Enzyme catalysis is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in countless biological reactions. These remarkable catalysts, also known as enzymes, have the extraordinary ability to accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. The intricate mechanisms behind enzyme catalysis have baffled scientists for centuries, and ongoing research continues to uncover astonishing facts about their functioning.
In this article, we will delve into the world of enzyme catalysis and explore 17 mind-blowing facts that highlight the power and versatility of these incredible biomolecules. From their essential role in digestion to the production of renewable energy, enzymes have proven to be indispensable players in the intricate dance of life. So, let’s embark on this captivating journey and unravel the mysteries of enzyme catalysis!
Key Takeaways:
- Enzymes are like biological superheroes, speeding up reactions by millions or even billions of times. They’re picky about their jobs and can be regulated to keep the body running smoothly.
- Enzymes are the unsung heroes of life, involved in everything from DNA replication to digestion. They can be used as diagnostic tools and even engineered to do new and exciting things.
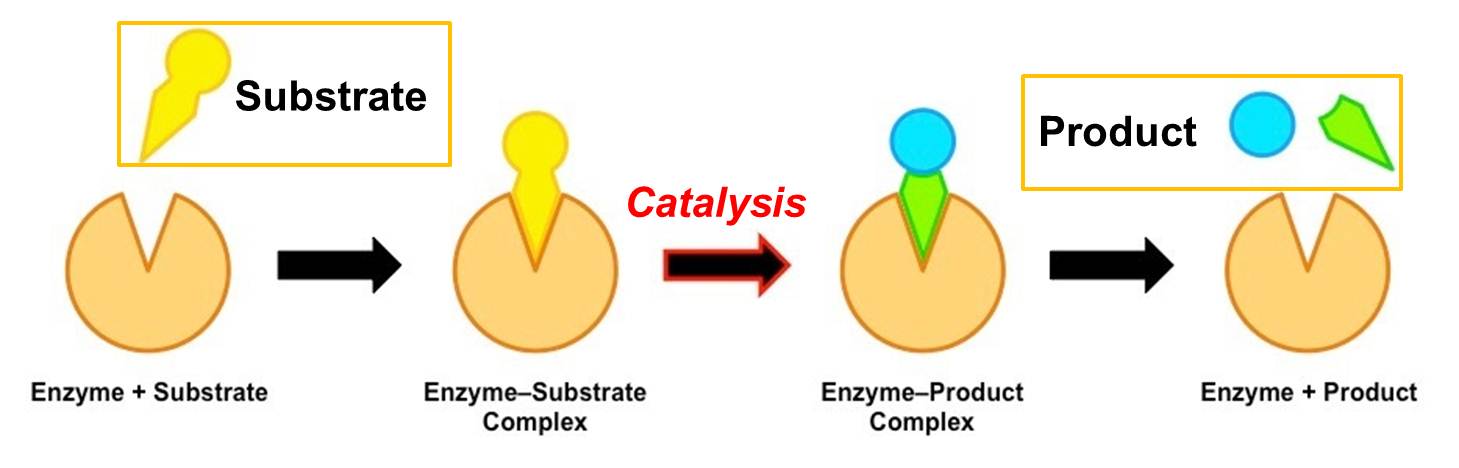
Enzymes are biological catalysts
Enzymes are specialized proteins that act as catalysts, increasing the speed of chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They accomplish this by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
Enzymes are highly efficient
Enzymes are incredibly efficient catalysts, capable of accelerating reactions by a factor of millions or even billions. This allows biochemical reactions to occur at a rate that is compatible with the needs of living organisms.
Enzymes are specific
Each enzyme is specific to a particular reaction or group of closely related reactions. This specificity is due to the unique shape and chemical composition of the enzyme’s active site, which only allows certain substrates to bind and react.
Enzymes can be regulated
Enzymes can be regulated to control the rate of reactions in response to the needs of the cell or organism. This regulation can occur through mechanisms such as feedback inhibition, allosteric regulation, and post-translational modifications.
Enzymes work under specific conditions
Enzymes are sensitive to changes in temperature and pH. They have an optimal range in which they function best, and deviations from this range can significantly impact their activity.
Enzymes can be denatured
Extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or extreme pH levels, can denature enzymes, causing them to lose their shape and function. This can have detrimental effects on the overall biological processes in which the enzymes are involved.
Enzymes can be classified
Enzymes can be classified into several categories based on the type of reaction they catalyze. These categories include hydrolases, transferases, oxidoreductases, ligases, isomerases, and lyases.
Enzymes can be used as diagnostic tools
Enzyme activity levels in the body can indicate certain health conditions. Medical professionals often use enzymes as diagnostic tools, measuring their activity levels in blood samples to detect diseases such as heart attacks, liver damage, or pancreatic disorders.
Enzymes can be inhibited
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that can bind to enzymes and reduce their activity. This inhibition can be reversible or irreversible and is utilized in various therapeutic applications, such as the development of drugs targeting specific enzymes.
Enzymes are involved in DNA replication
DNA replication, a crucial process for cell division and inheritance of genetic information, requires enzymes called DNA polymerases. These enzymes catalyze the synthesis of new DNA strands based on existing templates.
Enzymes play a role in digestion
Digestive enzymes, such as amylases, proteases, and lipases, are responsible for breaking down complex food molecules into smaller, more easily absorbable forms. This allows for the extraction of essential nutrients from the diet.
Enzymes can be used in industry
Enzymes have a wide range of applications in various industries. They are used in the production of food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and biofuels, among many others.
Enzymes are involved in photosynthesis
During photosynthesis, enzymes called rubisco catalyze the fixation of carbon dioxide (CO2) molecules from the atmosphere into simple organic compounds, a crucial step in the conversion of light energy into chemical energy.
Enzymes can be engineered
Scientists can modify and engineer enzymes to enhance their catalytic efficiency, stability, or substrate specificity. This field, known as enzyme engineering or protein engineering, has numerous applications in biotechnology and medicine.
Enzymes can have multiple coenzymes
Coenzymes are small organic molecules that bind to enzymes and assist in the catalytic process. Some enzymes require multiple coenzymes to carry out their reaction, increasing the complexity and specificity of the catalytic system.
Enzyme activity can be measured
Enzyme activity can be quantified using various methods, such as spectrophotometry or fluorometry. These techniques allow scientists to determine the rate at which an enzyme catalyzes a specific reaction and provide valuable information about enzyme kinetics.
Enzymes are essential for life
Without enzymes, life as we know it would not be possible. Enzyme catalysis is a fundamental process that drives countless biological reactions and ensures the efficient functioning of various metabolic pathways.
These 17 astonishing facts about enzyme catalysis highlight the incredible role enzymes play in the intricate workings of life. From their remarkable specificity to their crucial involvement in essential processes, enzymes continue to fascinate scientists and contribute to advancements in various fields.
Conclusion
Enzyme catalysis is a fascinating process that plays a vital role in biological systems. Through the action of enzymes, reactions that would otherwise be slow or unfavorable can occur at a rapid pace, enabling efficient metabolism and cellular function. The astonishing facts about enzyme catalysis showcase the remarkable nature of these catalysts and their impact on living organisms.
From their ability to lower activation energy to their specificity and versatility, enzymes demonstrate remarkable efficiency and selectivity. Their role in various industries, such as medicine and food production, also highlights their practical applications beyond biology. Understanding the intricacies of enzyme catalysis provides insights into the fundamental processes of life and opportunities for innovation and discovery.
As researchers continue to delve into the intricacies of enzyme catalysis, new breakthroughs are on the horizon. By further unraveling the mysteries behind these astonishing catalysts, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and elegance of the biological world.
FAQs
Q: What is enzyme catalysis?
A: Enzyme catalysis is the process by which enzymes facilitate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reactions to occur. Enzymes act as catalysts, allowing reactions to proceed at a faster rate without being consumed in the process.
Q: How do enzymes lower activation energy?
A: Enzymes lower activation energy by stabilizing the transition state of a reaction, making it easier for reactant molecules to reach the energy threshold for a reaction to occur. They achieve this through the precise arrangement of amino acid residues within their active sites.
Q: Are all enzymes specific for a particular substrate?
A: Yes, enzymes exhibit specificity for particular substrates. The active site of an enzyme is uniquely shaped to accommodate specific substrates and catalyze the corresponding reaction. This specificity allows enzymes to regulate metabolic pathways and interact with specific molecules in biological processes.
Q: Can enzymes catalyze any chemical reaction?
A: Enzymes are highly versatile catalysts and can catalyze a wide range of chemical reactions. However, each enzyme has a specific reaction or set of reactions that it can catalyze efficiently due to its unique active site structure and specificity for certain substrates.
Q: How are enzymes used in industries?
A: Enzymes have numerous applications in various industries. They are used in food production to enhance flavor, texture, and nutritional value. In medicine, enzymes are utilized for diagnostic tests and as therapeutic agents. They are also essential in biofuel production, waste management, and textile industry processes.
Enzymes, nature's catalytic marvels, hold countless more secrets waiting to be explored. Delve deeper into the astonishing world of enzyme catalysis, where efficiency meets specificity. Unravel the intricate relationship between enzymes and their essential partners, cofactors, as they work together to sustain life's vital processes. Step into the heart of enzymatic reactions and explore the extraordinary features of active sites, where the magic of catalysis unfolds. Embark on a journey through the fascinating realm of enzymes and discover the untold stories that lie within.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
