What is a pituitary adenoma? It's a type of tumor that forms in the pituitary gland, a small but mighty gland located at the base of the brain. This gland plays a crucial role in regulating hormones that control various bodily functions. While most pituitary adenomas are benign, meaning they're not cancerous, they can still cause significant health issues. These tumors can lead to hormonal imbalances, vision problems, and headaches. Some adenomas produce excess hormones, while others may not produce any hormones at all. Treatment options vary depending on the size and type of adenoma and can include medication, surgery, or radiation therapy. Understanding the nature of pituitary adenomas is essential for managing their impact on health. Whether you're a student, a curious reader, or someone affected by this condition, learning about these tumors can provide valuable insights into their effects and management.
Key Takeaways:
- Pituitary adenomas are common noncancerous tumors in the brain, affecting hormone levels and causing symptoms like vision problems and hormonal imbalances. Early detection and personalized treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
- Living with a pituitary adenoma can impact emotional, physical, and social aspects of life. Support groups, mental health care, and lifestyle adjustments play a key role in managing the condition and overall well-being.
What is a Pituitary Adenoma?
Pituitary adenomas are noncancerous tumors that develop in the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain. This gland plays a crucial role in regulating various hormones in the body. Understanding these tumors can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
-
Pituitary adenomas are common: They account for about 10-15% of all brain tumors. Despite their prevalence, many people remain unaware of their existence.
-
Most are benign: These tumors are usually noncancerous, meaning they don't spread to other parts of the body.
-
Size matters: Adenomas are classified based on size. Microadenomas are less than 10 mm, while macroadenomas are 10 mm or larger.
-
Hormone production: Some adenomas produce excess hormones, leading to various health issues, while others do not affect hormone levels.
-
Prolactinomas are common: The most frequent type of hormone-producing adenoma is a prolactinoma, which secretes excess prolactin.
Symptoms of Pituitary Adenoma
Symptoms can vary widely depending on the type and size of the adenoma. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to more effective treatment.
-
Vision problems: Large adenomas can press on the optic nerves, causing vision issues like double vision or loss of peripheral vision.
-
Headaches: Persistent headaches are a common symptom due to pressure on surrounding tissues.
-
Hormonal imbalances: Symptoms may include fatigue, weight changes, and mood swings due to hormone level alterations.
-
Menstrual changes: Women may experience irregular periods or amenorrhea due to hormonal effects.
-
Infertility: Both men and women can face fertility issues if hormone production is affected.
Diagnosis and Detection
Diagnosing a pituitary adenoma involves various tests and imaging techniques. Early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
-
MRI scans: Magnetic Resonance Imaging is the most effective tool for visualizing pituitary adenomas.
-
Blood tests: These tests measure hormone levels to identify any imbalances caused by the tumor.
-
Vision tests: Eye exams can detect vision changes that might indicate a growing adenoma.
-
Endocrinologist consultation: Specialists in hormone-related conditions can provide a comprehensive evaluation.
-
Incidental findings: Sometimes, adenomas are discovered incidentally during scans for unrelated issues.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the adenoma's size, type, and symptoms. Options range from medication to surgery.
-
Medication: Drugs can shrink certain types of adenomas or control hormone production.
-
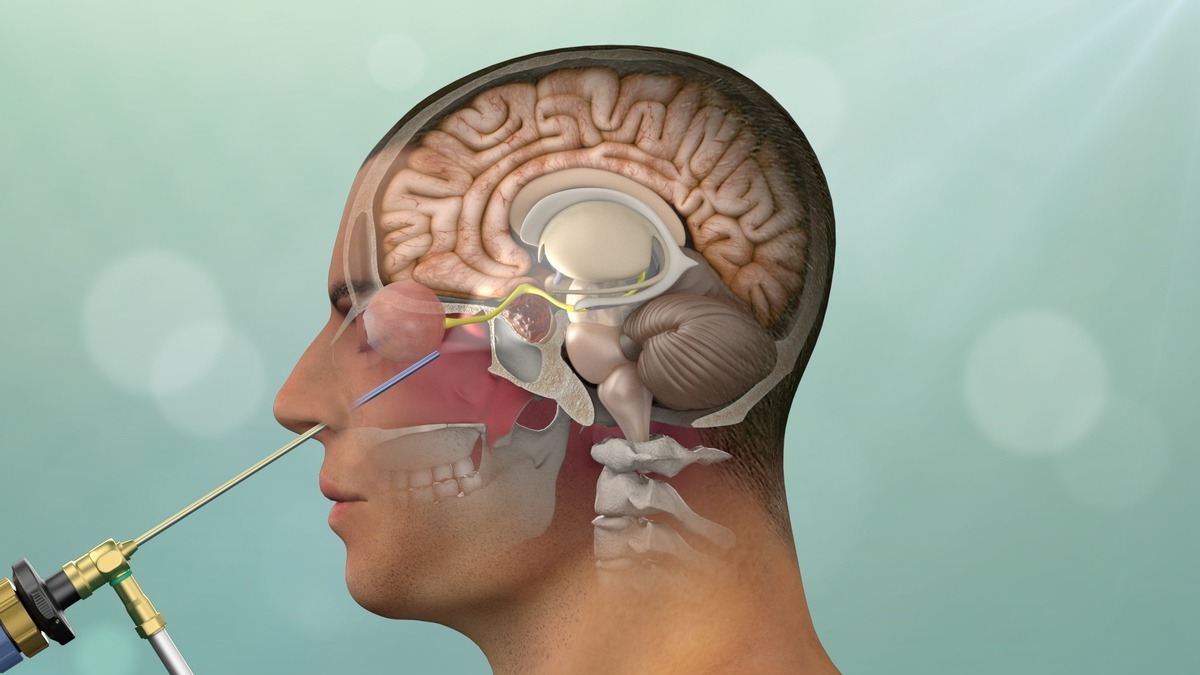
Surgery: Transsphenoidal surgery is a common procedure to remove the tumor through the nasal cavity.
-
Radiation therapy: Used when surgery isn't possible or to target remaining tumor cells post-surgery.
-
Observation: Small, non-symptomatic adenomas might only require regular monitoring.
-
Hormone replacement therapy: Necessary if the adenoma affects normal hormone production.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with a pituitary adenoma can affect various aspects of daily life. Understanding these impacts can help in managing the condition.
-
Emotional health: Hormonal changes can lead to mood swings, anxiety, or depression.
-
Physical health: Fatigue and weight changes can affect physical well-being and energy levels.
-
Social interactions: Symptoms like mood swings or vision problems can impact social life and relationships.
-
Work and productivity: Frequent medical appointments and symptoms might affect work performance.
-
Long-term management: Regular follow-ups and lifestyle adjustments are often necessary for ongoing management.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research continues to improve understanding and treatment of pituitary adenomas. These advances offer hope for better outcomes.
-
Genetic studies: Research into genetic factors may lead to earlier detection and personalized treatments.
-
New medications: Development of drugs targeting specific hormone pathways shows promise.
-
Improved surgical techniques: Advances in minimally invasive surgery reduce recovery time and complications.
-
Radiation technology: Innovations in radiation therapy offer more precise targeting of tumor cells.
-
Patient support networks: Growing online communities provide support and information for those affected.
Myths and Misconceptions
Misunderstandings about pituitary adenomas can lead to unnecessary fear or stigma. Clearing up these myths is important for awareness.
-
Not always symptomatic: Many people believe all adenomas cause symptoms, but some remain asymptomatic.
-
Not all require surgery: Surgery is not always necessary, especially for small or non-symptomatic adenomas.
-
Not a brain tumor: While located in the brain, pituitary adenomas differ from typical brain tumors in behavior and treatment.
-
Hormone therapy isn't always needed: Not all adenomas affect hormone levels, so hormone therapy isn't always required.
-
Lifestyle changes can help: Diet, exercise, and stress management can support overall health and well-being.
Famous Cases and Awareness
Some well-known individuals have brought attention to pituitary adenomas, raising awareness and understanding.
-
Celebrities: Public figures sharing their experiences can help reduce stigma and promote awareness.
-
Awareness campaigns: Organizations and campaigns work to educate the public about pituitary adenomas.
-
Documentaries and media: Films and articles highlight personal stories and medical advancements.
-
Patient advocacy: Advocacy groups provide resources and support for those affected by pituitary adenomas.
-
Educational resources: Books, websites, and seminars offer information for patients and healthcare providers.
Future Directions
The future holds promise for improved diagnosis, treatment, and understanding of pituitary adenomas. Continued research and innovation are key.
-
Biomarker discovery: Identifying biomarkers could lead to earlier and more accurate diagnosis.
-
Gene therapy: Exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment option for certain types of adenomas.
-
Artificial intelligence: AI technology could enhance imaging techniques and treatment planning.
-
Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles for better outcomes.
-
Global collaboration: International research efforts aim to accelerate advancements in understanding and treating pituitary adenomas.
Living with a Pituitary Adenoma
Managing life with a pituitary adenoma involves balancing medical care with personal well-being. Support and resources can make a difference.
-
Support groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide comfort and advice.
-
Mental health care: Counseling or therapy can help manage emotional and psychological impacts.
-
Lifestyle adjustments: Healthy habits and stress management techniques support overall health.
-
Regular check-ups: Ongoing medical care ensures timely adjustments to treatment plans.
-
Empowerment through education: Understanding the condition empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Understanding Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary adenomas, though often benign, can have significant effects on health. These tumors, located in the pituitary gland, can influence hormone levels, leading to various symptoms like headaches, vision problems, or hormonal imbalances. Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing these effects. Treatments range from medication to surgery, depending on the adenoma's size and impact. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help monitor and manage any changes. It's important for individuals to be aware of symptoms and seek medical advice if they suspect any issues. Knowledge about pituitary adenomas empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health. Remember, while these tumors can be challenging, advancements in medical science offer effective solutions. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize your well-being. Understanding your body and its signals is key to maintaining a healthy life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
