Molarity is a fundamental concept in chemistry that measures the concentration of a solute in a solution. It is widely used in various industries and research fields, including pharmaceuticals, environmental sciences, and biochemistry. Understanding molarity is crucial for conducting experiments, preparing solutions, and analyzing data accurately.
In this article, we will delve into 12 fascinating facts about molarity that will not only enhance your understanding of this concept but also provide you with valuable insights into its significance in the world of chemistry. From its definition and calculation to its applications in different areas, these facts will help you appreciate the role molarity plays in various scientific endeavors.
Key Takeaways:
- Molarity is the concentration of a solute in a solution, crucial for chemical calculations and dilutions, and used in real-life applications like pharmaceuticals and environmental analysis.
- Understanding molarity helps in determining reactants needed for chemical reactions, and is important in biology for processes like osmosis and enzyme kinetics.
Molarity Defined
Molarity is defined as the concentration of a solute in a solution, expressed as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is denoted by the symbol “M” and is widely used in chemical calculations and laboratory experiments.
The Formula
The formula to calculate molarity is straightforward: Molarity = Moles of Solute / Volume of Solution (in liters). This equation allows us to determine the molarity of a solution based on the amount of solute dissolved and the volume of the solution.
Importance in Dilutions
Molarity is particularly important in dilution calculations. By knowing the initial molarity and volume of a solution, we can determine the new molarity when the solution is diluted by adding a solvent.
Molarity and Stoichiometry
Molarity plays a crucial role in stoichiometry calculations. It allows us to determine the precise amount of reactants needed for a chemical reaction based on the desired molarity of the products.
Units of Molarity
Molarity is typically expressed in mol/L, which represents the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. However, other units such as mM (millimolar) or M (micromolar) can also be used depending on the concentration of the solution.
Standard Molarity Solution
A standard molarity solution, also known as a “standard solution,” is a solution of known molarity that is used for titrations and calibration purposes. It serves as a reference point to determine the unknown molarity of other solutions.
Molarity and pH
Molarity plays a role in determining the pH of a solution. In the case of an acid or a base, the concentration of H+ or OH- ions in the solution affects the pH value, which is a measure of acidity or alkalinity.
Molarity and Solubility
Molarity is closely related to the solubility of a solute in a solvent. The solubility of a substance is defined as the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a specific temperature and pressure.
Molarity in Biological Systems
In biology, molarity is used to describe the concentration of ions and molecules in biological systems. It is crucial for understanding processes such as osmosis, enzyme kinetics, and drug interactions.
Serial Dilutions
Serial dilutions, which involve a series of dilutions using the same factor, are commonly used in laboratory experiments. Molarity calculations are vital for achieving the desired concentration in each step of the dilution series.
Beer-Lambert Law
In spectroscopy, the Beer-Lambert Law relates the concentration (molarity) of a solute to the absorption of light. This law provides the foundation for determining the concentration of unknown substances in a solution.
Real-Life Applications
Molarity finds applications in various real-life scenarios, such as pharmaceutical formulations, food and beverage industry, environmental analysis, and medical diagnostics. It serves as a crucial tool for quality control and accurate measurements.
These were 12 fascinating facts about molarity that highlight its significance in the field of Chemistry. Understanding molarity is essential for mastering chemical calculations and conducting successful experiments. So, the next time you encounter molarity in your studies or research, you’ll have a deeper appreciation for its importance!
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the concept of molarity is crucial for anyone studying chemistry. Molarity is a fundamental unit that helps determine the concentration of a solution and plays a vital role in various chemical calculations. By knowing the molarity, scientists can accurately measure the amount of solute dissolved in a given volume of solvent.
Through this article, we have explored twelve fascinating facts about molarity. From its definition and formula to its applications in stoichiometry and determining reaction rates, molarity is a versatile concept that has significant implications in the field of chemistry.
Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply intrigued by the world of science, understanding molarity will unlock deeper insights into the world of chemical reactions and solutions.
FAQs
1. What is molarity?
Molarity is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution. It is defined as the number of moles of solute divided by the volume of the solution in liters.
2. How is molarity calculated?
Molarity is calculated using the formula: Molarity (M) = moles of solute / volume of solution (in liters).
3. What are some common units used for molarity?
The most common unit used for molarity is “moles per liter” (mol/L or M). However, other units such as millimoles per liter (mmol/L) or micromoles per liter (µmol/L) can also be used.
4. What is the significance of molarity in chemical reactions?
Molarity plays a crucial role in stoichiometry, where it is used to determine the amount of reactants necessary for a chemical reaction. It is also used to calculate reaction rates and understand the relationship between concentration and rate of reaction.
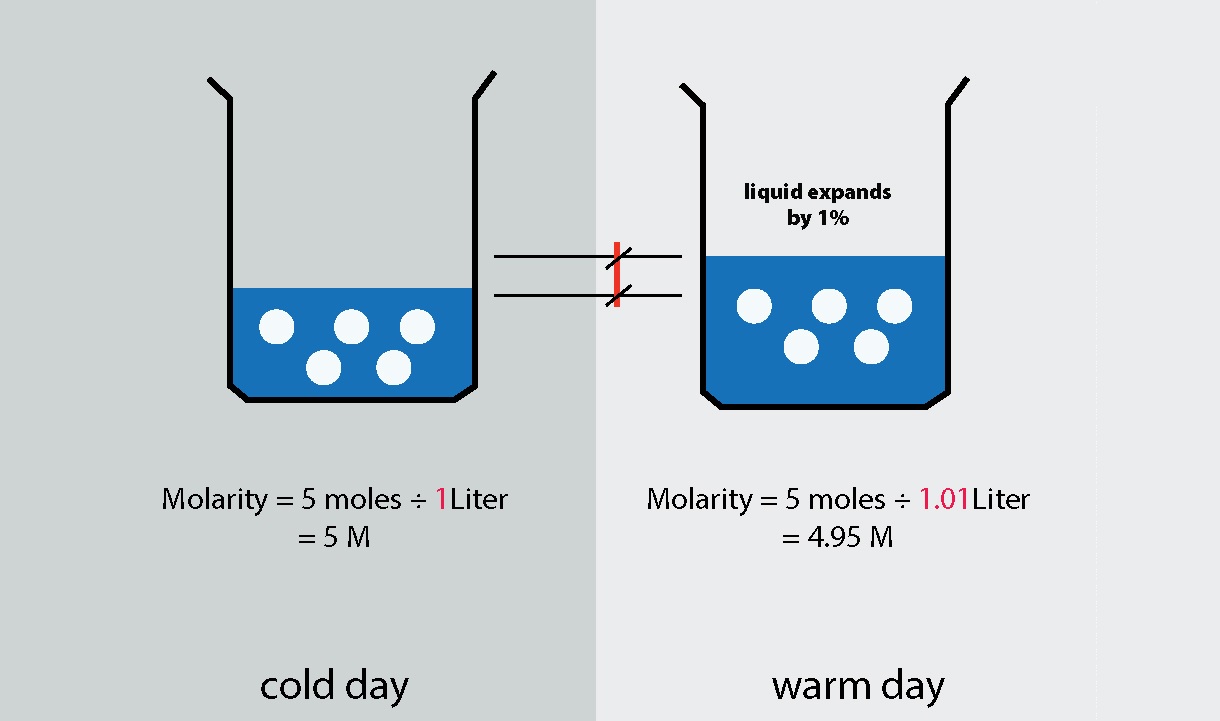
5. Can molarity change with temperature?
Yes, molarity can change with temperature as the volume of a liquid can change with temperature. Therefore, it is important to consider the temperature when working with molarity calculations.
6. How is molarity different from molality?
Molarity is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution, while molality is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solvent. Molarity takes into account the volume of the solution, whereas molality takes into account the mass of the solvent.
7. What are some real-life applications of molarity?
Molarity is used in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, environmental analysis, and food and beverage industry. It helps determine the proper dosage of medicine, monitor pollutants in water, and maintain desired concentrations in food and beverage production.
Molarity may seem straightforward, but many nuances make it a captivating subject. Exploring molar volume reveals surprising connections between gas laws and chemical reactions. Molar mass, a fundamental concept, helps scientists predict outcomes in the lab and beyond. While molarity focuses on solutions, wisdom teeth remind us that our bodies are complex systems too. Each topic offers a unique perspective on the world of chemistry and biology, inviting curious minds to keep learning.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
