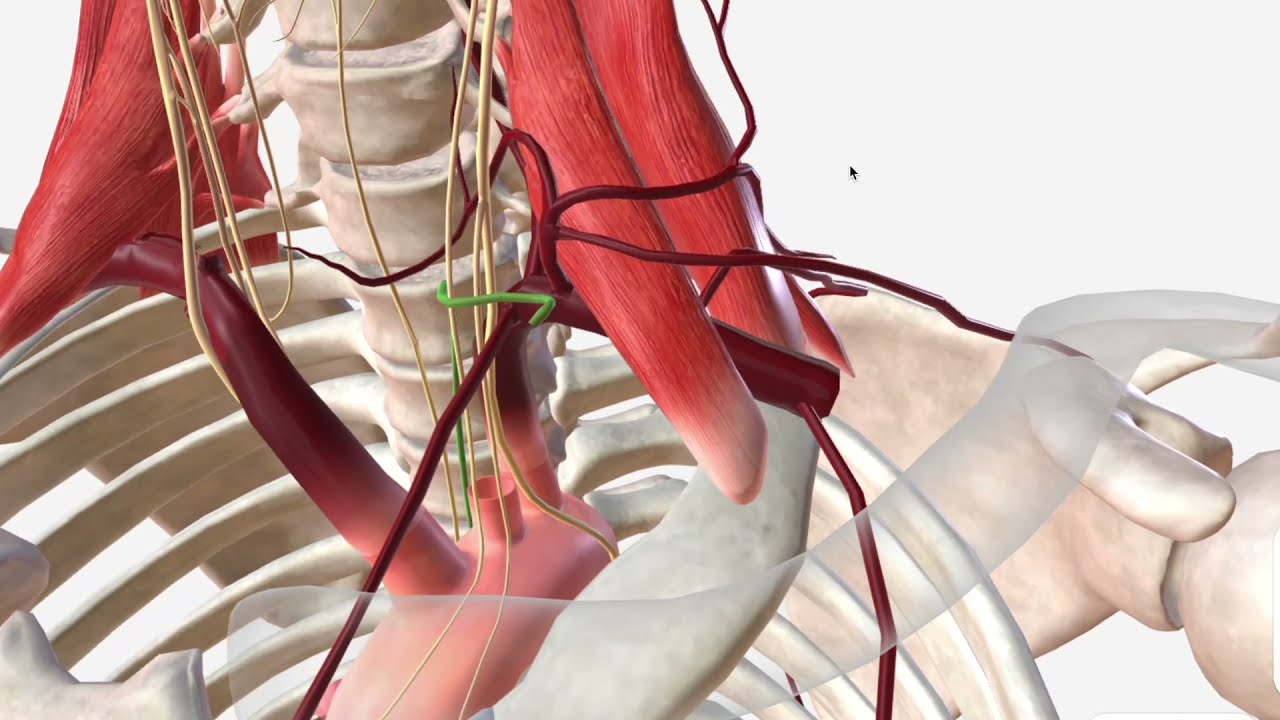
The subclavian artery is a vital blood vessel in the human body that plays a crucial role in delivering oxygenated blood to the upper limbs, neck, and brain. It is one of the main branches of the aortic arch and is responsible for the blood supply to the arms and shoulders. While it may seem like a relatively simple structure, the subclavian artery possesses a multitude of extraordinary features and functions that make it truly fascinating.
In this article, we will explore 18 extraordinary facts about the subclavian artery, ranging from its anatomical location to its potential medical conditions. Whether you are a student of human anatomy, a medical professional, or simply curious about the wonders of the human body, these facts about the subclavian artery are sure to captivate your interest and deepen your understanding of this remarkable vessel.
Key Takeaways:
- The subclavian artery is a major blood vessel supplying the head, neck, and upper limbs. It can be affected by diseases and conditions, making it crucial for medical professionals to understand its role and potential complications.
- Anatomical variations, arterial pulse, and medical interventions are essential aspects of the subclavian artery. Its extensive network of collateral blood vessels ensures proper blood supply to the upper body regions, highlighting its significance in the human body.
The subclavian artery is one of the major arteries in the human body.
The subclavian artery is a large blood vessel that arises from the aortic arch, specifically from the brachiocephalic trunk. It is responsible for supplying blood to the head, neck, shoulders, and upper limbs.
The subclavian artery has three main branches.
The subclavian artery gives rise to three important branches: the vertebral artery, the internal thoracic artery, and the thyrocervical trunk. These branches distribute blood to various parts of the body, ensuring proper oxygenation and nutrient supply.
The subclavian artery can have anatomical variations.
In some individuals, the subclavian artery may have variations in its origin or course. These variations can occur in the form of high origin, low origin, or even abnormal branching patterns. These anatomical variations are essential to consider during medical procedures or surgeries.
The subclavian artery plays a crucial role in the arterial pulse.
The subclavian artery contributes to the arterial pulse felt in the upper extremities. The palpation of the pulse in this artery is commonly performed during medical examinations to assess the blood flow and heart rate.
The subclavian artery is susceptible to certain diseases and conditions.
Like any other artery, the subclavian artery can be affected by atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque in the arterial walls. This condition can lead to reduced blood flow, causing symptoms such as arm pain, weakness, or numbness.
The subclavian artery can give rise to the steal syndrome.
In some cases, the subclavian artery may develop a condition called steal syndrome. This occurs when blood flow diverts from the brain to the affected arm, leading to neurological symptoms such as dizziness, headaches, or even strokes.
The subclavian artery can be affected by thoracic outlet syndrome.
Thoracic outlet syndrome is a condition where the nerves and blood vessels in the thoracic outlet, including the subclavian artery, get compressed or irritated. This can result in symptoms such as shoulder pain, arm weakness, and numbness.
The subclavian artery can be used for medical interventions.
The subclavian artery is a commonly accessed site for various medical procedures, such as angiography, angioplasty, or the placement of a stent. Its accessibility and proximity to vital structures make it a preferred choice in certain cases.
The subclavian artery supplies blood to the brain.
The subclavian artery gives rise to the vertebral arteries, which supply blood to the brain. These arteries travel through the vertebral column, ensuring a constant blood flow to the cerebral structures.
The subclavian artery branches supply blood to the upper limbs.
The branches originating from the subclavian artery, including the axillary artery and the brachial artery, distribute blood to the upper limbs, ensuring oxygenation and nourishment to the muscles and other structures.
The subclavian artery can be affected by aneurysms.
Aneurysms can develop in the subclavian artery due to weakened arterial walls. These bulging areas can pose a risk of rupture and potential complications, requiring careful monitoring or surgical intervention.
The subclavian artery has a cross-sectional diameter of approximately 8-10 mm.
The diameter of the subclavian artery may vary slightly among individuals, but on average, it measures around 8-10 mm. This diameter allows for efficient blood flow to the upper body structures.
The subclavian artery has a high branching point.
Compared to other major arteries, the subclavian artery has a relatively high branching point. This branching occurs just after the artery originates, providing essential blood supply to different regions of the body.
The subclavian artery is responsible for collateral circulation.
The subclavian artery contributes to collateral circulation, which is an alternate pathway for blood flow in case of blockages or narrowing of other major arteries. This collateral circulation helps maintain adequate blood supply to the affected areas.
The subclavian artery offers a key landmark for anatomical reference.
Medical professionals use the subclavian artery as a significant landmark for anatomical references and measurements in the neck and upper chest regions. Its accessibility and prominence make it a reliable point of reference.
The subclavian artery is located deep within the body.
The subclavian artery runs deep within the body, protected by layers of muscles, bones, and other structures. This provides it with necessary protection and stability.
The subclavian artery can have variations in its course.
Although the subclavian artery generally follows a specific course, it can deviate in certain cases. These variations can include tortuosity, where the artery takes a winding path, potentially leading to complications or clinical considerations.
The subclavian artery has an extensive network of collateral blood vessels.
The subclavian artery connects to other blood vessels in the body via an intricate network of collateral circulation. These collateral vessels provide alternative pathways for blood flow, ensuring essential perfusion to the upper body regions.
These are 18 extraordinary facts about the subclavian artery. This vital artery plays a crucial role in supplying blood to the head, neck, shoulders, and upper limbs. Its anatomical variations, potential diseases, and involvement in various medical interventions make it a fascinating subject of study. By understanding the nuances of the subclavian artery, medical professionals can assess and treat conditions related to this important blood vessel effectively.
Conclusion
The subclavian artery is a remarkable blood vessel that plays a vital role in the human anatomy. Its position and structure make it a critical conduit for the blood supply to the upper extremities, brain, and other vital organs. Understanding the various facts about the subclavian artery helps shed light on its importance and significance in maintaining overall health and functionality.
From its origin to its branches and functions, there is much to appreciate about this extraordinary artery. Whether it’s the knowledge of its anatomical variations or its association with certain medical conditions, the subclavian artery continues to amaze the medical community and researchers alike. By delving deeper into the intricacies of this blood vessel, we gain a greater understanding of its impact on human health and the incredible capabilities of the human body.
As medical research continues to advance, there is still much to discover about the subclavian artery. This vital organ continues to be a subject of great interest and importance, as it plays a crucial role in maintaining proper blood circulation and overall well-being.
FAQs
Q: What is the function of the subclavian artery?
A: The subclavian artery supplies oxygenated blood to the upper extremities, brain, and other vital organs in the chest and neck region.
Q: Are there any variations in the origin of the subclavian artery?
A: Yes, variations in the origin of the subclavian artery are relatively common. It can arise directly from the aortic arch, the brachiocephalic trunk, or the common carotid artery.
Q: Can the subclavian artery be affected by medical conditions?
A: Yes, various conditions such as atherosclerosis, thoracic outlet syndrome, and aneurysms can affect the subclavian artery, leading to restricted blood flow and potential health complications.
Q: Are there any diagnostic procedures to evaluate the subclavian artery?
A: Yes, imaging techniques such as Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography, and magnetic resonance angiography can be used to evaluate the subclavian artery and diagnose any abnormalities.
Q: How is the subclavian artery treated in case of blockages or narrowing?
A: Treatment options may include medication, lifestyle changes, angioplasty, stenting, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention such as bypass grafting to restore proper blood flow.
Exploring subclavian artery facts is just the beginning of your journey into cardiovascular health. Jump into cardiovascular health with our astounding facts about Jump Rope For Heart. Fascinated by medical marvels? Surprising facts about vascular surgeons await you. Don't miss our fascinating exploration of arterial diseases and how they impact the cardiovascular system. Dive deeper into the world of heart health today!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


