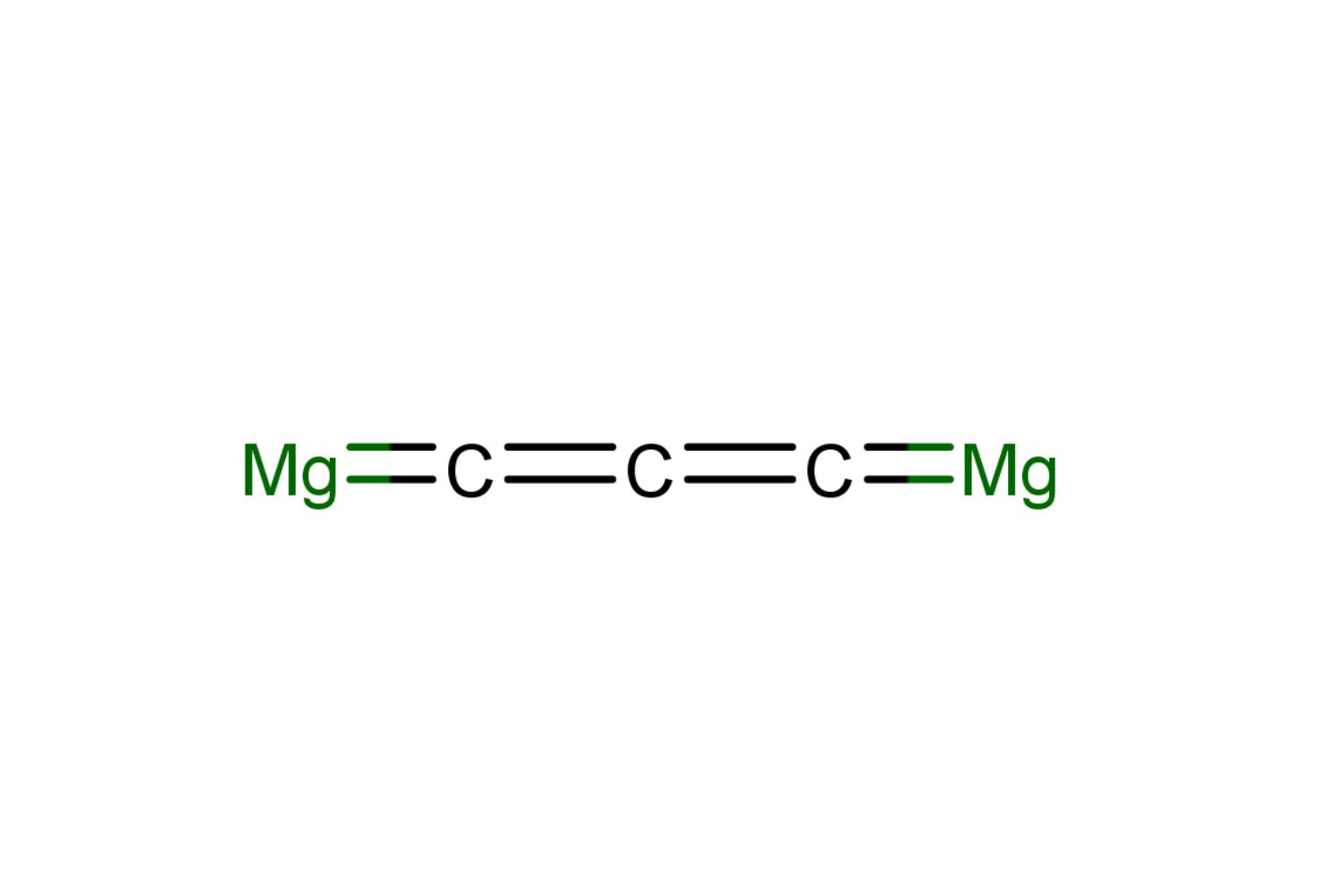
Magnesium carbide might not be a household name, but it plays a significant role in various industries. What exactly is magnesium carbide? Magnesium carbide is a chemical compound made up of magnesium and carbon. It’s known for its unique properties and applications, from acting as a reducing agent in chemical reactions to being used in the production of acetylene gas. This compound can be found in laboratories and industrial settings, where it helps in creating other useful chemicals. Understanding magnesium carbide can open up a world of fascinating facts about its uses, properties, and importance in science and industry. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 30 intriguing facts about this versatile compound!
Key Takeaways:
- Magnesium carbide, with its high melting point and ability to produce methane, is used in fuel production, metal industry, and research. However, it requires careful handling due to its reactivity with water.
- The environmental impact of magnesium carbide, including methane emissions and waste management, is a significant consideration. Researchers are exploring sustainable practices to minimize its environmental harm.
What is Magnesium Carbide?
Magnesium carbide is a chemical compound with unique properties and uses. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this compound.
- Chemical Formula: Magnesium carbide's chemical formula is Mg2C3.
- Appearance: It typically appears as a white or gray crystalline solid.
- Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of magnesium carbide is 84.53 g/mol.
- Melting Point: This compound has a high melting point of around 2,000°C (3,632°F).
- Density: Magnesium carbide has a density of approximately 2.36 g/cm³.
- Solubility: It is insoluble in water but reacts with it to produce methane.
How is Magnesium Carbide Produced?
Understanding the production process of magnesium carbide can shed light on its applications and properties.
- Raw Materials: Magnesium carbide is produced using magnesium and carbon.
- High Temperature: The production process requires extremely high temperatures, often above 1,500°C (2,732°F).
- Reaction: Magnesium reacts with carbon to form magnesium carbide and carbon monoxide.
- Industrial Methods: Industrial production often involves electric arc furnaces to achieve the necessary temperatures.
Uses of Magnesium Carbide
Magnesium carbide has several practical applications, making it a valuable compound in various industries.
- Chemical Reactions: It is used in chemical reactions to produce methane gas.
- Fuel Production: Methane produced from magnesium carbide can be used as a fuel source.
- Metal Industry: It plays a role in the metal industry for processes like desulfurization.
- Research: Scientists use it in research to study high-temperature reactions.
- Catalyst: Magnesium carbide can act as a catalyst in certain chemical processes.
Safety and Handling
Handling magnesium carbide requires caution due to its reactive nature.
- Reactivity: It reacts vigorously with water, producing flammable methane gas.
- Storage: Magnesium carbide should be stored in a dry, airtight container to prevent unwanted reactions.
- Protective Gear: When handling this compound, wearing protective gear like gloves and goggles is essential.
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation when working with magnesium carbide to avoid inhaling any gases produced.
- Fire Hazard: Due to methane production, it poses a fire hazard if not handled correctly.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of magnesium carbide is an important consideration.
- Methane Emissions: Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, so its production from magnesium carbide can contribute to climate change.
- Waste Management: Proper disposal of magnesium carbide waste is crucial to prevent environmental contamination.
- Regulations: Many countries have regulations in place to control the use and disposal of magnesium carbide to minimize environmental harm.
- Sustainable Practices: Researchers are exploring sustainable practices to reduce the environmental impact of magnesium carbide production and use.
Interesting Facts
Here are some intriguing tidbits about magnesium carbide that you might not know.
- Historical Use: Magnesium carbide was first synthesized in the early 20th century.
- Research Applications: It is used in high-temperature research to study the behavior of materials under extreme conditions.
- Unique Properties: Magnesium carbide's ability to produce methane makes it unique among carbides.
- Comparative Rarity: Unlike calcium carbide, magnesium carbide is less commonly used in industrial applications.
- Potential Uses: Ongoing research is exploring new potential uses for magnesium carbide in various fields.
- Educational Value: It serves as an excellent teaching tool in chemistry classes to demonstrate high-temperature reactions and carbide chemistry.
Final Thoughts on Magnesium Carbide
Magnesium carbide, a fascinating compound, holds a unique place in the world of chemistry. Its ability to react with water to produce acetylene gas makes it valuable in various industrial applications. This compound's role in metallurgy, particularly in steelmaking, showcases its importance in modern manufacturing. Despite its reactive nature, magnesium carbide is handled with care to harness its benefits safely. Understanding its properties and uses can help us appreciate the intricate balance of elements that drive technological advancements. Whether you're a student, a professional, or just curious, knowing these facts about magnesium carbide adds a spark to your knowledge base. Keep exploring the wonders of chemistry, and you'll find that even the smallest compounds can have a big impact on our world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
