Sex determination is a fascinating aspect of biology that has intrigued scientists for centuries. From the moment of conception, our biological sex is determined by a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. While many of us may think of sex determination as a straightforward binary process, where individuals are either male or female, the reality is far more intricate and mind-blowing.
In this article, we will explore 19 mind-blowing facts about sex determination that will shed light on the diverse mechanisms operating in different species. From the role of chromosomes and hormones to the influence of temperature, we will delve into the incredible world of sex determination. So, get ready to be amazed as we uncover the mysteries behind how nature determines the sex of living organisms.
Key Takeaways:
- Sex determination is not just about chromosomes; it can be influenced by temperature, social interactions, and even environmental factors. It’s a complex process that shapes the diversity of life on Earth.
- Understanding sex determination is not only mind-blowing but also important for conservation and medical research. It’s like solving a fascinating puzzle with implications beyond just biology.
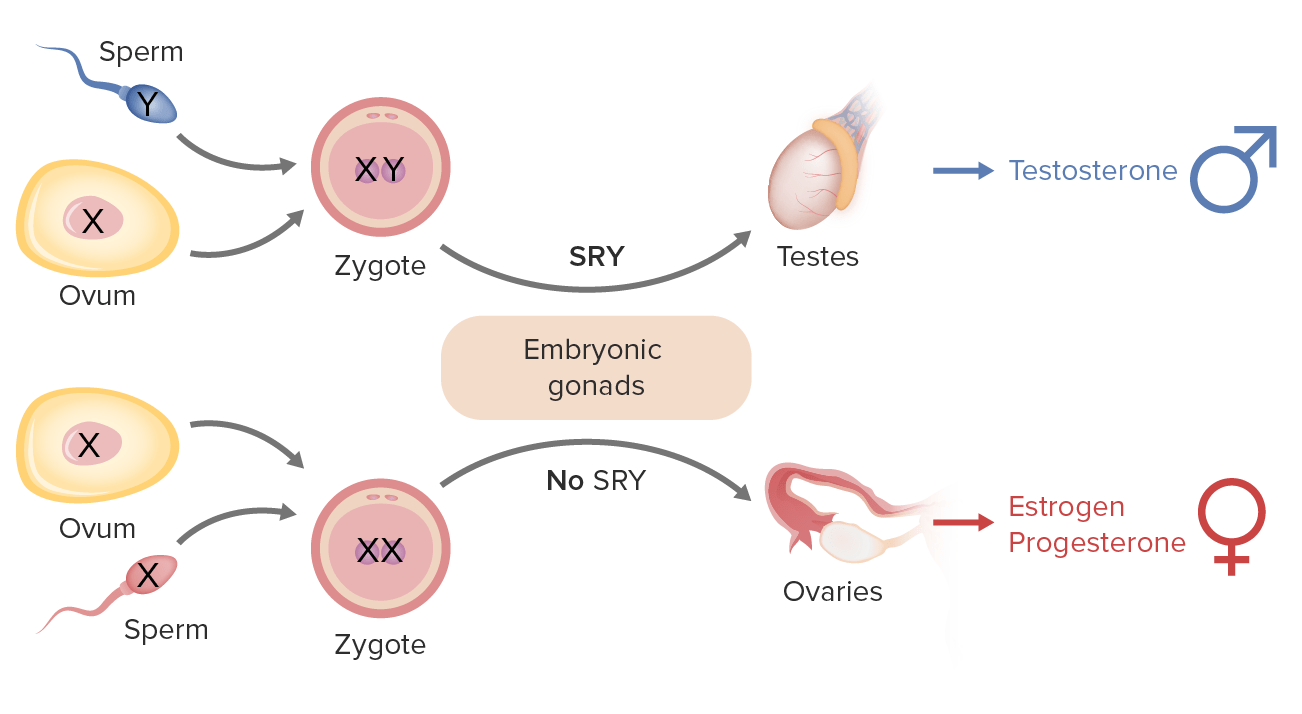
Sex determination is determined by chromosomes.
When it comes to sex determination, it all boils down to the presence or absence of specific chromosomes in an individual’s genetic makeup. In most species, including humans, females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
The sex determination system can vary among different organisms.
While humans and many other mammals have an XY system, other organisms may have different methods of determining sex. For example, birds have a ZW system, where females have ZW chromosomes, and males have ZZ chromosomes.
Some organisms can change their sex.
In certain species, such as clownfish and wrasses, individuals have the ability to change their sex. This phenomenon, known as sequential hermaphroditism, allows them to adapt to changing social or environmental conditions.
Temperature can influence sex determination in some reptiles.
While chromosomes play a crucial role in sex determination, some reptiles, such as turtles and crocodiles, have temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD). The temperature at which the eggs are incubated can determine whether they will develop into males or females.
Sex determination in bees is influenced by haplodiploidy.
Bees have a unique system of sex determination called haplodiploidy, where females develop from fertilized eggs and have two sets of chromosomes, while males develop from unfertilized eggs and have only one set of chromosomes.
The SRY gene is responsible for male development in humans.
In humans, the presence of the Y chromosome with the SRY (sex-determining region Y) gene triggers the development of male characteristics during embryonic development.
Some plants have both male and female reproductive organs.
Unlike animals, which have distinct male and female individuals, some plants have the ability to produce both male and female gametes within the same individual. This is known as monoecy or hermaphroditism.
Environmental factors can influence sex determination in certain fish.
In some fish species, such as the Japanese medaka, environmental factors like light, temperature, and social conditions can play a role in determining the sex of the offspring.
Sex chromosomes can evolve from regular chromosomes.
Sex chromosomes, such as the X and Y chromosomes in humans, can evolve from regular autosomes through a process known as sex chromosome evolution. This can happen due to genetic mutations and natural selection.
Sex determination can be influenced by genetic and hormonal factors.
While chromosomes provide the foundation for sex determination, the process is also influenced by genetic and hormonal factors. These factors can affect the development of reproductive organs and secondary sexual characteristics.
Some species exhibit environmental sex determination.
In certain reptiles, such as some species of lizards and turtles, the sex of the offspring is determined by the temperature at which the eggs are incubated. This is known as environmental sex determination (ESD).
Sex determination can be influenced by imprinted genes.
Imprinted genes, which are genes that are expressed differently depending on whether they are inherited from the mother or the father, can play a role in sex determination and sexual development.
Sex determination can occur later in life.
In some organisms, like certain species of fish and mollusks, the determination of sex can take place later in life. This is known as delayed or sequential sex determination.
Sex ratios can be skewed due to environmental factors.
Various environmental factors, such as temperature and nutrient availability, can influence the sex ratio of offspring in certain species. This can have important implications for population dynamics and species survival.
Epigenetic modifications can affect sex determination.
Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, can impact gene expression and potentially influence sex determination processes in certain organisms.
Sex determination can be influenced by social factors.
In socially complex species, such as some fish and mammals, social interactions and hierarchies can play a role in determining the sex of individuals within a population.
The environment can override genetic sex determination.
Under certain circumstances, the environment can override the genetic sex determination system. This can lead to individuals developing reproductive organs that do not align with their chromosomal sex.
Sex determination can be a complex interplay of multiple factors.
The process of sex determination is not always straightforward and can involve a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, environmental, and social factors. Understanding these interactions is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of sex determination.
Sex determination research has broader implications.
Studying sex determination not only helps us understand the fascinating biological process but also has broader implications for fields such as reproductive biology, conservation efforts, and medical research.
Conclusion
Sex determination is a fascinating biological process that involves intricate mechanisms and unique characteristics. From the role of chromosomes to the influence of genetics and environmental factors, scientists continue to uncover mind-blowing facts about how sex is determined in different organisms.
Through this article, we have explored various aspects of sex determination, including the diversity of systems, the impact of sex chromosomes, and the role of hormones. We have also delved into interesting phenomena like temperature-dependent sex determination and sequential hermaphroditism.
Understanding the complexities of sex determination enhances our knowledge of biology and evolution, providing crucial insights into reproductive strategies and population dynamics. It also highlights the incredible diversity and adaptability of life on Earth.
As scientists conduct further research and investigations, we can look forward to discovering even more mind-blowing facts about sex determination, unraveling the mysteries of this fundamental biological process.
FAQs
Q: How is sex determined in humans?
A: In humans, sex is determined by the presence of either XX (female) or XY (male) chromosomes. The presence of the Y chromosome triggers the development of male reproductive structures.
Q: What is temperature-dependent sex determination?
A: Temperature-dependent sex determination is a process observed in reptiles, where the incubation temperature during development determines the sex of the offspring. Certain temperatures result in male hatchlings, while others produce females.
Q: Can sex determination be influenced by environmental factors?
A: Yes, in some species, environmental factors such as temperature or social interactions can influence sex determination. For example, in some fish species, dominant males may become females if the existing female in a group dies.
Q: Are there organisms that can change their sex?
A: Yes, there are organisms that exhibit sequential hermaphroditism, where individuals can change their sex during their lifetime. For example, some fish species start as females and become males as they mature.
Q: Do all organisms have a two-sex system?
A: No, not all organisms have a two-sex system. There are various sex determination systems found in nature, including systems with more than two sexes or even species where sex is determined by environmental cues.
Dive into the captivating world of sex determination, where chromosomes and genes intertwine to shape the very essence of life. From the fascinating realm of genetics to the intricate dance of homologous chromosomes, the secrets of biological gender determination are waiting to be unlocked. Embark on a journey of discovery as we explore the mind-blowing facts that shed light on the complex mechanisms behind sex determination. Get ready to have your curiosity piqued and your understanding of life's building blocks transformed.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
