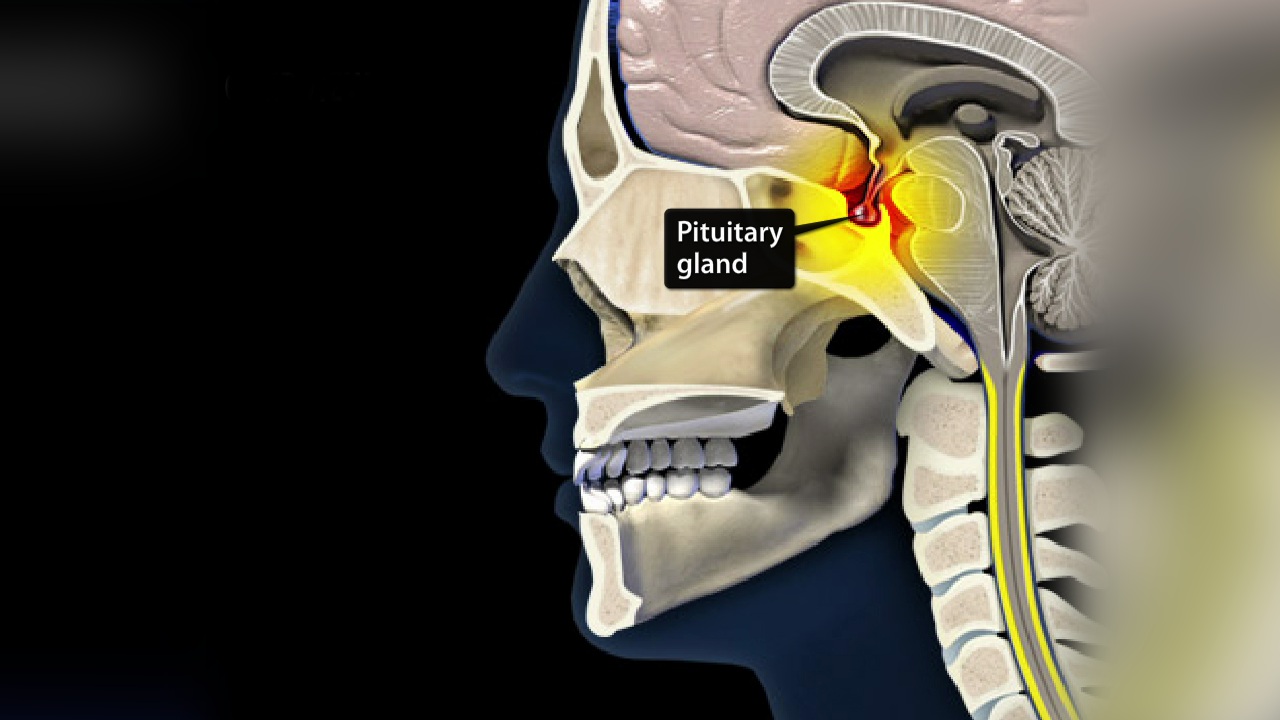
What is a pituitary tumor? It's a growth in the pituitary gland, a tiny organ at the brain's base. This gland, though small, plays a big role in controlling hormones that affect growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Most pituitary tumors are benign, meaning they're not cancerous. They can still cause problems by pressing on nearby structures or disrupting hormone production. Symptoms might include headaches, vision issues, or hormonal imbalances. Some people might not even know they have one until a doctor finds it during a scan for something else. Treatment options vary; they might include medication, surgery, or radiation. Understanding these tumors is crucial for managing health and well-being. Whether you're curious about symptoms, treatments, or just want to know more, this guide will help you navigate the world of pituitary tumors with ease.
Key Takeaways:
- Pituitary tumors are mostly non-cancerous and can affect hormone levels, leading to various health issues. Understanding symptoms and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
- Regular monitoring, hormone replacement therapy, and a healthy lifestyle can improve the quality of life for individuals living with pituitary tumors. Education, support, and ongoing research offer hope for better outcomes.
What is a Pituitary Tumor?
A pituitary tumor is an abnormal growth in the pituitary gland, a small organ at the base of the brain. This gland plays a crucial role in regulating hormones that control various bodily functions. Understanding these tumors can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
-
Pituitary tumors are mostly benign, meaning they are not cancerous. They don't spread to other parts of the body.
-
These tumors can affect hormone production, either increasing or decreasing hormone levels, which can lead to various health issues.
-
The pituitary gland is often called the "master gland" because it influences many other glands in the body.
-
Symptoms of a pituitary tumor can vary widely, including headaches, vision problems, and unexplained weight changes.
-
Some pituitary tumors are so small they go unnoticed and don't cause any symptoms.
Types of Pituitary Tumors
Pituitary tumors come in different types, each affecting the body in unique ways. Knowing the types can help in understanding potential symptoms and treatments.
-
Adenomas are the most common type of pituitary tumor. They are usually slow-growing and benign.
-
Microadenomas are smaller than 10 millimeters and often don't cause noticeable symptoms.
-
Macroadenomas are larger than 10 millimeters and may press on nearby structures, causing symptoms like vision problems.
-
Functioning tumors produce hormones, leading to conditions like Cushing's disease or acromegaly.
-
Non-functioning tumors don't produce hormones but can still cause symptoms by pressing on surrounding tissues.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of pituitary tumors is often unknown, certain factors can increase the risk of developing them.
-
Genetic conditions like Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) can increase the risk of pituitary tumors.
-
Family history of pituitary tumors may also play a role in developing these growths.
-
Most pituitary tumors occur sporadically, meaning they happen by chance without a clear cause.
-
Exposure to radiation, particularly to the head, may increase the risk of developing a pituitary tumor.
-
Pituitary tumors can occur at any age but are most commonly diagnosed in adults between 30 and 40 years old.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of a pituitary tumor is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Diagnosis often involves a combination of tests and imaging.
-
Common symptoms include headaches, vision changes, and hormonal imbalances.
-
Hormonal symptoms can include fatigue, mood changes, and changes in menstrual cycles or sexual function.
-
Vision problems occur when a tumor presses on the optic nerves, leading to blurry vision or loss of peripheral vision.
-
Blood tests can help diagnose pituitary tumors by checking hormone levels.
-
MRI or CT scans are often used to visualize the tumor and assess its size and impact on surrounding tissues.
Treatment Options
Treatment for pituitary tumors depends on the type, size, and symptoms. Options range from monitoring to surgery and medication.
-
Observation or "watchful waiting" is often recommended for small, non-symptomatic tumors.
-
Surgery is a common treatment, especially for tumors causing significant symptoms or hormone imbalances.
-
Transsphenoidal surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to remove pituitary tumors through the nose.
-
Medications can help manage hormone levels in functioning tumors, reducing symptoms.
-
Radiation therapy may be used if surgery isn't possible or if the tumor returns after treatment.
Living with a Pituitary Tumor
Living with a pituitary tumor can be challenging, but understanding the condition and managing symptoms can improve quality of life.
-
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring tumor growth and hormone levels.
-
Hormone replacement therapy may be necessary if the tumor or treatment affects hormone production.
-
Support groups and counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional impact of living with a pituitary tumor.
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can support overall well-being.
-
Educating family and friends about the condition can help build a supportive network.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research continues to improve understanding and treatment of pituitary tumors, offering hope for better outcomes.
-
Advances in imaging technology have improved the ability to diagnose and monitor pituitary tumors.
-
New medications are being developed to target specific hormone imbalances caused by functioning tumors.
-
Research into genetic factors is helping to identify individuals at higher risk for pituitary tumors.
-
Clinical trials are exploring innovative treatments, including targeted therapies and immunotherapy.
-
Collaboration between researchers and healthcare professionals is leading to more personalized treatment approaches.
Myths and Misconceptions
Misunderstandings about pituitary tumors can lead to unnecessary fear or confusion. Clearing up these myths is important for accurate knowledge.
-
Myth: All pituitary tumors are cancerous. Fact: Most are benign and don't spread.
-
Myth: Surgery is always necessary. Fact: Many tumors can be managed with medication or monitoring.
-
Myth: Pituitary tumors only affect older adults. Fact: They can occur at any age, though more common in adults.
-
Myth: Vision problems are the first sign. Fact: Symptoms vary widely and may not include vision changes.
-
Myth: Once treated, pituitary tumors never return. Fact: Some tumors can recur, requiring ongoing monitoring.
Famous Cases and Awareness
Public figures and awareness campaigns have helped bring attention to pituitary tumors, encouraging early diagnosis and treatment.
-
Actress Mary Tyler Moore raised awareness about pituitary tumors after her diagnosis.
-
Awareness campaigns emphasize the importance of recognizing symptoms and seeking medical advice.
-
Support organizations provide resources and information for those affected by pituitary tumors.
-
Celebrities sharing their experiences can reduce stigma and encourage others to seek help.
-
Increased awareness has led to more research funding and improved treatment options.
Impact on Daily Life
Pituitary tumors can affect daily life in various ways, from physical symptoms to emotional challenges. Understanding these impacts can help in managing the condition.
-
Fatigue and hormonal changes can affect energy levels and mood.
-
Vision problems may impact daily activities, such as driving or reading.
-
Hormonal imbalances can affect weight, metabolism, and overall health.
-
Emotional support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals is crucial for coping with the condition.
-
Adapting to lifestyle changes, such as medication schedules or dietary adjustments, can help manage symptoms effectively.
Final Thoughts on Pituitary Tumors
Pituitary tumors, though often benign, can have significant impacts on health. Understanding these growths is crucial for early detection and effective management. Symptoms like headaches, vision problems, and hormonal imbalances should never be ignored. Early diagnosis can lead to better outcomes, often involving a combination of surgery, medication, and radiation therapy.
Advancements in medical technology have improved treatment options, making recovery more achievable. It's important to maintain regular check-ups and communicate openly with healthcare providers. Awareness and education about pituitary tumors empower individuals to take proactive steps in their health journey.
Remember, knowledge is power. By staying informed, you can make better decisions for yourself or loved ones who might be affected. Always seek professional medical advice for any concerns. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and prioritize your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
