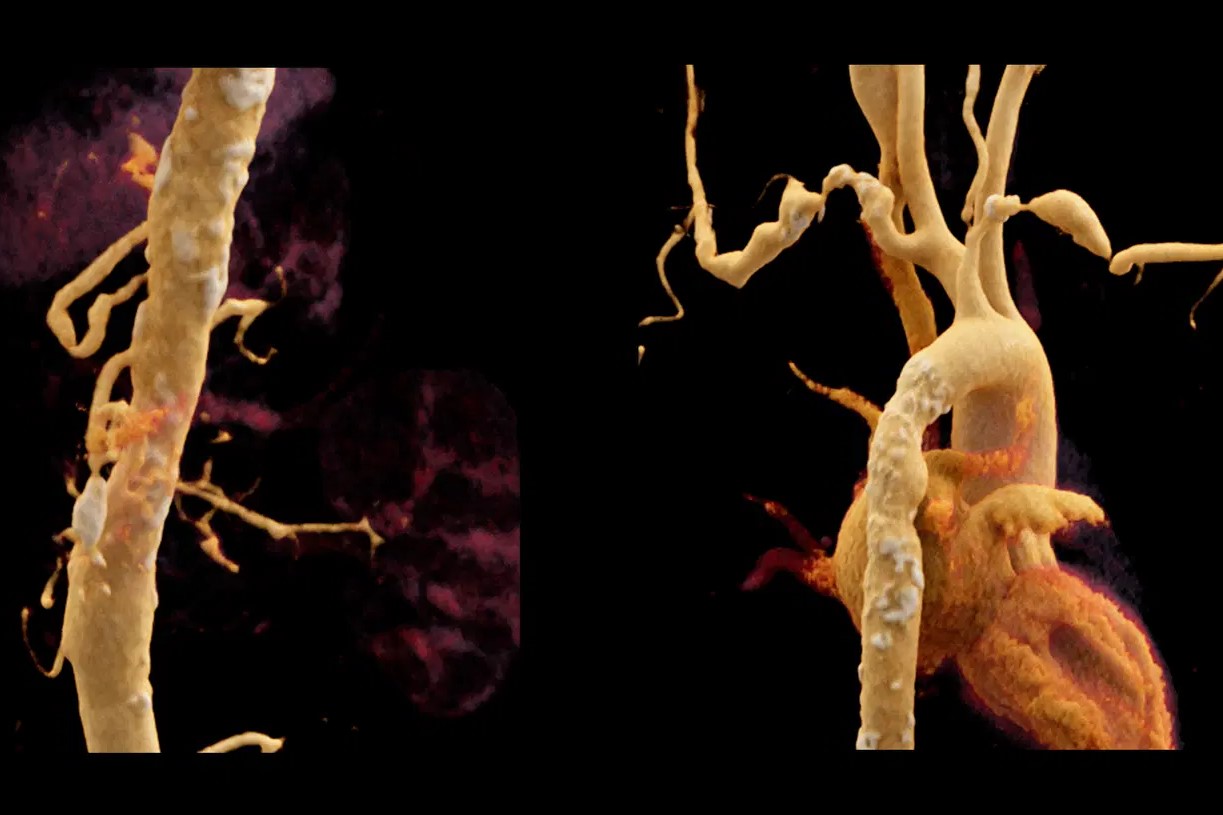
Takayasu arteritis is a rare inflammatory disease affecting large arteries, especially the aorta and its branches. Named after Japanese doctor Mikito Takayasu, who first described it in 1908, this condition primarily impacts young women under 40. Symptoms often include fatigue, weight loss, and muscle pain, making it tricky to diagnose early. As the disease progresses, it can lead to narrowed arteries, causing reduced blood flow to organs and limbs. Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests like MRI or CT scans to detect artery inflammation. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and preventing complications, often using medications like steroids or immunosuppressants. Understanding Takayasu arteritis is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Key Takeaways:
- Takayasu Arteritis is a rare disease that affects young women, causing symptoms like fatigue and high blood pressure. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
- Patients with Takayasu Arteritis may need lifelong medical care and support. Ongoing research offers hope for better treatments and a potential cure in the future.
What is Takayasu Arteritis?
Takayasu Arteritis is a rare, chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the aorta and its main branches. It can lead to significant health issues if not managed properly. Here are some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Takayasu Arteritis is named after Dr. Mikito Takayasu, a Japanese ophthalmologist who first described the disease in 1908.
-
This condition is also known as "pulseless disease" because it can cause weakened or absent pulses in the arms and legs.
-
It primarily affects young women, especially those of Asian descent, typically between the ages of 10 and 40.
-
The exact cause of Takayasu Arteritis remains unknown, but it is believed to involve an autoimmune response where the body's immune system attacks its own arteries.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how Takayasu Arteritis is diagnosed can help in early detection and treatment.
-
Common symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, fever, and muscle pain.
-
As the disease progresses, patients may experience high blood pressure, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
-
Diagnosis often involves imaging tests like MRI, CT scans, and angiography to visualize the arteries.
-
Blood tests can also be used to detect inflammation markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Treatment Options
Managing Takayasu Arteritis requires a combination of medications and sometimes surgical interventions.
-
Corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
-
Immunosuppressive drugs like methotrexate and azathioprine may be used to control the disease.
-
In severe cases, surgical procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery might be necessary to restore blood flow.
-
Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with Takayasu Arteritis can be challenging, but understanding its impact can help patients cope better.
-
Chronic fatigue and pain can affect daily activities and overall quality of life.
-
Patients may need to make lifestyle adjustments, such as adopting a low-sodium diet to manage high blood pressure.
-
Regular exercise, as recommended by a healthcare provider, can help maintain cardiovascular health.
-
Emotional support from family, friends, and support groups can be invaluable in managing the psychological impact of the disease.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Takayasu Arteritis and improve treatment options.
-
Genetic studies are being conducted to identify potential genetic factors that may contribute to the disease.
-
New biologic therapies targeting specific immune pathways are being explored as potential treatments.
-
Advances in imaging technology are helping doctors diagnose and monitor the disease more accurately.
-
Patient registries and collaborative research efforts are essential for gathering data and improving outcomes for those with Takayasu Arteritis.
Interesting Historical Facts
The history of Takayasu Arteritis offers some intriguing insights into its discovery and understanding.
-
Dr. Takayasu initially observed the disease in a young woman who had peculiar blood vessel changes in her retina.
-
The disease was later named "Takayasu Arteritis" in honor of his contributions to its identification.
-
Early descriptions of the disease date back to ancient medical texts, though it was not recognized as a distinct condition until the 20th century.
-
The term "pulseless disease" was coined by Japanese researchers in the 1950s to describe the characteristic absence of pulses in affected patients.
Global Perspective
Takayasu Arteritis affects people worldwide, with some regional variations in its prevalence and presentation.
-
It is more common in Asia, particularly in Japan, India, and China.
-
In Western countries, the disease is less common but still affects individuals of all ethnic backgrounds.
-
Research suggests that environmental factors, such as infections, may play a role in triggering the disease in genetically predisposed individuals.
-
International collaborations and research networks are crucial for advancing our understanding of Takayasu Arteritis on a global scale.
Personal Stories and Experiences
Hearing from those who live with Takayasu Arteritis can provide valuable insights and inspiration.
-
Many patients share their journeys through blogs, social media, and support groups, offering hope and encouragement to others.
-
Personal stories often highlight the importance of early diagnosis and the challenges of managing a chronic illness.
-
Some patients have become advocates for Takayasu Arteritis awareness and research, helping to raise funds and support for the cause.
-
Each individual's experience with the disease is unique, underscoring the need for personalized treatment approaches.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths and misconceptions about Takayasu Arteritis that need to be addressed.
-
One common myth is that only older adults can develop the disease, but it primarily affects young women.
-
Another misconception is that the disease is always fatal, but with proper treatment, many patients lead fulfilling lives.
-
Some people believe that Takayasu Arteritis only affects the heart, but it can impact any large artery in the body.
-
Education and awareness are key to dispelling these myths and ensuring accurate information is available.
Support and Resources
Various resources are available to help those affected by Takayasu Arteritis.
-
Organizations like the Vasculitis Foundation provide information, support, and advocacy for patients and their families.
-
Online forums and social media groups offer a platform for patients to connect, share experiences, and seek advice.
-
Healthcare providers, including rheumatologists and cardiologists, play a crucial role in managing the disease and providing support.
-
Educational materials, such as brochures and videos, can help patients and their families better understand the condition and its management.
Conclusion
Takayasu Arteritis is a complex and challenging disease, but with ongoing research, improved treatments, and strong support networks, those affected can lead fulfilling lives. Here are a few more facts to wrap up our exploration.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for preventing complications and improving outcomes.
-
Patients with Takayasu Arteritis often require lifelong medical care and monitoring.
-
Advances in medical research continue to offer hope for better treatments and a potential cure in the future.
-
Awareness and education about Takayasu Arteritis are essential for improving diagnosis and treatment.
-
Support from family, friends, and healthcare providers can make a significant difference in the lives of those affected by the disease.
-
Many patients find strength and resilience in their journey with Takayasu Arteritis, inspiring others with their courage and determination.
-
Research into the genetic and environmental factors contributing to the disease is ongoing, with the goal of developing more targeted therapies.
-
Collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and patients is key to advancing our understanding of Takayasu Arteritis.
-
The global community of Takayasu Arteritis patients and advocates continues to grow, raising awareness and support for this rare disease.
-
Every patient's story is unique, highlighting the importance of personalized care and treatment approaches for Takayasu Arteritis.
Final Thoughts on Takayasu Arteritis
Takayasu Arteritis, a rare inflammatory disease, primarily affects the aorta and its major branches. This condition can lead to serious complications like aneurysms, strokes, and heart attacks. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and preventing long-term damage. Common treatments include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and sometimes surgery. Regular monitoring through imaging tests helps track disease progression. Patients often face challenges due to the disease's unpredictable nature and the side effects of long-term medication use. Support from healthcare providers, family, and patient communities can make a significant difference. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options empowers patients to make better decisions about their health. Understanding Takayasu Arteritis not only helps those affected but also raises awareness about this rare condition, fostering a more supportive environment for everyone involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
