Actinium(III) Fluoride might sound like something out of a sci-fi movie, but it's a real chemical compound with some pretty cool facts. This compound, represented by the formula AcF3, combines the rare element actinium with fluorine. Actinium itself is a radioactive element, discovered in 1899, and is part of the actinide series on the periodic table. When combined with fluorine, it forms a white crystalline solid that's fascinating to chemists and scientists alike. Actinium(III) Fluoride is primarily used in research, especially in the study of radioactive materials. Curious about what makes this compound so special? Here are 30 intriguing facts that will shed light on its unique properties and uses.
Key Takeaways:
- Actinium(III) Fluoride is a highly radioactive compound used in neutron sources and cancer treatment. It must be handled with extreme care and disposed of following strict guidelines to minimize environmental impact.
- Actinium(III) Fluoride, with its unique properties and radioactive nature, is crucial for scientific research and specialized applications. Safety measures and strict regulations are essential for its handling and disposal.
What is Actinium(III) Fluoride?
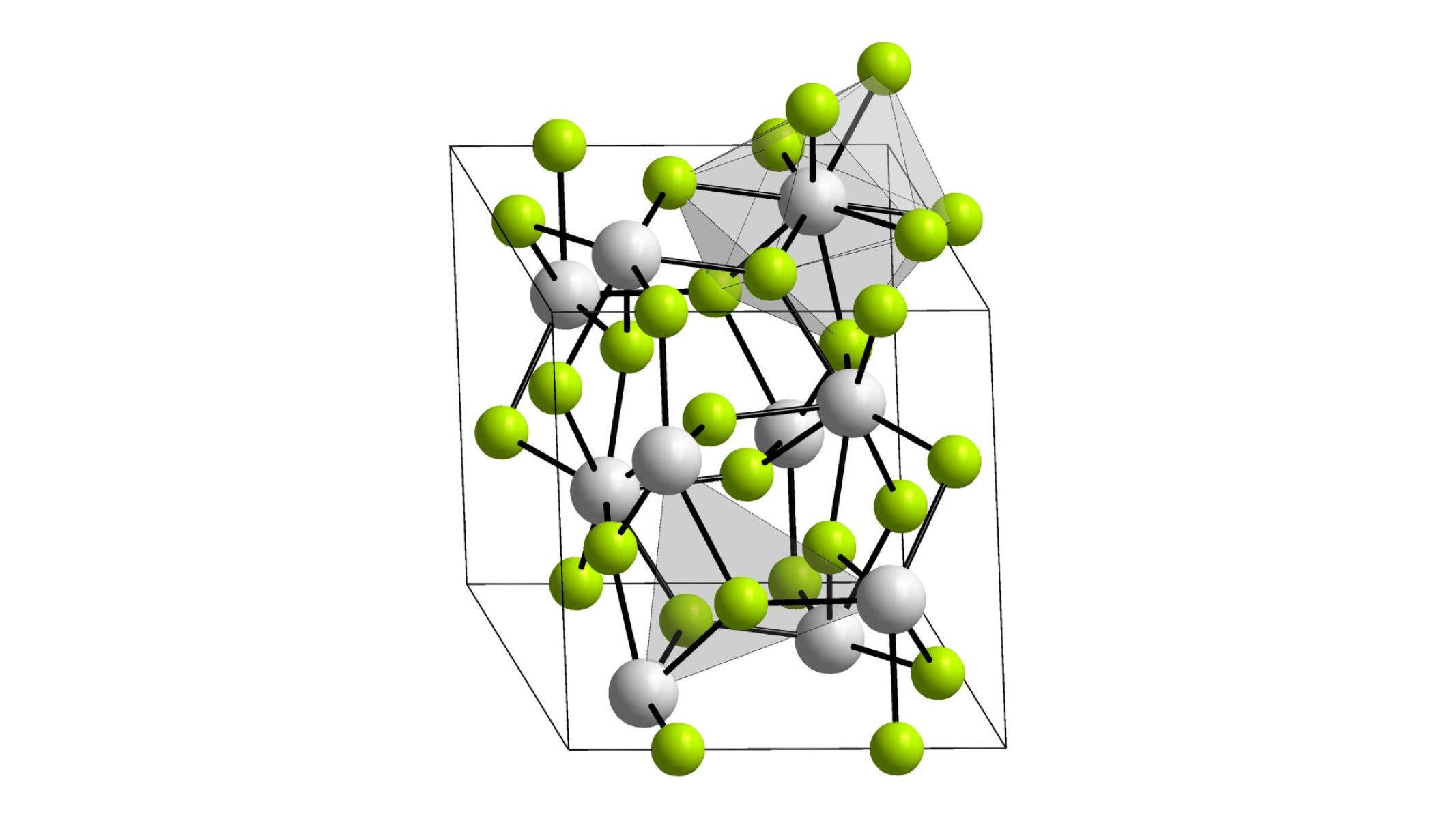
Actinium(III) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula AcF₃. It consists of actinium and fluorine atoms. This compound is part of the larger family of actinide fluorides.
- Actinium(III) fluoride is a white, crystalline solid.
- It has a molecular weight of approximately 308.08 g/mol.
- The compound is highly radioactive due to the presence of actinium.
- Actinium(III) fluoride is insoluble in water.
- It is typically synthesized through the reaction of actinium oxide with hydrogen fluoride.
Properties of Actinium(III) Fluoride
Understanding the properties of actinium(III) fluoride helps in its handling and application. Here are some key properties:
- The melting point of actinium(III) fluoride is around 1400°C.
- It has a density of approximately 7.5 g/cm³.
- Actinium(III) fluoride is paramagnetic, meaning it is weakly attracted by a magnetic field.
- The compound exhibits fluorescence under UV light.
- It has a hexagonal crystal structure, similar to other actinide fluorides.
Uses of Actinium(III) Fluoride
Despite its radioactivity, actinium(III) fluoride has some specialized uses, particularly in scientific research.
- It is used in neutron sources due to its ability to emit neutrons.
- Actinium(III) fluoride can be used in radiotherapy for cancer treatment.
- It serves as a precursor for other actinium compounds.
- The compound is used in nuclear batteries for space missions.
- It is also employed in research to study the properties of actinides.
Safety and Handling
Due to its radioactivity, actinium(III) fluoride must be handled with extreme care. Here are some safety considerations:
- Protective gear is essential when handling actinium(III) fluoride.
- The compound should be stored in shielded containers to prevent radiation exposure.
- Ventilation systems are necessary to avoid inhalation of any dust or fumes.
- Regular monitoring for radiation levels is crucial in areas where the compound is used.
- Disposal of actinium(III) fluoride must follow strict regulatory guidelines.
Interesting Facts about Actinium(III) Fluoride
Here are some intriguing tidbits about this unique compound:
- Actinium was discovered in 1899 by Friedrich Oskar Giesel.
- The name "actinium" comes from the Greek word "aktinos," meaning ray or beam.
- Actinium(III) fluoride is one of the few compounds where actinium exhibits a +3 oxidation state.
- The compound is often used in scientific demonstrations to show radioactive properties.
- Actinium(III) fluoride can be synthesized in a laboratory setting with the right equipment.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of actinium(III) fluoride is significant due to its radioactivity. Here’s what you need to know:
- Radioactive contamination can occur if the compound is not handled properly.
- It has a long half-life, making it persist in the environment for extended periods.
- Strict regulations govern the use and disposal of actinium(III) fluoride to minimize environmental impact.
- The compound can contribute to radiation pollution if released into the environment.
- Research is ongoing to find safer ways to handle and dispose of actinium(III) fluoride.
Final Thoughts on Actinium(III) Fluoride
Actinium(III) Fluoride, a compound with the formula AcF3, holds a unique place in the world of chemistry. Known for its radioactive properties, it’s used primarily in scientific research. This compound, discovered in the early 20th century, has a melting point of 1,400°C and is typically synthesized through the reaction of actinium oxide with hydrogen fluoride. Despite its limited practical applications, Actinium(III) Fluoride remains a subject of interest due to its role in understanding radioactive elements and their behaviors. Handling this compound requires strict safety protocols because of its radioactivity. While not commonly encountered outside specialized fields, Actinium(III) Fluoride continues to contribute to advancements in nuclear science. Understanding its properties and uses helps scientists unlock further secrets of the periodic table.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
