Membranes are everywhere! From the cells in your body to the latest tech gadgets, they play a vital role in countless processes. But what exactly are membranes? Membranes are thin layers that act as barriers, controlling what goes in and out of a space. They can be found in living organisms, like the cell membrane, or in man-made objects, like water filters. These versatile structures are essential for life and technology. In this post, we’ll dive into 37 fascinating facts about membranes that will help you understand their importance and how they work. Get ready to be amazed by the world of membranes!
What Are Membranes?
Membranes are fascinating structures found in both living organisms and man-made systems. They play crucial roles in various processes, from protecting cells to filtering water. Here are some intriguing facts about membranes.
-
Membranes are thin layers that separate different environments. They can be found in biological systems, like cell membranes, or in industrial applications, like water filtration.
-
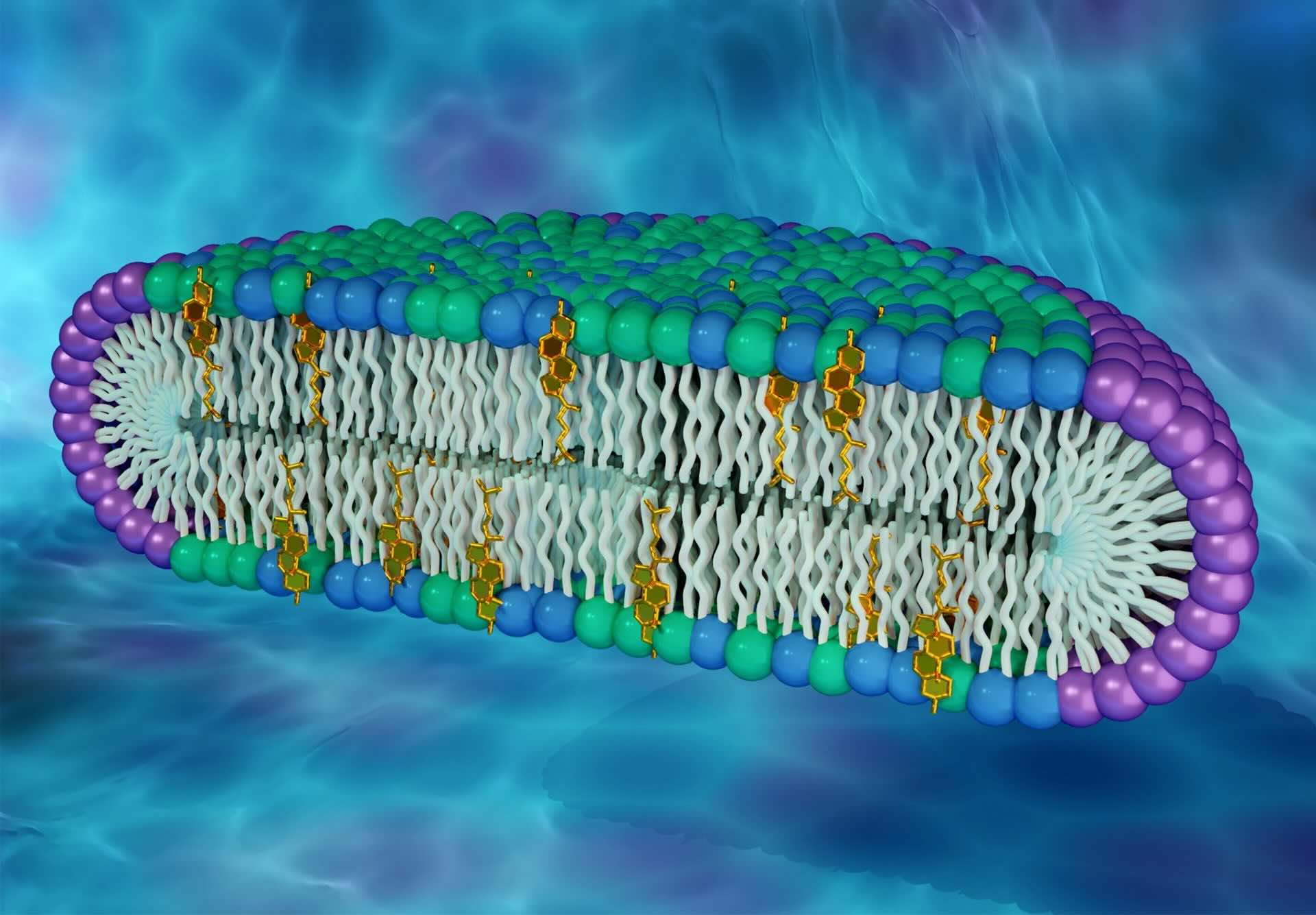
Cell membranes are primarily composed of lipids and proteins. These molecules create a flexible yet sturdy barrier that protects the cell.
-
The lipid bilayer is a fundamental component of cell membranes. It consists of two layers of lipid molecules, with hydrophobic tails facing inward and hydrophilic heads facing outward.
-
Membranes are selectively permeable. This means they allow certain substances to pass through while blocking others, maintaining the internal environment of the cell.
-
Proteins embedded in the membrane serve various functions. Some act as channels or pumps to move substances in and out of the cell, while others function as receptors for signaling molecules.
Functions of Membranes
Membranes are not just barriers; they perform a variety of essential functions. Let's explore some of these roles.
-
Membranes help maintain homeostasis. By controlling the movement of substances, they keep the internal conditions of the cell stable.
-
They play a key role in communication. Membrane proteins can receive signals from other cells and relay them to the cell's interior.
-
Membranes are involved in energy production. In mitochondria, the inner membrane contains proteins that generate ATP, the cell's energy currency.
-
They aid in cell recognition. Glycoproteins on the membrane surface help cells identify each other, which is crucial for immune response and tissue formation.
-
Membranes facilitate cell adhesion. They help cells stick to each other and to the extracellular matrix, forming tissues and organs.
Types of Membranes
There are various types of membranes, each with unique properties and functions. Here are some examples.
-
Plasma membranes surround the cell, providing a protective barrier and regulating the entry and exit of substances.
-
Nuclear membranes enclose the nucleus, protecting the cell's genetic material and controlling the flow of information to and from the nucleus.
-
Mitochondrial membranes have two layers. The outer membrane is smooth, while the inner membrane is folded into cristae, increasing the surface area for energy production.
-
Chloroplast membranes are found in plant cells. They contain pigments like chlorophyll, which capture light energy for photosynthesis.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membranes form a network of tubules and sacs. The rough ER has ribosomes on its surface, while the smooth ER is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
Membrane Transport Mechanisms
Membranes use various mechanisms to transport substances. These processes are vital for cell survival and function.
-
Passive transport does not require energy. Substances move from areas of high concentration to low concentration through diffusion or facilitated diffusion.
-
Active transport requires energy, usually in the form of ATP. It moves substances against their concentration gradient, from low to high concentration.
-
Osmosis is a type of passive transport. It involves the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane.
-
Endocytosis is a process where the cell membrane engulfs external substances, forming a vesicle that brings them into the cell.
-
Exocytosis is the reverse of endocytosis. It involves the fusion of a vesicle with the cell membrane to release its contents outside the cell.
Industrial Applications of Membranes
Membranes are not limited to biological systems; they have numerous industrial applications as well.
-
Membrane filtration is used in water treatment. It removes contaminants, making water safe for drinking and other uses.
-
Reverse osmosis is a popular method for desalination. It uses a semipermeable membrane to remove salt from seawater, producing fresh water.
-
Membranes are used in gas separation. They can selectively allow certain gases to pass through, separating them from a mixture.
-
In the food industry, membranes help concentrate and purify products. For example, they are used in the production of dairy products like cheese and yogurt.
-
Membrane bioreactors combine biological treatment with membrane filtration. They are used in wastewater treatment to remove organic matter and pathogens.
Membrane Technology Advancements
Advancements in membrane technology have led to innovative solutions in various fields. Here are some recent developments.
-
Nanofiltration membranes have tiny pores that can remove small particles and dissolved substances. They are used in water purification and pharmaceutical production.
-
Graphene oxide membranes are incredibly thin and strong. They have potential applications in desalination, gas separation, and energy storage.
-
Bio-inspired membranes mimic natural systems. For example, aquaporin-based membranes replicate the water channels found in living cells, offering efficient water filtration.
-
Smart membranes can respond to environmental changes. They can alter their permeability or other properties in response to stimuli like temperature or pH.
-
Hybrid membranes combine different materials to enhance performance. They can offer improved selectivity, permeability, and durability.
Membrane-Related Disorders
Membrane dysfunction can lead to various health issues. Here are some examples of membrane-related disorders.
-
Cystic fibrosis is caused by a defective membrane protein. This leads to thick, sticky mucus buildup in the lungs and other organs.
-
Muscular dystrophy involves mutations in genes encoding membrane proteins. This results in muscle weakness and degeneration.
-
Alzheimer's disease is associated with changes in membrane composition. These changes can affect the function of neurons and contribute to cognitive decline.
-
Hypercholesterolemia involves high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It can result from defects in membrane receptors that regulate cholesterol uptake.
-
Hereditary spherocytosis is a genetic disorder affecting red blood cell membranes. It causes the cells to become spherical and fragile, leading to anemia.
Fun Facts About Membranes
Membranes have some surprising and fun aspects too. Here are a few to wrap up.
-
The fluid mosaic model describes the cell membrane. It suggests that the membrane is a dynamic, fluid structure with proteins floating in a sea of lipids.
-
Some bacteria have specialized membranes called magnetosomes. These contain magnetic particles that help the bacteria navigate using Earth's magnetic field.
Membranes: The Unsung Heroes
Membranes play a crucial role in countless biological and industrial processes. From protecting cells to filtering water, these thin barriers are everywhere. They help maintain homeostasis in living organisms, ensuring cells get the nutrients they need while keeping harmful substances out. In industry, membranes are vital for water purification, gas separation, and even in the food and beverage sector.
Understanding membranes can lead to advancements in medicine, environmental science, and technology. Researchers are constantly exploring new materials and methods to improve membrane efficiency and durability. As we continue to innovate, the importance of membranes will only grow.
Next time you drink clean water or marvel at the complexity of life, remember the membranes working behind the scenes. They may be invisible to the naked eye, but their impact is immense. Keep learning about these fascinating structures and appreciate their silent yet significant contributions.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
