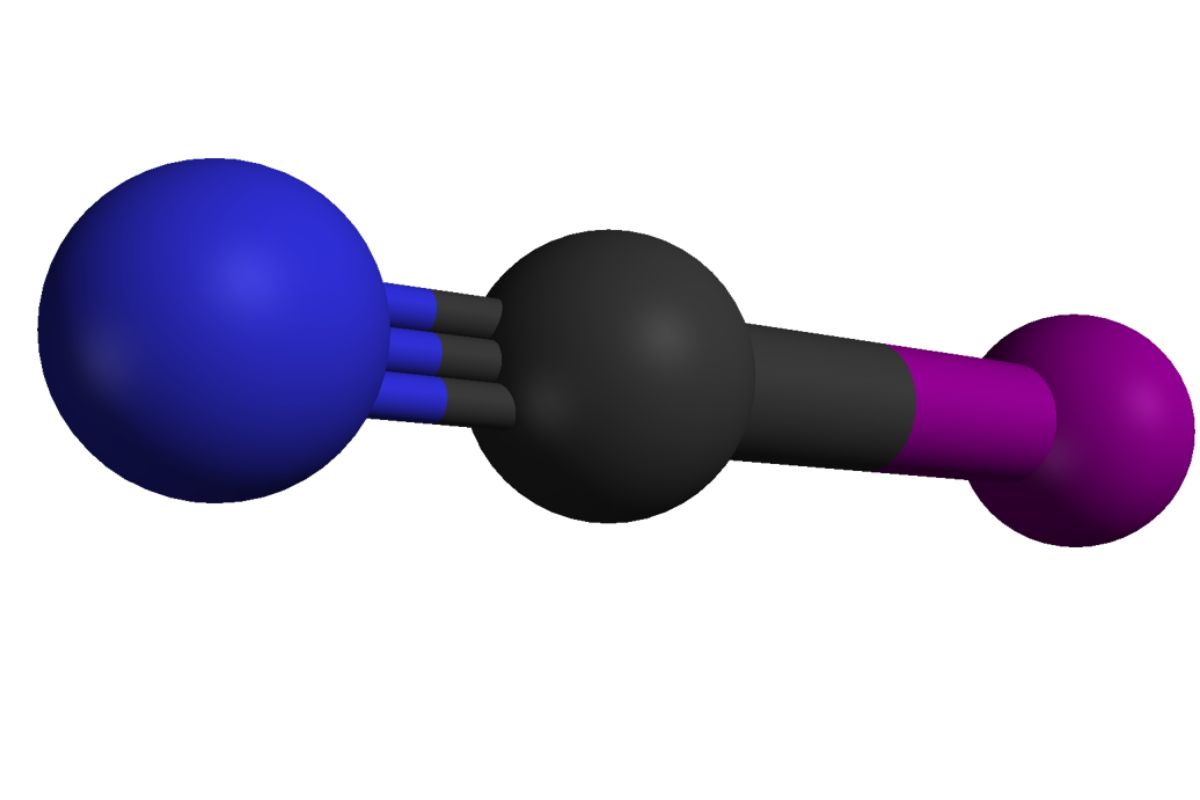
Cyanogen iodide might sound like something out of a chemistry textbook, but it's more intriguing than you think. This compound, with the formula ICN, is a crystalline solid that packs a punch in various fields. From its role in organic synthesis to its use as a fumigant, cyanogen iodide has a diverse range of applications. Did you know it can also be a reagent in the detection of certain metals? Or that it has a fascinating history in the world of photography? Whether you're a science enthusiast or just curious, these 30 facts about cyanogen iodide will shed light on its many uses and properties. Buckle up for a journey through the world of ICN!
Key Takeaways:
- Cyanogen iodide, with the chemical formula ICN, is a pungent, white crystalline solid that is soluble in water, alcohol, and ether. It has a melting point of around 146°C and is highly reactive with metals.
- Proper safety measures are crucial when handling cyanogen iodide due to its toxic nature. It can contaminate water sources, contribute to air pollution, and affect plant and animal life if not handled and disposed of properly.
What is Cyanogen Iodide?
Cyanogen iodide is a fascinating chemical compound with a variety of uses and properties. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this substance.
- Chemical Formula: Cyanogen iodide has the chemical formula ICN.
- Appearance: It appears as a white crystalline solid.
- Odor: This compound has a pungent odor, similar to that of cyanide.
- Solubility: It is soluble in water, alcohol, and ether.
- Melting Point: The melting point of cyanogen iodide is around 146°C (295°F).
Historical Background
Understanding the history of cyanogen iodide can provide insight into its development and applications.
- Discovery: Cyanogen iodide was first synthesized in the early 19th century.
- Early Uses: Initially, it was used in chemical research and experiments.
- Military Use: During World War I, it was considered for use as a chemical weapon.
- Research: It has been extensively studied for its chemical properties and reactions.
- Industrial Use: Over time, its applications expanded into various industrial processes.
Chemical Properties
The chemical properties of cyanogen iodide make it unique and useful in different fields.
- Reactivity: Cyanogen iodide is highly reactive, especially with metals.
- Decomposition: It decomposes when exposed to light, releasing iodine and cyanogen gas.
- Toxicity: This compound is highly toxic and can be lethal if inhaled or ingested.
- Stability: It is relatively stable under normal conditions but can become unstable when heated.
- Oxidizing Agent: Cyanogen iodide acts as a strong oxidizing agent.
Applications in Science
Cyanogen iodide has several scientific applications due to its unique properties.
- Biochemistry: It is used in biochemistry for protein sequencing and analysis.
- Microbiology: In microbiology, it serves as a disinfectant and antiseptic.
- Chemical Synthesis: It is employed in the synthesis of various organic compounds.
- Analytical Chemistry: Cyanogen iodide is used in analytical chemistry for detecting certain elements.
- Spectroscopy: It plays a role in spectroscopic studies due to its distinct absorption characteristics.
Safety and Handling
Due to its toxic nature, proper safety measures are crucial when handling cyanogen iodide.
- Protective Gear: Always wear protective clothing, gloves, and eye protection.
- Ventilation: Ensure good ventilation when working with this compound to avoid inhalation.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry place away from light and incompatible substances.
- Disposal: Dispose of cyanogen iodide according to local environmental regulations.
- First Aid: In case of exposure, seek immediate medical attention.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of cyanogen iodide is an important consideration.
- Water Contamination: It can contaminate water sources if not handled properly.
- Air Pollution: Decomposition releases harmful gases that can contribute to air pollution.
- Soil Contamination: Spills can lead to soil contamination, affecting plant and animal life.
- Biodegradability: Cyanogen iodide is not readily biodegradable, posing long-term environmental risks.
- Regulations: Many countries have strict regulations on the use and disposal of cyanogen iodide to minimize its environmental impact.
Final Thoughts on Cyanogen Iodide
Cyanogen iodide, a fascinating compound, offers a mix of unique properties and practical applications. From its use in chemical synthesis to its role in disinfection, this substance has proven its worth in various fields. Its toxic nature demands careful handling, but with proper precautions, it serves as a valuable tool in scientific research and industrial processes.
Understanding the facts about cyanogen iodide helps appreciate its significance and potential. Whether you're a chemistry enthusiast or just curious, knowing these details can broaden your perspective on how such compounds impact our world. Keep exploring and learning about the wonders of chemistry; there's always something new to discover.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
