When it comes to inheritance, we often think of traits being passed down from our parents, like eye color or hair texture. However, there is a fascinating aspect of inheritance known as sex-linked inheritance. This type of inheritance involves the transmission of specific genetic traits through the sex chromosomes, X and Y. Sex-linked inheritance follows a unique pattern and can result in interesting outcomes that go beyond the typical Mendelian inheritance. In this article, we will explore 11 extraordinary facts about sex-linked inheritance that will shed light on the complexities and marvels of genetic inheritance. From understanding how certain traits are passed down differently between males and females to discovering the role of sex chromosomes in disease susceptibility, sex-linked inheritance offers a captivating understanding of our genetic makeup. So, let’s dive deep into the fascinating world of sex-linked inheritance and uncover its amazing secrets.
Key Takeaways:
- Males and females inherit traits differently due to their sex chromosomes. This can lead to conditions like hemophilia and color blindness, with males being more affected. Genetic counseling can help families understand and manage these inherited traits.
- Crossing over during meiosis and ongoing research play a role in understanding sex-linked inheritance. This can lead to new insights and potential treatments for genetic conditions.
Sex-Linked Inheritance is Determined by the Sex Chromosomes
Sex-linked inheritance refers to the transmission of genes that are located on the sex chromosomes. In humans, males have one X and one Y chromosome, while females have two X chromosomes. This means that certain genetic traits can be passed down differently based on an individual’s sex.
The X Chromosome Carries More Genes than the Y Chromosome
The X chromosome is much larger than the Y chromosome and contains a significantly higher number of genes. As a result, most sex-linked inheritance is associated with genes found on the X chromosome.
Males Are More Likely to Inherit Sex-Linked Traits
Since males only have one copy of the X chromosome, any gene located on it will be expressed. This means that if a male inherits a recessive trait on the X chromosome, it will be visible. Females, on the other hand, have two X chromosomes, providing a backup copy that can potentially mask the expression of the trait.
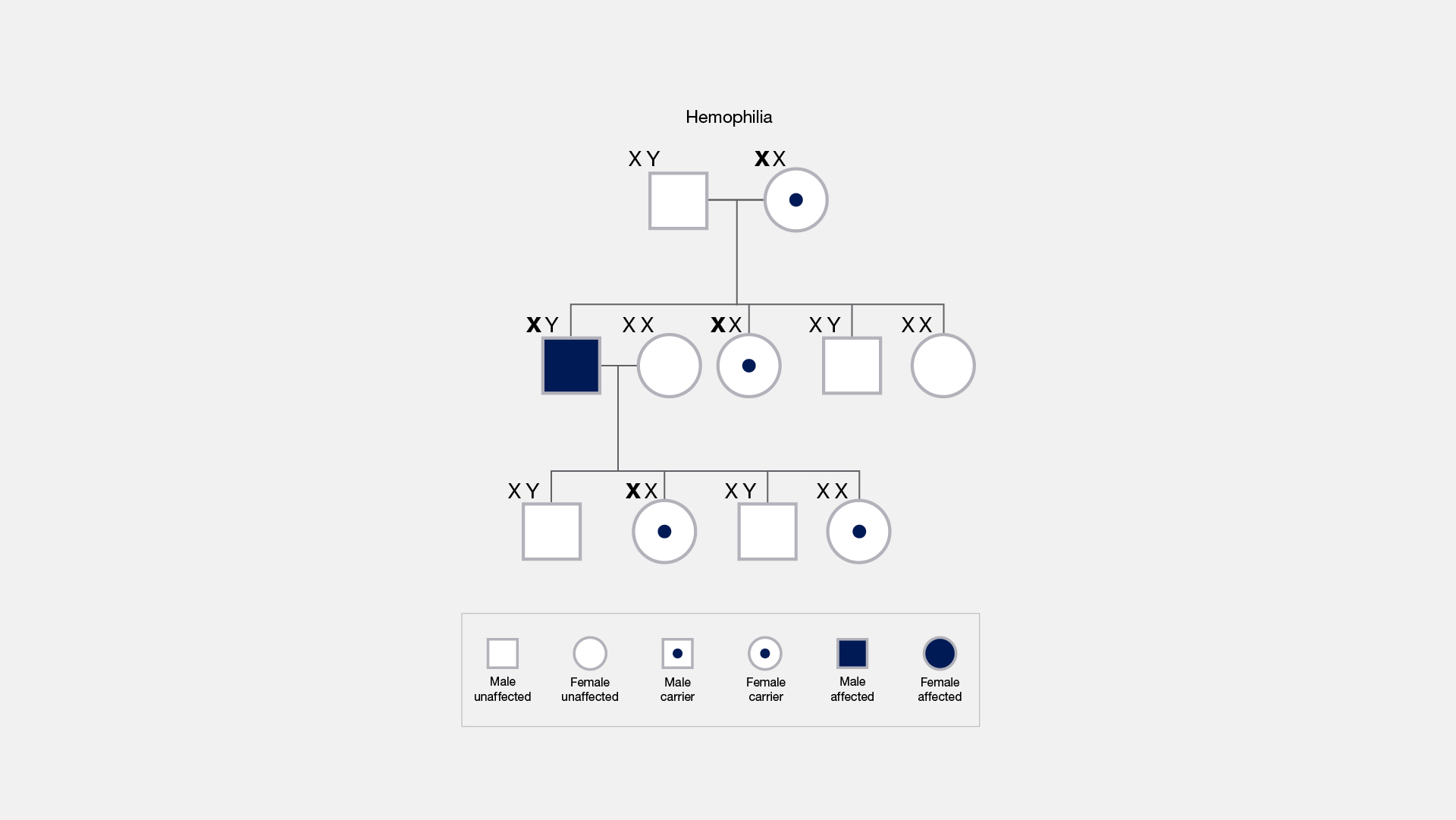
Hemophilia is a Famous Example of Sex-Linked Inheritance
Hemophilia, a bleeding disorder, is one of the most well-known sex-linked traits. The gene responsible for hemophilia is located on the X chromosome, and its inheritance pattern follows a classic sex-linked pattern, with males more likely to be affected and females typically being carriers.
Color Blindness Can Be Sex-Linked
Color blindness is another example of a sex-linked trait. The gene that causes color blindness is located on the X chromosome, making men more prone to this condition. While color blindness can affect both males and females, it is more common among males due to the inheritance pattern.
Sex-Linked Traits Can Skip Generations
Due to the inheritance pattern of sex-linked traits, it is possible for such traits to skip generations. For example, a female carrier may not exhibit any symptoms, but her son could inherit the trait and display the associated characteristic.
Sex-Linked Inheritance Can Be Linked to Recessive or Dominant Traits
Sex-linked inheritance can be associated with both recessive and dominant traits. In the case of recessive traits, males are more likely to express the phenotype since they only have one copy of the X chromosome. For dominant traits, both males and females can display the characteristic if they inherit the dominant allele.
Crossing Over Can Affect Sex-Linked Inheritance
Crossing over, the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, can occur during meiosis and can impact sex-linked inheritance. If a crossover event happens between the X and Y chromosome in males, it can result in the exchange of genetic material and potentially affect the inheritance of sex-linked traits.
Sex-Linked Traits Can Manifest Differently in Males and Females
Because males only have one X chromosome, any gene located on it will be expressed. This can sometimes lead to more severe manifestations of certain genetic conditions compared to females, who typically have two X chromosomes with a potential protective effect.
Genetic Counseling Can Help with Sex-Linked Inheritance
Genetic counseling can be beneficial for families affected by sex-linked inheritance. It can provide information about the inheritance pattern, potential risks, and available options for preventing or managing certain genetic conditions associated with sex-linked traits.
Research Continues to Uncover New Insights into Sex-Linked Inheritance
Scientists are continually studying sex-linked inheritance to gain a deeper understanding of how genes on the sex chromosomes contribute to various traits and diseases. Ongoing research brings new insights that can lead to improved diagnostics, treatments, and interventions in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sex-linked inheritance is a fascinating field in biology that delves into the mechanisms and patterns of inheritance related to genes found on the sex chromosomes. From the discovery of sex determination to the identification of specific genes linked to various traits and disorders, research in this area has provided remarkable insights into the complexity of genetic inheritance.
Understanding sex-linked inheritance has been instrumental in advancing our knowledge of genetics and evolution. It has also been invaluable in practical applications, such as diagnosing and treating genetic disorders, predicting the likelihood of certain traits in offspring, and even determining the ancestry of individuals.
The extraordinary facts about sex-linked inheritance mentioned in this article highlight the diverse ways in which genes on the sex chromosomes are inherited and expressed. These facts underscore the importance of considering the sex chromosomes when studying inheritance patterns and provide a foundation for further exploration into the intriguing world of genetics.
FAQs
1. What is sex-linked inheritance?
Sex-linked inheritance refers to the transmission of genes located on the sex chromosomes (X and Y) from parents to offspring. These genes exhibit inheritance patterns that differ between males and females due to the distinct composition of their sex chromosomes.
2. How are sex-linked traits inherited?
Sex-linked traits are inherited in a manner that depends on whether they are carried on the X or Y chromosome. Genes on the X chromosome follow a different pattern of inheritance compared to those on the autosomes, while genes on the Y chromosome are exclusively passed from fathers to sons.
3. What are some examples of sex-linked disorders?
Some examples of sex-linked disorders include hemophilia, color blindness, and muscular dystrophy. These conditions are more commonly observed in males because having only one copy of the X chromosome makes them susceptible to inheriting a defective gene.
4. Can females be carriers of sex-linked disorders?
Yes, females can be carriers of sex-linked disorders. While they have two copies of the X chromosome, just like males, they can inherit a defective gene on one X chromosome and remain unaffected themselves. However, they can pass on the faulty gene to their offspring, who may exhibit symptoms if they inherit the gene from both parents.
5. Is sex-linked inheritance only found in humans?
No, sex-linked inheritance is not limited to humans. It is observed in various organisms, including other mammals, birds, and some insects. The specific genes and traits affected by sex-linked inheritance differ across species, but the underlying principles remain the same.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
