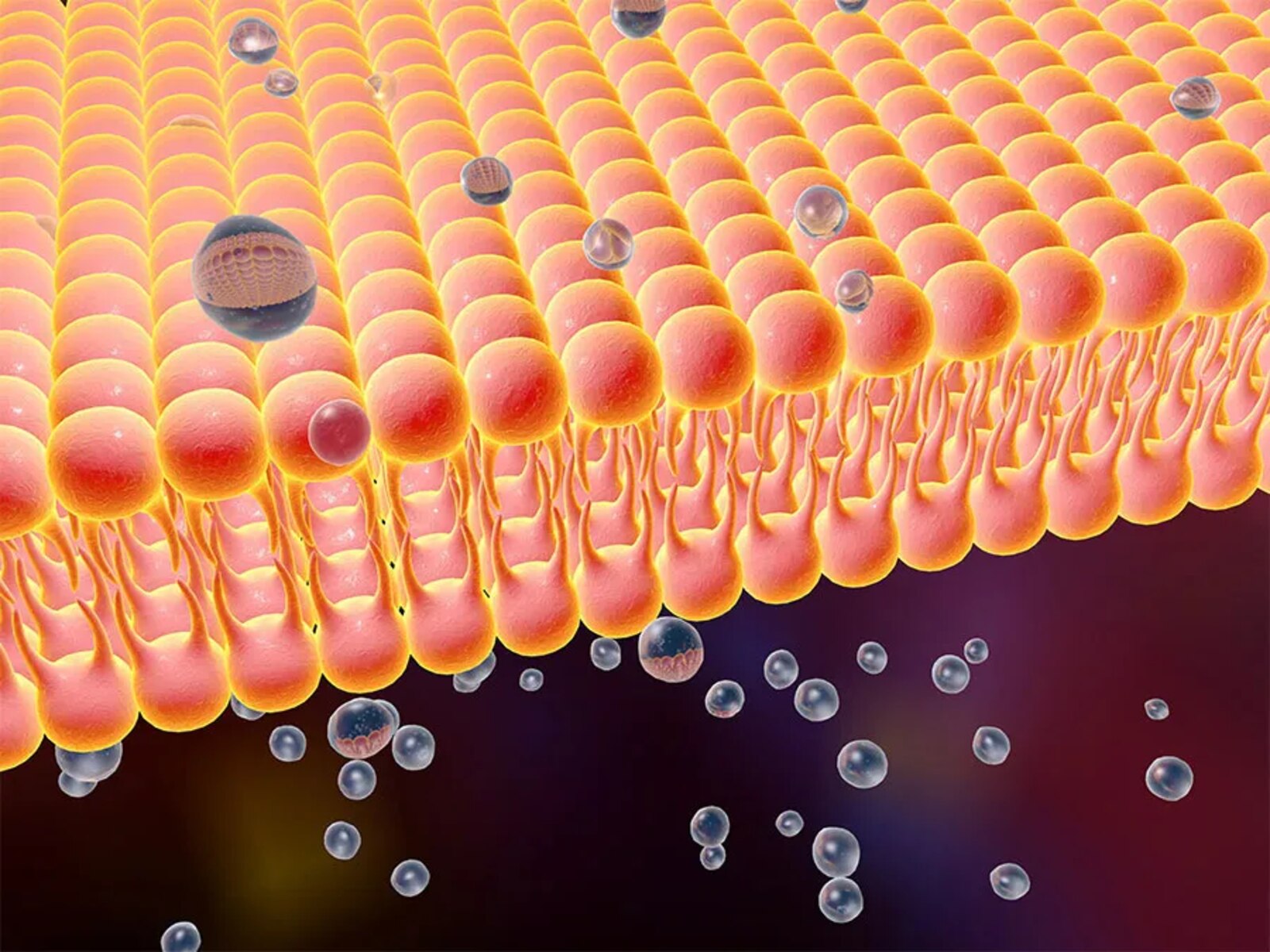
Diffusion is a fundamental process that plays a crucial role in numerous biological processes. It is the movement of particles or molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, driven by the natural kinetic energy of the particles. While diffusion may sound like a simple concept, its implications in biology are vast and intriguing.
In this article, we will uncover some astounding facts about diffusion that will deepen your understanding of this essential biological phenomenon. From its role in cell function to its impact on the environment, diffusion is a fascinating process that operates at various scales, from the microscopic to the macroscopic.
Let’s dive in and explore nine captivating facts about diffusion that will leave you amazed by its ubiquitous presence and significance in the world of biology.
Key Takeaways:
- Diffusion is the cool way that tiny particles move from crowded areas to less crowded areas, helping cells get what they need and get rid of waste without using up energy.
- It’s not just biology – diffusion is everywhere! It helps plants drink water, cells stay balanced, and even scientists study it to understand how things move in the world.
Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Diffusion plays a crucial role in numerous biological processes by allowing substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients to move in and out of cells. It is driven by the random motion of particles and does not require energy expenditure from the cell.
Diffusion occurs in various biological systems, from the transport of respiratory gases in the lungs to the exchange of nutrients and waste products in cells.
Whether it’s the uptake of oxygen by red blood cells or the release of carbon dioxide in body tissues, diffusion ensures the efficient movement of molecules across cell membranes. This process allows for important biological functions, such as the delivery of nutrients to cells and the removal of metabolic waste.
Diffusion is influenced by factors such as temperature, concentration gradient, and the size of the particles.
Higher temperatures increase the rate of diffusion as particles gain more kinetic energy and move at a faster pace. A larger concentration gradient, or the difference in concentration between two areas, also enhances the rate of diffusion. Additionally, smaller particles diffuse more quickly compared to larger ones due to their higher molecular speed.
Factors such as surface area and distance also affect the rate of diffusion.
A larger surface area provides more room for particles to diffuse, increasing the overall rate of diffusion. On the other hand, a greater distance that particles need to travel results in slower diffusion. These factors are important considerations in biological systems where efficient diffusion is crucial for proper function.
Facilitated diffusion is a specialized form of diffusion that relies on carrier proteins to transport substances across cell membranes.
This process is vital for the uptake of essential molecules such as glucose and amino acids. Carrier proteins bind to specific molecules and undergo conformational changes to transfer them across the membrane. Facilitated diffusion allows for the selective movement of substances, ensuring the proper balance of molecules within the cell.
Osmosis is a type of diffusion that specifically involves the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane.
Water moves from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration, allowing for the maintenance of proper fluid balance in cells and tissues. Osmosis is essential for processes such as kidney function, regulation of cell volume, and absorption of water in plants.
Diffusion is not only limited to gases and small molecules, but it also plays a significant role in the movement of ions and larger particles.
Through processes such as ion channels and endocytosis/exocytosis, cells are able to transport ions and macromolecules across membranes. These specialized mechanisms ensure the precise movement of specific substances needed for normal cellular function and signal transmission.
Diffusion is a key process in the field of molecular biology and is extensively studied to understand various biological phenomena.
Researchers use diffusion as a tool to investigate the movement of molecules, such as studying the binding and release of chemical messengers in cells. Understanding the principles of diffusion provides valuable insights into the intricate workings of biological systems.
Diffusion is not only limited to biological systems but is also observed in various other fields, including physics, chemistry, and engineering.
The concept of diffusion has broad applications beyond biology. It plays a vital role in areas such as material science, environmental studies, and even the spread of diseases. The study of diffusion has contributed significantly to advancements in these fields, further highlighting its significance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diffusion is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in various biological systems. It is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, driven by the natural tendency to achieve equilibrium. Diffusion occurs in a wide range of biological processes, including gas exchange in the respiratory system, nutrient absorption in the digestive system, and waste removal in the excretory system.Understanding the intricacies of diffusion can help us comprehend how substances move within living organisms and how essential functions are carried out. From the complex network of alveoli in our lungs to the intricate network of capillaries in our circulatory system, diffusion ensures the efficient exchange of gases and nutrients. It is truly a remarkable phenomenon that enables life as we know it.By delving into the astounding facts about diffusion, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms at work within our bodies and the remarkable efficiency of biological processes. So next time you take a deep breath or enjoy a nutritious meal, remember the incredible role that diffusion plays in sustaining life.
FAQs
Q: What is diffusion?
A: Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. It occurs as a result of the random motion of molecules and is driven by the goal of achieving equilibrium.
Q: Why is diffusion important in biology?
A: Diffusion is essential for various biological processes such as gas exchange, nutrient absorption, and waste removal. It ensures the efficient movement of substances within living organisms and helps maintain homeostasis.
Q: How does diffusion occur in the respiratory system?
A: In the respiratory system, diffusion occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. Oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide, a waste product, diffuses from the bloodstream into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Q: Can diffusion occur in both liquids and gases?
A: Yes, diffusion can occur in both liquids and gases. In liquids, it occurs at a slower rate compared to gases due to the closer proximity of molecules. However, the principles of diffusion remain the same.
Q: What factors affect the rate of diffusion?
A: The rate of diffusion is influenced by factors such as the concentration gradient, temperature, surface area, and size of the particles. A steeper concentration gradient, higher temperature, larger surface area, and smaller particle size generally result in faster diffusion.
Q: How is diffusion different from osmosis?
A: While diffusion refers to the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, osmosis specifically describes the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane.
Q: Can diffusion occur in living cells?
A: Yes, diffusion occurs within living cells. Substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and small molecules can diffuse across the cell membrane to enter or exit the cell.
Q: Is diffusion a passive or active process?
A: Diffusion is a passive process as it does not require the input of energy. It occurs spontaneously due to the inherent random motion of particles.
Q: Can diffusion be influenced by external factors?
A: Yes, diffusion can be influenced by external factors such as the presence of a barrier or a concentration gradient created by other substances. These factors can affect the rate and direction of diffusion.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
